Трябва да сте влезли в
-
moreX
-
Компоненти
-
-
Category
-
полупроводници
- Диоди
- Тиристори
-
Електрически изолирани модули
- Електроизолирани модули VISHAY (IR).
- Електроизолирани модули INFINEON (EUPEC).
- Електрически изолирани модули на Semikron
- Електроизолирани модули POWEREX
- Електроизолирани модули IXYS
- Електроизолирани модули от POSEICO
- Електрически изолираните модули на ABB
- Електроизолационни модули от TECHSEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Мостови токоизправители
-
Транзистори
- GeneSiC транзистори
- Mitsubishi SiC MOSFET модули
- STARPOWER SiC MOSFET модули
- ABB SiC MOSFET модули
- IGBT модули от MITSUBISHI
- Транзисторни модули MITSUBISHI
- MITSUBISHI MOSFET модули
- Транзисторни модули ABB
- IGBT модули от POWEREX
- IGBT модули - от INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Полупроводникови елементи от силициев карбид
- Go to the subcategory
- Шофьори
- Силови блокове
- Go to the subcategory
- Преобразуватели за ток и напрежение LEM
-
Пасивни компоненти (кондензатори, резистори, предпазители, филтри)
- Резистори
-
Предпазители
- Миниатюрни предпазители за електронни системи серия ABC и AGC
- Бързодействащи тръбни предпазители
- Забавени вложки с GL/GG и AM характеристики
- Изключително бързи предпазители
- Британски и американски стандартни бързодействащи предпазители
- Бързодействащи предпазители европейски стандарт
- Тягови предпазители
- Предпазители за високо напрежение
- Go to the subcategory
-
Кондензатори
- Кондензатори за двигатели
- Електролитни кондензатори
- Icel филмови кондензатори
- Силови кондензатори
- Кондензатори за постояннотокови вериги
- Кондензатори за компенсация на мощността
- Кондензатори за високо напрежение
- Кондензатори за индукционно нагряване
- Импулсни кондензатори
- DC LINK кондензатори
- Кондензатори за AC/DC вериги
- Go to the subcategory
- Филтри против смущения
- Суперкондензатори
-
Защита от пренапрежение
- Отводители за пренапрежение за радиочестотни приложения
- Отводители на пренапрежения за системи за зрение
- Отводители за пренапрежение в електропроводи
- LED предпазители от пренапрежение
- Отводители за фотоволтаици
- Отводители на пренапрежения за системи за претегляне
- Отводители за пренапрежение за fieldbus
- Go to the subcategory
- Разкриващи емисионни филтри TEMPEST
- Go to the subcategory
-
Релета и контактори
- Теория на релетата и контакторите
- AC 3-фазни твърдотелни релета
- DC твърдотелни релета
- Регулатори, системи за управление и аксесоари
- Мек старт и реверсивни контактори
- Електромеханични релета
- Контактори
- Ротационни превключватели
-
Еднофазни AC твърдотелни релета
- Еднофазни променливотокови полупроводникови релета Серия 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Еднофазни AC полупроводникови релета CWA и CWD серия
- Еднофазни AC полупроводникови релета серии CMRA и CMRD
- Еднофазни AC твърдотелни релета PS серия
- AC твърдотелни релета двойни и четворни серии D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Еднофазни полупроводникови релета от серия GN
- Еднофазни променливотокови твърдотелни релета серия CKR
- Монофазни AC релета за DIN шина ERDA и ERAA СЕРИЯ
- Монофазни AC релета за ток 150А
- Двойни твърдотелни релета, интегрирани с радиатор на DIN шина
- Go to the subcategory
- AC еднофазни печатни твърдотелни релета
- Интерфейсни релета
- Go to the subcategory
- Ядра и други индуктивни компоненти
- Радиатори, Варистори, Термична защита
- Фенове
- Климатик, Аксесоари за табла, Охладители
-
Батерии, зарядни устройства, буферни захранвания и преобразуватели
- Батерии, зарядни устройства - теоретично описание
- Литиево-йонни батерии. Персонализирани батерии. Система за управление на батерията (BMS)
- Батерии
- Зарядни за батерии и аксесоари
- UPS и буферни захранвания
- Конвертори и аксесоари за фотоволтаици
- Съхранение на енергия
- Водородни горивни клетки
- Литиево-йонни клетки
- Go to the subcategory
-
Автоматизация
- Подемници Spiralift
- Части за дронове Futaba
- Крайни изключватели, Микро ключове
- Сензори, Преобразуватели
