-
BackX
-
Components
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductors
- Diodes
- Thyristors
-
Electro-insulated Modules
- Electro-insulated Modules | VISHAY (IR)
- Electro-insulated Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Electro-insulated Modules | Semikron
- Electro-insulated Modules | POWEREX
- Electro-insulated Modules | IXYS
- Electro-insulated Modules | POSEICO
- Electro-insulated Modules | ABB
- Electro-insulated Modules | TECHSEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Bridge Rectifiers
-
Transistors
- Transistors | GeneSiC
- SiC MOSFET Modules | Mitsubishi
- SiC MOSFET Modules | STARPOWER
- Module SiC MOSFET ABB’s
- IGBT Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | MITSUBISHI
- MOSFET Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | ABB
- IGBT Modules | POWEREX
- IGBT Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor elements
- Go to the subcategory
- Gate Drivers
- Power Blocks
- Go to the subcategory
- Electrical Transducers
-
Passive components (capacitors, resistors, fuses, filters)
- Resistors
-
Fuses
- Miniature Fuses for electronic circuits - ABC & AGC Series
- Tubular Fast-acting Fuses
- Time-delay Fuse Links with GL/GG & AM characteristics
- Ultrafast Fuse Links
- Fast-acting Fuses (British & American standard)
- Fast-acting Fuses (European standard)
- Traction Fuses
- High-voltage Fuse Links
- Go to the subcategory
- Capacitors
- EMI Filters
- Supercapacitors
- Power surge protection
- TEMPEST emission revealing filters
- Surge arrester
- Go to the subcategory
-
Relays and Contactors
- Relays and Contactors - Theory
- 3-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- DC Semiconductor Relays
- Controllers, Control Systems and Accessories
- Soft Starters and Reversible Relays
- Electromechanical Relays
- Contactors
- Rotary Switches
-
Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- AC ONE PHASE RELAYS 1 series| D2425 | D2450
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CWA and CWD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CMRA and CMRD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays - PS series
- Double and quadruple semiconductor AC relays - D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D series
- One phase semiconductor relays - gn series
- Ckr series single phase solid state relays
- One phase AC semiconductor relays for DIN bus - ERDA I ERAA series
- 150A AC single phase relays
- Rail Mountable Solid State Relays With Integrated Heat Sink - ENDA, ERDA1 / ERAA1 series
- Go to the subcategory
- Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays for PCBs
- Interface Relays
- Go to the subcategory
- Cores and Other Inductive Components
- Heatsinks, Varistors, Thermal Protection
- Fans
- Air Conditioning, Accessories for Electrical Cabinets, Coolers
-
Batteries, Chargers, Buffer Power Supplies and Inverters
- Batteries, Chargers - Theoretical Description
- Modular Li-ion Battery Building Blocks, Custom Batteries, BMS
- Batteries
- Battery Chargers and Accessories
- Uninterruptible Power Supply and Buffer Power Supplies
- Inverters and Photovoltaic Equipments
- Energy storage
- Fuel cells
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Go to the subcategory
-
Automatics
- Spiralift Lifts
- Futaba Drone Parts
- Limit Switches, Microswitches
- Sensors, Transducers
-
Infrared Thermometers (Pyrometers)
- IR-TE Series - Water-proof Palm-sized Radiation Thermometer
- IR-TA Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-H Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BA Series - High-speed Compact Radiation Thermometer
- IR-FA Series - Fiber Optic Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BZ Series - Compact Infrared Thermometers
- Go to the subcategory
- Counters, Time Relays, Panel Meters
- Industrial Protection Devices
- Light and Sound Signalling
- Thermographic Camera
- LED Displays
- Control Equipments
- Go to the subcategory
-
Cables, Litz wires, Conduits, Flexible connections
- Wires
- Cable feedthroughs and couplers
- Litz wires
-
Cables for extreme applications
- Extension and Compensation cables
- Thermocouple cables
- Connection cables for PT sensors
- Multi-conductor wires (temp. -60C to +1400C)
- Medium voltage cables
