
Musíte být přihlášen
Category


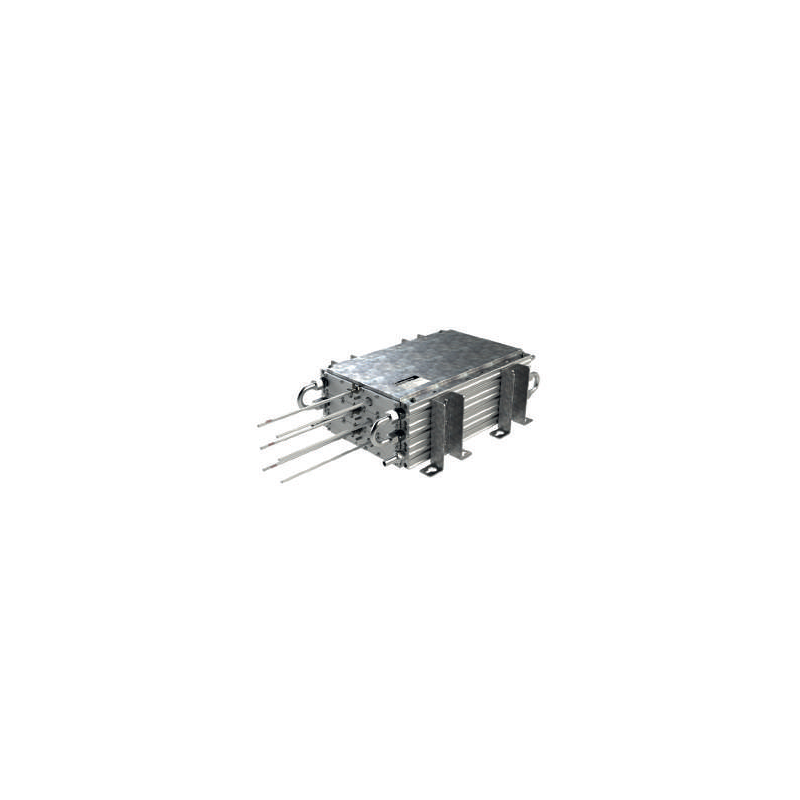
Fotografie slouží pouze pro informační účely. Zobrazit specifikaci produktu
please use latin characters
| Type | Resistance Range R [Ω] min-max | Rated Power for Initial Temperature and Temperature Change T, Hottest Spot Temperature on Surface 190°C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Temperature 20°C | Input Temperature 40°C | Input Temperature 50°C | ||||||||
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 40 | ||
| CBW 180 | 0,04- 13 | 1200 | 1150 | 1050 | 1050 | 1000 | 930 | 960 | 930 | 860 |
| CBW 210 | 0,05 - 2000 | 1650 | 1600 | 1500 | 1450 | 1400 | 1300 | 1350 | 1300 | 1200 |
| CBW 260 | 0,07 – 2000, | 2350 | 2300 | 2150 | 2050 | 2000 | 1850 | 1950 | 1850 | 1700 |
| CBW 330 | 0,09 - 2000 | 2950 | 2850 | 2700 | 2600 | 2500 | 2300 | 2400 | 2300 | 2150 |
| CBW 400 | 0,11 - 2000 | 3550 | 3450 | 3200 | 3100 | 3000 | 2800 | 2900 | 2800 | 2550 |
| CBW 460 | 0,14 - 2000 | 4100 | 4000 | 3750 | 3600 | 3500 | 3250 | 3400 | 3250 | 3000 |
| CBW 560 | 0,18- 110 | 4950 | 4800 | 4500 | 4350 | 4200 | 3900 | 4050 | 3900 | 3600 |
| CBW 660 | 0,22- 130 | 5900 | 5700 | 5350 | 5200 | 5000 | 4650 | 4800 | 4650 | 4300 |
| CBW 760 | 0,27- 150 | 6700 | 6500 | 6100 | 5900 | 5700 | 5300 | 5500 | 5300 | 4900 |
| CBW 860 | 0,31 - 180 | 7650 | 7450 | 6950 | 6750 | 6500 | 6050 | 6250 | 6050 | 5550 |
| CBW 960 | 0,35 - 220 | 8500 | 8250 | 7700 | 7450 | 7200 | 6700 | 6950 | 6700 | 6150 |
CBW resistors are used in wind turbines as filtering resistors and on board medium-power traction systems, such as trams - as braking resistors. In some tram systems, recovered power is used for heating the interior of the tram on cold days.
