-
BackX
-
Components
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductors
- Diodes
- Thyristors
-
Electro-insulated Modules
- Electro-insulated Modules | VISHAY (IR)
- Electro-insulated Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Electro-insulated Modules | Semikron
- Electro-insulated Modules | POWEREX
- Electro-insulated Modules | IXYS
- Electro-insulated Modules | POSEICO
- Electro-insulated Modules | ABB
- Electro-insulated Modules | TECHSEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Bridge Rectifiers
-
Transistors
- Transistors | GeneSiC
- SiC MOSFET Modules | Mitsubishi
- SiC MOSFET Modules | STARPOWER
- Module SiC MOSFET ABB’s
- IGBT Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | MITSUBISHI
- MOSFET Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | ABB
- IGBT Modules | POWEREX
- IGBT Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor elements
- Go to the subcategory
- Gate Drivers
- Power Blocks
- Go to the subcategory
- Electrical Transducers
-
Passive components (capacitors, resistors, fuses, filters)
- Resistors
-
Fuses
- Miniature Fuses for electronic circuits - ABC & AGC Series
- Tubular Fast-acting Fuses
- Time-delay Fuse Links with GL/GG & AM characteristics
- Ultrafast Fuse Links
- Fast-acting Fuses (British & American standard)
- Fast-acting Fuses (European standard)
- Traction Fuses
- High-voltage Fuse Links
- Go to the subcategory
- Capacitors
- EMI Filters
- Supercapacitors
- Power surge protection
- Go to the subcategory
-
Relays and Contactors
- Relays and Contactors - Theory
- 3-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- DC Semiconductor Relays
- Controllers, Control Systems and Accessories
- Soft Starters and Reversible Relays
- Electromechanical Relays
- Contactors
- Rotary Switches
-
Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- AC ONE PHASE RELAYS 1 series| D2425 | D2450
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CWA and CWD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CMRA and CMRD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays - PS series
- Double and quadruple semiconductor AC relays - D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D series
- One phase semiconductor relays - gn series
- Ckr series single phase solid state relays
- One phase AC semiconductor relays for DIN bus - ERDA I ERAA series
- 150A AC single phase relays
- Rail Mountable Solid State Relays With Integrated Heat Sink - ENDA, ERDA1 / ERAA1 series
- Go to the subcategory
- Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays for PCBs
- Interface Relays
- Go to the subcategory
- Cores and Other Inductive Components
- Heatsinks, Varistors, Thermal Protection
- Fans
- Air Conditioning, Accessories for Electrical Cabinets, Coolers
-
Batteries, Chargers, Buffer Power Supplies and Inverters
- Batteries, Chargers - Theoretical Description
- Modular Li-ion Battery Building Blocks, Custom Batteries, BMS
- Batteries
- Battery Chargers and Accessories
- Uninterruptible Power Supply and Buffer Power Supplies
- Inverters and Photovoltaic Equipments
- Energy storage
- Fuel cells
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Go to the subcategory
-
Automatics
- Futaba Drone Parts
- Limit Switches, Microswitches
- Sensors, Transducers
-
Infrared Thermometers (Pyrometers)
- IR-TE Series - Water-proof Palm-sized Radiation Thermometer
- IR-TA Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-H Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BA Series - High-speed Compact Radiation Thermometer
- IR-FA Series - Fiber Optic Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BZ Series - Compact Infrared Thermometers
- Go to the subcategory
- Counters, Time Relays, Panel Meters
- Industrial Protection Devices
- Light and Sound Signalling
- Thermographic Camera
- LED Displays
- Control Equipments
-
Recorders
- Hybrid Recorders - AL3000 Series | CHINO
- Graphic Recorder - KR2000 Series | CHINO
- Ubiquitous Recorders - KR5000 Series | CHINO
- Palm-sized Temperature/Humidity Meters - HN-CH Series | CHINO
- Consumables for Recorders
- 71VR1 - Compact Paperless Recorder | M-SYSTEM
- Graphic Recorder - KR3000 Series | CHINO
- PC Recorders - R1M Series | M-SYSTEM
- PC Recorders - R2M Series | M-SYSTEM
- PC Recorders - RZMS Series | M-SYSTEM
- PC Recorders - RZUS Series | M-SYSTEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Go to the subcategory
-
Cables, Litz wires, Conduits, Flexible connections
- Wires
- Litz wires
- Cables for extreme applications
- Sleevings
-
Braids
- Flat Braids
- Round Braids
- Very Flexible Flat Braids
- Very Flexible Round Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids and Sleevings
- Flexible Earthing Connections
- Galvanized and Stainless Steel Cylindrical Braids
- PCV Insulated Copper Braids (temp. up to 85C)
- Flat Aluminium Braids
- Junction Set - Braids and Tubes
- Go to the subcategory
- Traction Equipment
- Cable Terminals
- Flexible Insulated Busbars
- Flexible Multilayer Busbars
- Cable Duct Systems
- Hoses
- Go to the subcategory
- View all categories
-
Semiconductors
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- CNC Machine Tools