- Ignition wires
- Heating cables
- Single conductor cables (temp. -60C to +450C)
- Railway cables
- Heating cables Ex
- Cables for the defense industry
- Go to the subcategory
- Sleevings
-
Braids
- Flat Braids
- Round Braids
- Very Flexible Flat Braids
- Very Flexible Round Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids and Sleevings
- Flexible Earthing Connections
- PCV Insulated Copper Braids (temp. up to 85C)
- Flat Aluminium Braids
- Junction Set - Braids and Tubes
- Steel Braids
- Go to the subcategory
- Traction Equipment
- Cable Terminals
- Flexible Insulated Busbars
- Flexible Multilayer Busbars
- Cable Duct Systems
- Go to the subcategory
- View all categories
-
Semiconductors
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- CNC Machine Tools
- DC and AC Drives (Inverters)
- Energetics
- Energy bank
- Equipment and Components for Hazardous Areas [Ex]
- Equipment for Distribution, Control and Telecommunications Cabinets
- HVAC Automation
- Induction Heating
- Industrial Automation
- Industrial Protective Devices
- Machines for Drying and Wood Processing
- Machines for Thermoforming Plastics
- Mining, Metallurgy and Foundry
- Motors and Transformers
- Power Supplies (UPS) and Rectifier Systems
- Printing
- Temperature Measurement and Regulation
- Test and Laboratory Measurements
- Tram and Railway Traction
- Welding Machines
-
Assembly
-
-
Inductors
-
-
Induction devices
-
-
Service
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Power Modules for Combining Innovation, Flexibility and Power Capability in the Various 3-Level Topologies

Power Modules for Combining Innovation, Flexibility and Power Capability in the Various 3-Level Topologies
Three level topologies have demonstrated higher efficiencies, filter optimization potential and the capability of handling high DC-link voltages. To maximize the advantages offered by the 3-level topologies, Mitsubishi Electric offers new power modules which unlock the potential to realize innovative solutions for different power segments.
By Narender Lakshmanan and Thomas Radke, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. and Satoshi Kawabata, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Japan Power Device Works
Power conversion applications have always had to deliver high performance while maintaining the required quality of power. The harmonic profile of the output power can be improved by increasing the switching frequency. However, an increase in switching frequency compromises the inverter efficiency. Historically, the conventional 2-level inverters have served the industry with its seemingly uncomplicated topology where developers have always had to strike a balance between efficiency and filter optimization. With the invention of the 3-level topologies, many new avenues are now open for improving the output harmonic profile without compromising on the system efficiency. With the option of being able to apply the ‘zero’ level, this topology brings with it the following inherent benefits:
- Efficiency and output power capability [1]: The superior switching loss profile of a 3-level inverter ensures that better efficiencies can be achieved. Thus, for the same dc-link, a 3-level based inverter can deliver a higher output power compared to the corresponding 2-level inverter.
- AC filtering [5]: For the same switching frequency, the 3-level topology utilizes the availability of the ‘zero’ level to deliver an AC output of higher power quality than the corresponding 2-level inverter. This naturally allows a significant reduction of the output filter inductance.
- dv/dt Filter [5]: Since the phase to neutral output of a 3-level inverter shifts between 0V and (+/- Vdc)/2 (unlike the 2-level output), the corresponding dv/dt across the load is naturally reduced by about 50%.
- Common mode voltage reduction [5][6]: In comparison with 2-level, significant reduction (about 25%) of common mode voltage is possible in the 3-level topology.
While every segment of the inverter industry can avail the benefits associated with the 3-level topologies, grid connected inverters (Solar, Wind, HVDC), UPS and medium-tohigh power drives stand to benefit significantly by employing this innovative approach [3][4].