- Пирометри
- Броячи, Релета за време, Панелни измервателни уреди
- Индустриална защитна екипировка
- Светлинни и звукови сигнали
- Термовизионна камера
- LED дисплеи
- Бутони и превключватели
- Go to the subcategory
-
Кабели, Litz проводници, Тръбопроводи, Гъвкави връзки
- Проводници
- Кабелни щуцери и ръкави
- лица
-
Кабели за специални приложения
- Удължителни и компенсаторни кабели
- Кабели за термодвойки
- Свързващи кабели за PT сензори
- Многожилни кабели темп. -60°C до +1400°C
- Кабели средно напрежение SILICOUL
- Кабели за запалване
- Нагревателни кабели
- Едножилни кабели темп. -60°C до +450°C
- Железопътни проводници
- Нагревателни кабели в Ex
- Кабели за отбранителната промишленост
- Go to the subcategory
- тениски
-
Плитки
- Плоски плитки
- Кръгли плитки
- Много гъвкави плитки - плоски
- Много гъвкави плитки - кръгли
- Цилиндрични медни оплетки
- Медни цилиндрични оплетки и капаци
- Гъвкави ленти за заземяване
- Цилиндрични оплетки от поцинкована и неръждаема стомана
- Медни оплетки с PVC изолация - температура до 85 градуса
- Плоски алуминиеви оплетки
- Комплект за свързване - оплетки и тръби
- Go to the subcategory
- Тягово оборудване
- Накрайници за кабели
- Изолирани гъвкави релси
- Многослойни гъвкави шини
- Системи за управление на кабели
- Go to the subcategory
- View all categories
-
полупроводници
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- CNC машини
- DC и AC задвижвания (инвертори)
- Двигатели и трансформатори
- Енергетика
- Енергийни банки
- Заваръчни машини и заварчици
- Захранвания (UPS) и токоизправителни системи
- Измерване и регулиране на температурата
- Изследвания и лабораторни измервания
- Индукционно нагряване
- Индустриална автоматизация
- Индустриална защитна екипировка
- Компоненти за зони с опасност от експлозия (EX)
- Машини за сушене и обработка на дървесина
- Машини за термоформоване на пластмаси
- Минно дело, металургия и леярство
- Оборудване за разпределителни и контролни шкафове
- ОВК автоматизация
- Печат
- Трамвайна и железопътна тяга
-
Инсталация
-
-
Индуктори
-
-
Индукционни устройства
-
-
Обслужване
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Basics of Electromagnetic Compatibility: What It Is and Why It's Important? 1 of 8

Basics of Electromagnetic Compatibility: What It Is and Why It's Important? 1 of 8
Definition of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is a field of science and engineering that deals with preventing electromagnetic interference and ensuring that electronic devices and systems can operate alongside each other without mutual electromagnetic interference. In short, EMC concerns the ability of devices to function in environments with various sources of electromagnetic disturbances and minimize their impact on other devices.
In today's world, where electronics and communication systems are widely used in various fields such as industry, transportation, medicine, and telecommunications, issues related to EMC are of immense importance. Without proper electromagnetic compatibility, there is a risk of disturbances that can lead to system failures, data loss, and even pose a threat to user safety.
Within the field of Electromagnetic Compatibility, there are standards and regulations that define the minimum requirements for electromagnetic emissions and immunities. Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) develop standards that must be followed to meet EMC requirements. Compliance with these standards allows for effective cooperation between different electronic devices and minimizes the risk of electromagnetic interference.
It is important for manufacturers, designers, and engineers to have an awareness and understanding of Electromagnetic Compatibility and to implement appropriate techniques for designing, testing, and securing devices to ensure their reliability, durability, and compliance with regulations. Through proper EMC practices, the risk of electromagnetic interference can be minimized, thereby ensuring stable and safe operation of electronics in various environments.