- DC and AC Drives (Inverters)
- Energetics
- Energy bank
- Equipment and Components for Hazardous Areas [Ex]
- Equipment for Distribution, Control and Telecommunications Cabinets
- HVAC Automation
- Induction Heating
- Industrial Automation
- Industrial Protective Devices
- Machines for Drying and Wood Processing
- Machines for Thermoforming Plastics
- Mining, Metallurgy and Foundry
- Motors and Transformers
- Power Supplies (UPS) and Rectifier Systems
- Printing
- Temperature Measurement and Regulation
- Test and Laboratory Measurements
- Tram and Railway Traction
- Welding Machines
-
Assembly
-
-
Inductors
-
-
Induction devices
-
-
https://www.dacpol.eu/pl/naprawy-i-modernizacje
-
-
Service
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Heat Management: The Key to Effective Performance and Reliability of Prototypes

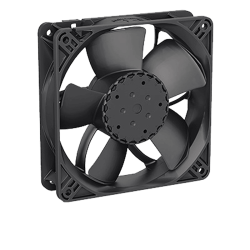
Industrial fans play a key role in thermal management of electronic systems. As devices become more advanced and miniaturized, the issue of cooling gains in importance. Efficient heat dissipation is not only a necessity but often a decisive factor in ensuring the reliability and performance of prototypes. In research and development (R&D) environments, where innovative designs are tested, appropriately selected fans form the foundation of effective thermal management.
The development of electronic systems presents new challenges for designers related to cooling. Generated heat can significantly reduce the performance and reliability of devices, and in extreme cases, lead to permanent damage. Key aspects include the increasing density of components on PCBs, which results in higher heat concentrations, and energy efficiency requirements that demand fans to provide effective cooling with minimal energy consumption. Additionally, eliminating mechanical and acoustic disturbances is important, as unwanted noise and vibrations can interfere with precise measurements and tests.
Innovative technological solutions in fans enable meeting the demands of modern research and development projects. Axial fans are characterized by simple construction and high airflow efficiency, making them ideal for quick and effective air circulation. Radial (centrifugal) fans are excellent for cooling systems with high airflow resistance, generating higher pressure. Brushless DC (BLDC) fans, on the other hand, are gaining popularity in applications requiring reliability and long lifespan, enabling precise speed control.
Effective cooling does not solely rely on the operation of the fan; key cooperation with other thermal management elements, such as radiators and heat transfer systems (e.g., heat-pipes), is essential. Fans mounted directly on radiators improve cooling efficiency by enhancing forced convection. In R&D environments, the use of temperature sensors to control fans allows for dynamic adjustment of their operation, contributing to reduced energy consumption.
Adapting fans to the specific needs of research and development projects requires appropriate analysis and testing. Key aspects include airflow and pressure; high airflow is necessary in systems generating a large amount of heat, while static pressure plays a more significant role in systems with complex airflow geometries. Limiting the noise level generated by fans is also important in research environments.
In the future, technologies used in fans will evolve to meet the growing market demands. We can expect the development of fans with magnetic drives and the use of advanced blade materials, which could significantly improve their efficiency. Integration with IoT systems will enable dynamic cooling control depending on operating conditions.
In conclusion, industrial fans are a crucial element in designing cooling systems for prototypes in R&D environments. The selection of appropriate models and technologies can significantly impact the stability, efficiency, and reliability of the system. DACPOL's offering, including advanced axial, radial and brushless fans, supports engineers in implementing innovative projects by providing solutions tailored to the most demanding R&D applications.
Citations:
[1] https://www.wentylacyjny.pl/2525-2-2-trwale-wentylatory-osiowe-do-chlodzenia-wentylacji-i-klimatyzacji.html
[2] https://www.instalacjebudowlane.pl/9256-26-76-wentylatory-ec-do-wydajnego-chlodzenia-w-centrach-danych.html
[3] https://hilelectronic.com/pl/design-power-pcb/
[4] https://www.rynekinstalacyjny.pl/artykul/wentylatory/156046,wentylatory-wymagania-i-oczekiwania-dotyczace-efektywnosci-energetycznej
[5] https://elektronikab2b.pl/technika/54036-projektowanie-pcb-dla-ukladow-duzej-mocy
[6] https://www.venture.pl/wentylatory/wentylatory-promieniowe
Related products
Related posts
 Thermally conductive materials in power storages
Thermally conductive materials in power storages
 Folia samoprzylepna z wypełnieniem ceramicznym
Folia samoprzylepna z wypełnieniem ceramicznym
 Heat management - Challenges for electric vehicles
Heat management - Challenges for electric vehicles





















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Leave a comment