Power Modules from Mitsubishi Electric for 3-level NPC inverters
The CM400ST-24S1 module has already been introduced and presented in good detail ([2] Bodos article Feb’2015). A new series of power modules with innovative packaging optimized for 3-level applications has been developed. The comprehensive line-up is shown in Figure 1. The CM500C2Y-24S is provided as a dedicated neutral clamp switch for efficiently realizing the T type 3-level topology.
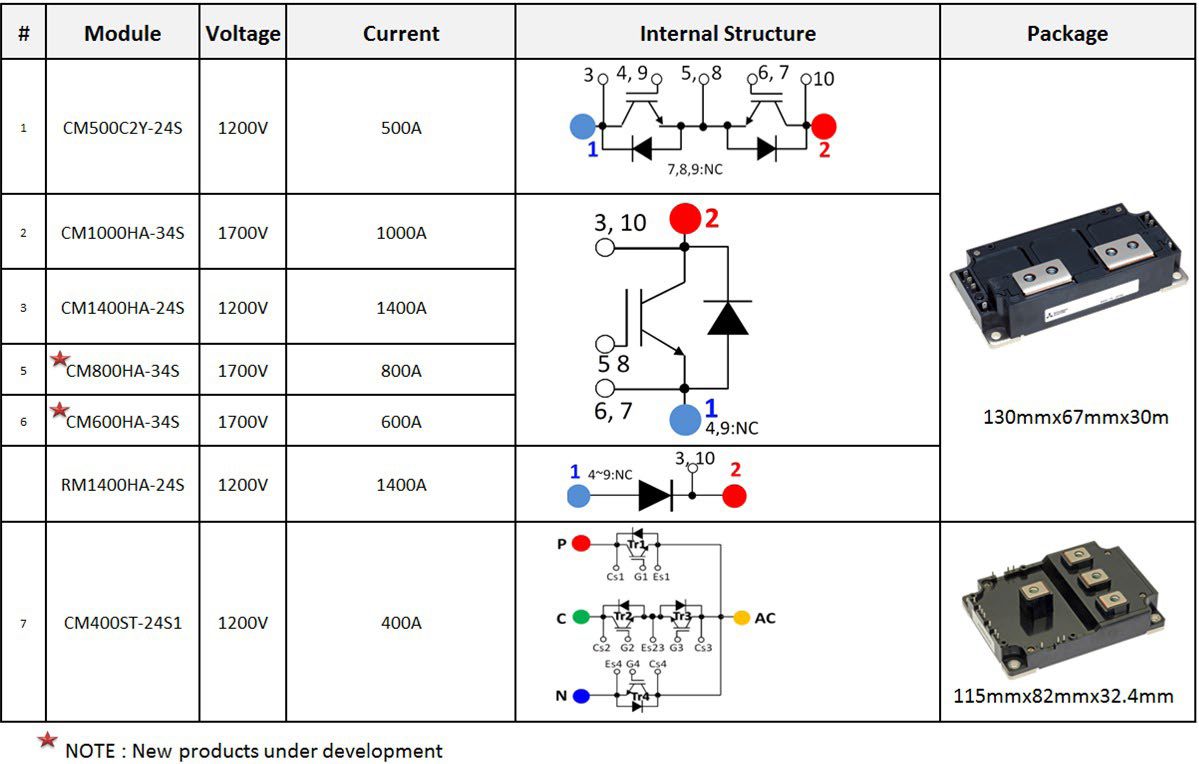
Figure 1: Line-up of the products dedicated for 3-level solutions
These power modules from Mitsubishi Electric are optimized for 3-level topologies with regards to the following parameters:
- Compact package size: For realizing an I type topology, in comparison with its counterparts from other manufacturers, the 1 in 1 modules (each 130 mm x 67 mm x 30 mm in size) offer about 20% reduction in mounting area. This was achieved by taking advantage of the superior thermal behavior of the Aluminium nitride (AlN) substrate and combining it with the CSTBT™ chip technology.
- Reduced internal inductance: The 1 in 1 modules have an internal inductance of only 8 nH. Internal stray inductance plays an important role in 3-level topologies as several elements are connected in series unlike the traditional 2-level topologies.