The maximum continuous power depends absolutely on the incoming water temperature and the temperature increase of the water, which is directly dependent on the water flow. Table 3 shows the maximum continuous power at a given water flow and different ΔT.
| Flow Rate L/h | ∆T Water | ∆T Water/Glycol 60/40 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| 7 kW | 710 | 470 | 350 | 280 | 240 | 1070 | 710 | 530 | 420 | 360 |
| 6 kW | 610 | 400 | 300 | 240 | 200 | 920 | 600 | 450 | 360 | 300 |
| 5 kW | 510 | 340 | 250 | 200 | 170 | 770 | 510 | 380 | 300 | 260 |
| 4 kW | 400 | 270 | 200 | 160 | 130 | 600 | 410 | 300 | 240 | 200 |
| 3 kW | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | 450 | 300 | 230 | 180 | 150 |
| 2 kW | 200 | 130 | 100 | 80 | 70 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 110 |
| 1 kW | 100 | 65 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 150 | 100 | 80 | 60 | 50 |
The pressure drop strongly depends on the used nozzles. Many customers use their own nozzles, which makes it difficult to provide standard values. For CBW460 resistor with SW22x45.5 and a flow rate of 120 l/h, the pressure drop is 55 mBar per channel, 110 mBar in total, for two cooling tubes included.
| Temperature Coefficient | 100 ppm/K | |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 3500 VAC at 1 minute | |
| Insulation Resistance | > 20MΩ / housing | |
| Overload at One-second Pulse per Hour | 70 - 250 x (depending on the resistor) | |
| Overload at Five-second Pulse per Hour | 20 - 60 x (depending on the resistor) | |
| Environment | - 40 °C / +70 °C | |
| Value Loss for Wirewound Version | Linear: 40°C = Pn to 70°C = 0.85 * Pn | |
| Value Loss for TW 200°C Version | Linear: 40°C = Pn to 70°C = 0.65 * Pn | |
| Value Loss for Vertical Mounting | No loss | |
| Value Loss for Horizontal Mounting | 0.8 * Pn | |
| Value Loss at High Altitudes | 1000m | No loss |
| 1500m | 0.94 * Pn | |
| 3000m | 0.82 * Pn | |
| Mounting Instructions | It is recommended to keep a distance of 200mm to the nearest element to prevent heating of neighboring components. | |
| If two or more inhibitory resistors are mounted next to each other, a distance of 400mm between them should be maintained. If closer, reduce the rated power. | ||
| Cooling | The rated power of the resistors applies to passive, air cooling conditions. | |
| Vibrations | According to EN 60068-2-6 Frequency Range 1-100Hz Acceleration/Amplitude | |
| 1 - 13 Hz | ± 1mm | |
| 13 - 100 Hz | at ± 0.7G | |
| Corrosion Resistance | According to IEC 60721-3-3/3K3 (C2 medium) 200h cyclic salt mist IEC60068-2-52 | |
| Connection Recommendations | To minimize EMC interference, the use of screens, especially with any PWM, is recommended. | |
| Resistance Tolerance | 10% (optionally 5%) | |
| Operating Voltage | Can Version | UL: 600VAC / 850VDC; IEC: 690VAC /975VDC |
| Wirewound Version | 1000VAC / 1400VDC | |
| Resistor Heating Time Constant | 1000-3000s | |
| Thermal Switch (optional) | Thermal Switch | 130 / 160 / 180 / 200 °C, 2A, 250 VAC NC |
| Minimum Voltage | 2V | |
| Minimum Current | 10mA | |
| Rated Current/Voltage | 2.5A @ 250VAC cos ʕ=1 | |
| Dielectric Voltage | 2000VAC (3500VAC between TS and R) | |
| Temperature Requirements for Cables | IP 21 | 80°C |
| IP 65 | 90°C |
CBW power resistors are used in solutions where large power pulses or high average power are present. The resistive elements are immersed in sand. This serves as a high thermal capacity, capable of absorbing large energy pulses. Energy is conducted through the sand and absorbed by the water. Approximately 90% of the total dissipation will be captured by the water, while the remaining portion is emitted into the air. It is also possible to insulate the aluminum housing, thereby promoting the dispersion of almost the entire energy into the water.
CBW resistors are employed in wind turbines as filtering resistors and in medium-power traction vehicles such as trams, where they function as braking resistors. In certain tram systems, the recovered power is utilized to heat the interior of the tram during cold days.
