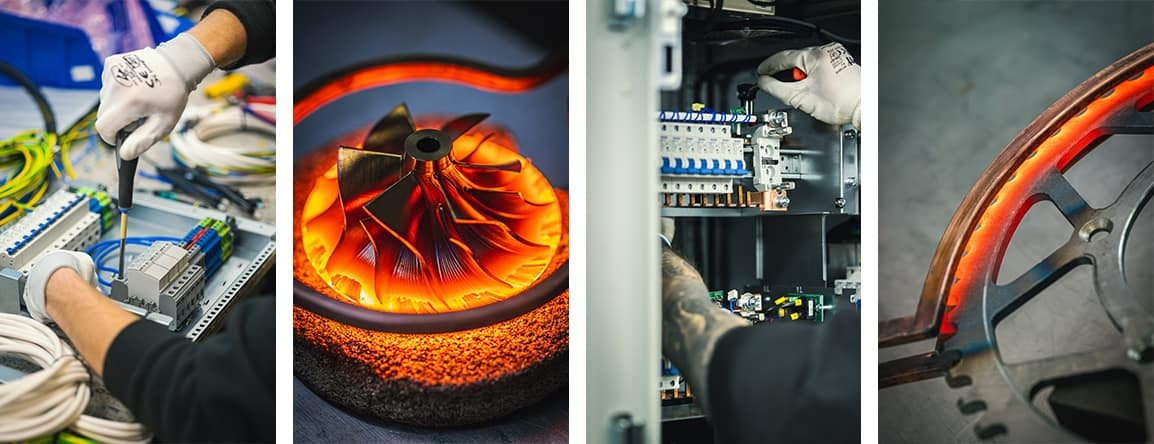
Der Artikel beschreibt Wasserstoff-Brennstoffzellen – eine Technologie, die Wasserstoff effizient und umweltfreundlich in elektrische Energie umwandelt. Er behandelt die Funktionsprinzipien der Brennstoffzellen, deren Anwendungen in der Automobilindustrie, im industriellen Bereich und in der Energieversorgung sowie Vorteile wie schnelles Tanken, große Reichweite und die Möglichkeit der Integration mit erneuerbaren Energiequellen. Diese Technologie stellt eine vielversprechende Lösung für nachhaltige Entwicklung und die Energiewende dar.
Komponenten für Leistungselektronik, Industrieautomatik, Elektronik, Energietechnik, Elektrotechnik
Lieferanten
Alle Lieferanten anzeigenProduktkategorien
Alle Kategorien anzeigenNeueste Beiträge
-
Wie Kühlung und Klimatisierung von Schaltschränken die Lebensdauer elektronischer Komponenten beeinflussenRead more
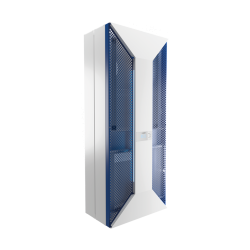
Der Artikel behandelt die Bedeutung der Kühlung und Klimatisierung von Schaltschränken zur Erhaltung der Lebensdauer elektronischer Komponenten. Er erklärt, wie stabile Temperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit die Zuverlässigkeit industrieller Systeme verbessern, beschreibt verschiedene Kühlmethoden, die Rolle des Gehäusedesigns und der Bauteilanordnung sowie die Bedeutung der Energieeffizienz in modernen Industrieanlagen.
-
Wie verändern induktive Geräte Produktionsprozesse?Read more
Der Artikel erläutert das Funktionsprinzip der Induktionserwärmung und zeigt, warum diese Technologie in der modernen Industrie immer häufiger eingesetzt wird. Beschrieben werden der Aufbau und die Funktionsweise induktiver Geräte, ihre wichtigsten Vorteile gegenüber herkömmlichen Erwärmungsmethoden sowie ein breites Anwendungsspektrum – von Härten und Löten bis hin zum Metallschmelzen und zu Laborprüfungen. Darüber hinaus stellt der Artikel die Möglichkeiten von DACPOL SERVICE vor und hebt die Rolle des Unternehmens als technologischer Partner bei der Planung, Implementierung und Wartung von Induktionserwärmungssystemen hervor.