- Reduced overall inductance: The combination of a low internal inductance, a reduced mounting area and the location of terminals for easy connections ensure a reduced overall inductance for the set-up.
- Access to auxiliary terminals: The module provides access to the auxiliary terminals on two sides for the connecting the gate driver (without having the need to disturb the bus bar arrangement).
An example of how low inductance I-type and T-type 3-level topology bus bar designs can be realized is represented in Figure 2. As shown in this example, it is obvious that these modules are specifically optimized for 3-level topologies, thereby addressing the challenges associated with DC bus bar inductance, power density and flexibility.
Figure 3 shows the different power levels achievable by developing various 3-level topologies employing power modules from Mitsubishi Electric. The power levels are based on a conservative dimensioning of junction-case temperature rise of 25K considering a switching frequency of 2 kHz. Depending on the cooling system and the switching frequency, the output can obviously be further maximized.
Power levels
- 125 kW to 500 kW range: For a DC link voltage of 850 V, the CM400ST-24S1 with its inbuilt T type topology can deliver up to 250 kW in stand-alone mode. When used in parallel, about 500 kW output can be delivered.
- 500 kW to 2 MW range: When a DC link voltage of 1200V is utilized, two CM1000HA-34S (1000A/1700V) together with two CM500C2Y-24S (500A /1200V) in parallel can be employed to achieve more than 1 MW output. On the other hand, when an 850V DC link is considered, two CM1400HA-24S (1400A/1200V) can be employed together with two CM500C2Y in parallel to achieve more than 1 MW output power. With a DC link of 2400V, six CM1000HA-34S can be employed to develop a 1.8 MW inverter. Remarkably, utilizing a 1700V DC link, more than 2 MW output can be achieved by employing four CM1400HA-24S modules along with two RM1400HA-24S (neutral clamp diodes).