The maximum continuous power is absolutely dependent on the incoming water temperature and the increase in water temperature, which is directly linked to water flow rate. Table 3 displays the maximum continuous power at a given water flow rate and varying ΔT.
| Flow Rate L/h | ∆ T Water | ∆ T Water/Glycol 60/40 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| 7 kW | 710 | 470 | 350 | 280 | 240 | 1070 | 710 | 530 | 420 | 360 |
| 6 kW | 610 | 400 | 300 | 240 | 200 | 920 | 600 | 450 | 360 | 300 |
| 5 kW | 510 | 340 | 250 | 200 | 170 | 770 | 510 | 380 | 300 | 260 |
| 4 kW | 400 | 270 | 200 | 160 | 130 | 600 | 410 | 300 | 240 | 200 |
| 3 kW | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | 450 | 300 | 230 | 180 | 150 |
| 2 kW | 200 | 130 | 100 | 80 | 70 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 110 |
| 1 kW | 100 | 65 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 150 | 100 | 80 | 60 | 50 |
The pressure drop strongly depends on the used nozzles. Many customers use their own nozzles, which makes it difficult to provide standard values. For the CBW460 resistor with SW22x45.5 and a flow rate of 120 l/h, the pressure drop is 55 mBar per channel, 110 mBar in total, for two cooling tubes in the set.
Máte zájem o tento produkt? Potřebujete další informace nebo individuální ceny?
musíš být přihlášen
| Type | Resistance Range R [Ω] min-max | Rated Power for Initial Temperature and Temperature Change T, Hottest Spot Temperature on Surface 190°C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Temperature 20°C | Input Temperature 40°C | Input Temperature 50°C | ||||||||
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 40 | ||
| CBW 180 | 0,04- 13 | 1200 | 1150 | 1050 | 1050 | 1000 | 930 | 960 | 930 | 860 |
| CBW 210 | 0,05 - 2000 | 1650 | 1600 | 1500 | 1450 | 1400 | 1300 | 1350 | 1300 | 1200 |
| CBW 260 | 0,07 – 2000, | 2350 | 2300 | 2150 | 2050 | 2000 | 1850 | 1950 | 1850 | 1700 |
| CBW 330 | 0,09 - 2000 | 2950 | 2850 | 2700 | 2600 | 2500 | 2300 | 2400 | 2300 | 2150 |
| CBW 400 | 0,11 - 2000 | 3550 | 3450 | 3200 | 3100 | 3000 | 2800 | 2900 | 2800 | 2550 |
| CBW 460 | 0,14 - 2000 | 4100 | 4000 | 3750 | 3600 | 3500 | 3250 | 3400 | 3250 | 3000 |
| CBW 560 | 0,18- 110 | 4950 | 4800 | 4500 | 4350 | 4200 | 3900 | 4050 | 3900 | 3600 |
| CBW 660 | 0,22- 130 | 5900 | 5700 | 5350 | 5200 | 5000 | 4650 | 4800 | 4650 | 4300 |
| CBW 760 | 0,27- 150 | 6700 | 6500 | 6100 | 5900 | 5700 | 5300 | 5500 | 5300 | 4900 |
| CBW 860 | 0,31 - 180 | 7650 | 7450 | 6950 | 6750 | 6500 | 6050 | 6250 | 6050 | 5550 |
| CBW 960 | 0,35 - 220 | 8500 | 8250 | 7700 | 7450 | 7200 | 6700 | 6950 | 6700 | 6150 |
CBW resistors are used in wind turbines as filtering resistors and on board medium-power traction systems, such as trams - as braking resistors. In some tram systems, recovered power is used for heating the interior of the tram on cold days.
The maximum continuous power depends absolutely on the incoming water temperature and the temperature increase of the water, which is directly dependent on the water flow. Table 3 shows the maximum continuous power at a given water flow and different ΔT.
| Flow Rate L/h | ∆T Water | ∆T Water/Glycol 60/40 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| 7 kW | 710 | 470 | 350 | 280 | 240 | 1070 | 710 | 530 | 420 | 360 |
| 6 kW | 610 | 400 | 300 | 240 | 200 | 920 | 600 | 450 | 360 | 300 |
| 5 kW | 510 | 340 | 250 | 200 | 170 | 770 | 510 | 380 | 300 | 260 |
| 4 kW | 400 | 270 | 200 | 160 | 130 | 600 | 410 | 300 | 240 | 200 |
| 3 kW | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | 450 | 300 | 230 | 180 | 150 |
| 2 kW | 200 | 130 | 100 | 80 | 70 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 110 |
| 1 kW | 100 | 65 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 150 | 100 | 80 | 60 | 50 |
The pressure drop strongly depends on the used nozzles. Many customers use their own nozzles, which makes it difficult to provide standard values. For CBW460 resistor with SW22x45.5 and a flow rate of 120 l/h, the pressure drop is 55 mBar per channel, 110 mBar in total, for two cooling tubes included.