Basic Principles of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is based on several key principles aimed at minimizing electromagnetic interference and ensuring the uninterrupted operation of electronic devices and systems. Here are the basic principles of EMC:
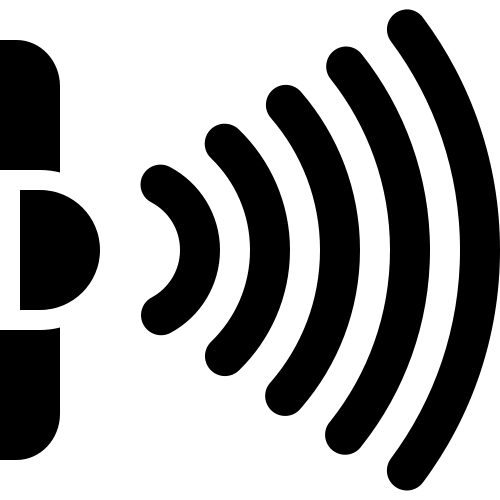

Principle of Emission
This principle concerns controlling the electromagnetic interference emissions generated by devices. Electronic devices can produce various types of electromagnetic signals that can interfere with the operation of other devices. The task of EMC is to limit these emissions by employing appropriate design techniques, shielding, filtering, and other measures to minimize the generation of electromagnetic disturbances.
Principle of Immunity
This principle pertains to the resistance of devices to electromagnetic disturbances originating from other sources. Electronic devices should be resilient to electromagnetic disturbances that may occur in the environment, such as radio signals, electromagnetic fields, or electrical surges. Through proper design, shielding, attenuation, and other techniques, devices can be more resistant to disturbances and maintain their operational integrity.
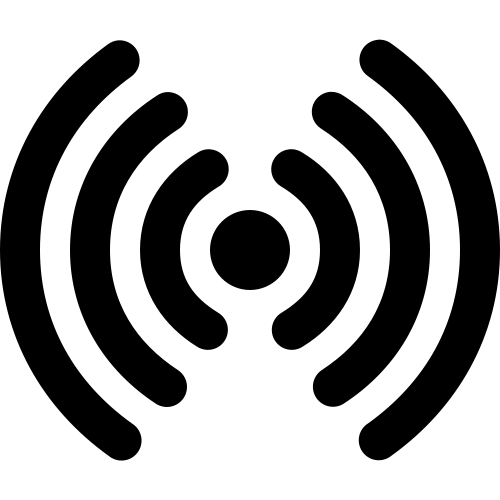

Principle of Separation
This principle concerns ensuring adequate separation between devices to avoid mutual electromagnetic interference. Devices should be designed and placed in such a way as to minimize interaction between them. Examples of actions consistent with this principle include proper cable and wire arrangement, use of screens and shields, and appropriate spatial planning of electronic systems.
Principle of Control
This principle involves monitoring and controlling the quality of signals and voltages in electronic devices. By monitoring and regulating electrical signals and eliminating unwanted interference, the quality and stability of device operation can be effectively controlled.
Understanding and applying these basic principles of EMC is crucial for designers, engineers, and manufacturers of electronic devices. By adhering to these principles, the risk of electromagnetic interference can be minimized, ensuring reliability, durability, and compliance with regulatory requirements for electronic devices.
The Essence and Significance of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) in Today's Technological Environments:
In today's digital world, where electronic devices and communication systems are an integral part of our lives, the essence of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is becoming increasingly important. EMC is crucial for ensuring the uninterrupted operation of devices and systems in the presence of diverse sources of electromagnetic disturbances.
The main objective of EMC is to minimize electromagnetic interference, which can cause failures, malfunctions, data loss, or even risk to user safety. The introduction of electromagnetic disturbances can lead to communication interference, instability in device operation, transmission errors, and contribute to performance limitations and improper functioning of electronic control systems.
It is important to understand that in today's technological environments, there are many different sources of electromagnetic disturbances. This may include radio transmissions, telecommunication systems, power grids, electric motors, medical devices, and even everyday consumer electronics. The impact of these disturbances on the operation of other devices can be significant and lead to serious consequences.
Therefore, the significance of EMC cannot be underestimated. Compliance with EMC principles and standards is not only a legal requirement in certain industries but also a necessary condition for ensuring the reliability, durability, and safety of electronic devices. EMC practices allow for the identification, control, and minimization of both electromagnetic emission and immunity disturbances, as well as the appropriate design, testing, and protection of electronic systems.
In the present times, when technology and electronics are integral parts of our professional and personal lives, proper EMC management is incredibly important. It contributes to ensuring the reliability of our devices, minimizing the risk of failures, protecting the health and safety of users, and facilitating stable and efficient operation in diverse environments.
Related product
Related posts
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers





Leave a comment