- Extended Megawatt range: It is obvious that by paralleling the options provided above, extended megawatt range inverters can be realized. An alternative solution for this class is to employ multi-level topologies.
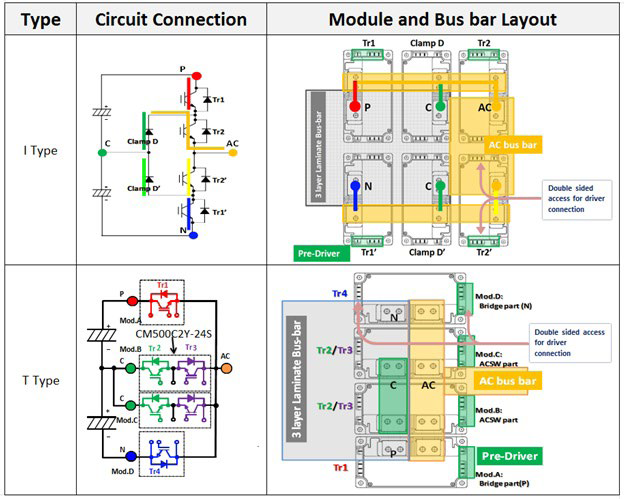
Figure 2: Sample 3-level constructions which can be realized for using Mitsubishi Electric power modules
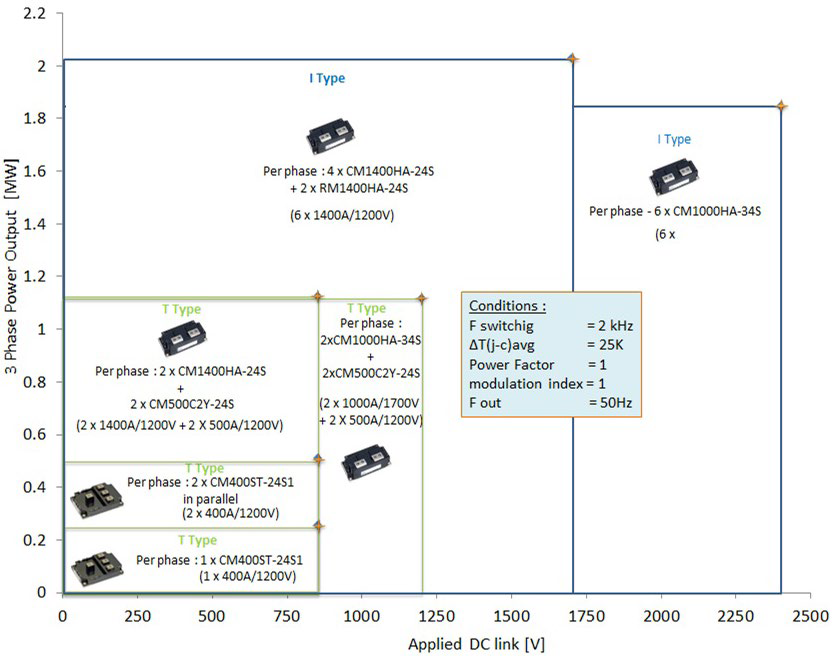
Figure 3: Power capability matrix for different 3-level solutions
As a result of these new products being available, the designer can choose the best fitting solution considering the power and DC voltage requirements. The designer is thus able to evaluate and accordingly select a suitable system voltage to achieve significant system level benefits and thereby maximize overall efficiency.
Employing the appropriate solution
Figure 4 shows that for an inverter with 1200V dc-link voltage, the maximum output current achievable for different switching frequencies for a maximum allowable ΔT(j-c) avg = 25K (imposed on the first element in any module to reach this limit) depends on the topology employed. The T type topology has advantages with respect to a lower part count and the corresponding volume reduction. However, the equivalent I type topology brings forth interesting system level benefits. Considering a fixed switching frequency of 3 kHz, it can be seen that the I type inverter is capable of delivering 1.41 times more current than the equivalent T type topology. Such benefit in power capability can also be used to allow an increase in the switching frequency (a factor of 2.66 for the 800A range) bringing significant benefits in passive component reduction. Depending on the weightage allocated to passives dimensioning and device count, an appropriate decision can be made.
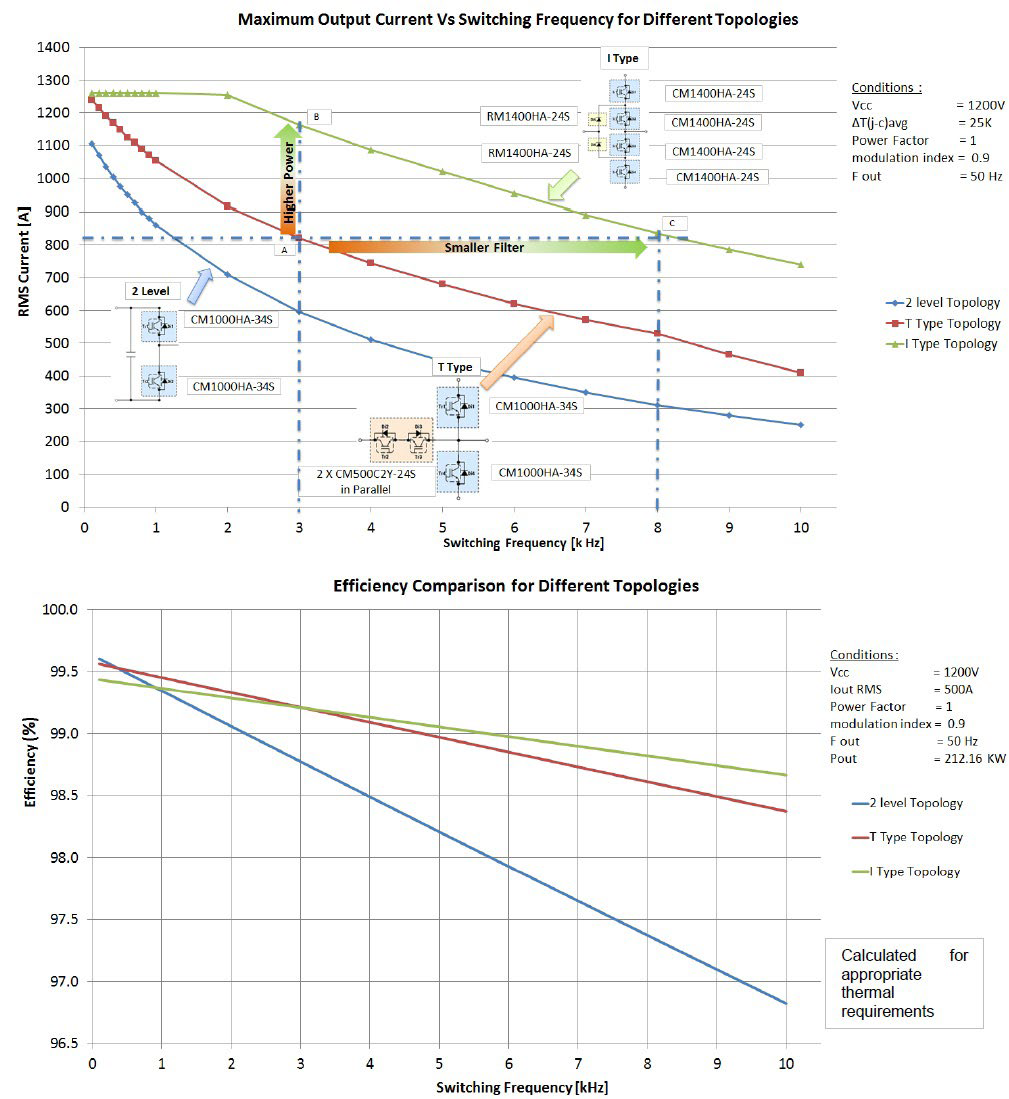
Figure 4: Analysis and comparison of performance using 3-level and 2-level topologies
Conclusion