| Temperature Coefficient | 100 ppm/K | |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 3500 VAC at 1 minute | |
| Insulation Resistance | > 20MΩ / housing | |
| Overload at One-second Pulse per Hour | 70 - 250 x (depending on the resistor) | |
| Overload at Five-second Pulse per Hour | 20 - 60 x (depending on the resistor) | |
| Environment | - 40 °C / +70 °C | |
| Value Loss for Wirewound Version | Linear: 40°C = Pn to 70°C = 0.85 * Pn | |
| Value Loss for TW 200°C Version | Linear: 40°C = Pn to 70°C = 0.65 * Pn | |
| Value Loss for Vertical Mounting | No loss | |
| Value Loss for Horizontal Mounting | 0.8 * Pn | |
| Value Loss at High Altitudes | 1000m | No loss |
| 1500m | 0.94 * Pn | |
| 3000m | 0.82 * Pn | |
| Mounting Instructions | It is recommended to keep a distance of 200mm to the nearest element to prevent heating of neighboring components. | |
| If two or more inhibitory resistors are mounted next to each other, a distance of 400mm between them should be maintained. If closer, reduce the rated power. | ||
| Cooling | The rated power of the resistors applies to passive, air cooling conditions. | |
| Vibrations | According to EN 60068-2-6 Frequency Range 1-100Hz Acceleration/Amplitude | |
| 1 - 13 Hz | ± 1mm | |
| 13 - 100 Hz | at ± 0.7G | |
| Corrosion Resistance | According to IEC 60721-3-3/3K3 (C2 medium) 200h cyclic salt mist IEC60068-2-52 | |
| Connection Recommendations | To minimize EMC interference, the use of screens, especially with any PWM, is recommended. | |
| Resistance Tolerance | 10% (optionally 5%) | |
| Operating Voltage | Can Version | UL: 600VAC / 850VDC; IEC: 690VAC /975VDC |
| Wirewound Version | 1000VAC / 1400VDC | |
| Resistor Heating Time Constant | 1000-3000s | |
| Thermal Switch (optional) | Thermal Switch | 130 / 160 / 180 / 200 °C, 2A, 250 VAC NC |
| Minimum Voltage | 2V | |
| Minimum Current | 10mA | |
| Rated Current/Voltage | 2.5A @ 250VAC cos ʕ=1 | |
| Dielectric Voltage | 2000VAC (3500VAC between TS and R) | |
| Temperature Requirements for Cables | IP 21 | 80°C |
| IP 65 | 90°C |
CBW power resistors are used in solutions where large power pulses or high average power are present. The resistive elements are immersed in sand. This serves as a high thermal capacity, capable of absorbing large energy pulses. Energy is conducted through the sand and absorbed by the water. Approximately 90% of the total dissipation will be captured by the water, while the remaining portion is emitted into the air. It is also possible to insulate the aluminum housing, thereby promoting the dispersion of almost the entire energy into the water.
CBW resistors are employed in wind turbines as filtering resistors and in medium-power traction vehicles such as trams, where they function as braking resistors. In certain tram systems, the recovered power is utilized to heat the interior of the tram during cold days.
The maximum continuous power is absolutely dependent on the incoming water temperature and the increase in water temperature, which is directly linked to water flow rate. Table 3 displays the maximum continuous power at a given water flow rate and varying ΔT.
| Flow Rate L/h | ∆ T Water | ∆ T Water/Glycol 60/40 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| 7 kW | 710 | 470 | 350 | 280 | 240 | 1070 | 710 | 530 | 420 | 360 |
| 6 kW | 610 | 400 | 300 | 240 | 200 | 920 | 600 | 450 | 360 | 300 |
| 5 kW | 510 | 340 | 250 | 200 | 170 | 770 | 510 | 380 | 300 | 260 |
| 4 kW | 400 | 270 | 200 | 160 | 130 | 600 | 410 | 300 | 240 | 200 |
| 3 kW | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | 450 | 300 | 230 | 180 | 150 |
| 2 kW | 200 | 130 | 100 | 80 | 70 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 110 |
| 1 kW | 100 | 65 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 150 | 100 | 80 | 60 | 50 |
The pressure drop strongly depends on the used nozzles. Many customers use their own nozzles, which makes it difficult to provide standard values. For the CBW460 resistor with SW22x45.5 and a flow rate of 120 l/h, the pressure drop is 55 mBar per channel, 110 mBar in total, for two cooling tubes in the set.
Vaše hodnocení nelze odeslat
Nahlásit komentář
Zpráva odeslána
Váš podnět nelze odeslat
Napište svůj názor
Zkontrolovat před odesláním
Vaši recenzi nelze odeslat