While each module is designed to deliver the best electrical performance, the module packaging itself and the layout as well is optimized for 3-level inverter design. Combining these aspects with the variety of combinations possible using these different modules, designers now are allowed greater flexibility in realizing solutions which cater to their specific needs. To sum things up - it is clear, that there is flexibility in mechanical layout and flexibility in system level design parameters (choice of DC-link, filter). By addressing the specific needs of individual applications, it is obvious that solutions based on Mitsubishi Electric 3-level modules help achieve the maximum possible overall efficiency along with the best possible performance.
References
[1] MELCOSIM: IGBT thermal and loss simulation software, available at www. mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/ simulator/
[2] Marco Honsberg and Thomas Radke : “4in1 400A/1200V Module with T-type Topology for 3-Level Applications” Bodos Power Feb’2015, pages 26-28.
[3] Marco Honsberg, Thomas Radke : “3-level IGBT modules with Trench Gate IGBT and their thermal analysis in UPS, PFC and PV operation modes” - EPE 2009 – Barcelona - ISBN: 9789075815009
[4] Marco Honsberg and Thomas Radke : “A family of 3-level IGBT modules from 10A to 600A equipped with Trench Gate IGBT and their thermal performance under typical conditions for UPS and PV inverter operation” PCIM 2009 ISBN: 978-3-8007-3158-9
[5] L. Caballero, S. Ratés, O. Caubet, S. Busquets-Monge: Advantages of ac-ac power converters based on ANPC topology for wind applications”
[6] International Journal of Conceptions on Electrical & Electronics Engineering Vol. 1, Issue. 2, December 2013; ISSN: 2345 – 9603 : “Reduction of common mode voltage in three level neutral point diode clamped multilevel inverter using space vector pulse width modulation”
[7] Application note : 3-level application using 1 in 1, 2 in 1 and the 4 in 1 modules.
Related posts
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Leave a comment