

Category


Photos are for informational purposes only. View product specification
please use latin characters
Tube generators
Tube generator (the lamp is a triode) are devices used for surface heat treatment with a working frequency from 100kHz to 4MHz. However, the most common devices in the industry work with a frequency of about 400kHz. By modernizing lamp generators, it is important to exchange essential components of the device. The replacement of these components is aimed at repairing or improving the functioning of the device in a technical sense as well as achieving better technological effects by these devices. Generators subject to modernization are usually devices designed and constructed by both domestic and foreign producers in the 50's, 60's, 70's and 80's of the last century. Tube generators are now often (due to the fact that high-speed semiconductor switches have appeared on the market) replaced by transistor generators (with IGBT or MOSFET type transistors).
The advantages of transistor generators
Transistor generators have the following advantages:
The advantages of tube generators
Tube generators have the following advantages:
The construction of tube generators
Tube generator consists essentially of two blocks:
The process of modernisation of generators
Modernization of generator should be considered in several aspects:
Conducting the modernization activities, means that tube generators produced several decades ago can still be very useful for applications even in technologically demanding heat treatment processes and with much smaller financial outlays than would be required by investments in modern transistor generators.
The DACPOL company offers a comprehensive selection of replacements for the non-manufactured LAMINA lamps: T-25W, T-25P, T26W/22, T26W/23, T-26P/22, T-26P/23, T-10P/22, T-12W/21, T-60W/12, T-60W/22, T-60V/12. We select the lamp, make a replacement and comprehensive service and start the generator.
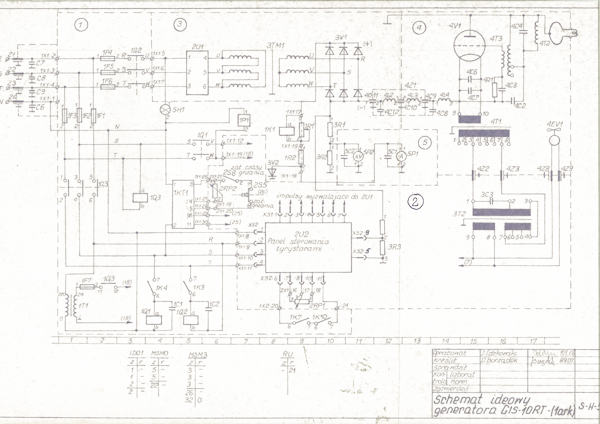
The attached drawing shows the basic schematic diagram of the modernized GIS-10 generator; after modernization the generator was named GIS-10RT (RT - thyristor controller). Numerals (in a circle) 1, 3 indicate the high voltage power circuit of the high voltage power supply. The number 4 indicates the correct block of the induction generator. Figures 2 and 5 indicate the control, measuring, protecting and supplying cathodes of the triodes. GIS generators were produced in the 1960s and early 1970s at WAREL plants and after modernization they have been working successfully in small factories to this day. Prior to the modernization, the thyratron rectifier on the side of the 3TM1 high voltage transformer was used to regulate the power (3V1 diode rectifier is now in place). Modernization consisted in removing the thyratron controller and installing a 2U1 thyristor regulator with the 2U2 control panel and the diode rectifier (diode stacks) on the high voltage side 3V1. If necessary, the resonance system 4V1, 4T3, 4T4, 4T2 shall be modernized.
An example description of the modernisation
The modernization of the HFG / J40 generator was carried out in 2017 in FAMUR S.A. company that produce equipment for mining. Generator HFG/J40 was produced in 1962 in the austrian company ELIN. Its operating frequency: 400kHz, and power (guaranted by the manufacturer) on output terminal: 40kW. At the beginning of the 90s of the last century, the ELCAL company modernized the generator, which consisted of replacing the BBC triode, the triode of national production type T26W, and replacing the thyratron regulator with the thyristor regulator type: PRW 210/440 and rectifying diode stacks. Selected photos showing the device before modernization are presented below.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Modernization consisted of:
After modernization, the output power of the generator increased by approx. 20%.
Selected photos showing the device after modernization are presented below.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Are you interested in this product? Do you need additional information or individual pricing?
Tube generators
Tube generator (the lamp is a triode) are devices used for surface heat treatment with a working frequency from 100kHz to 4MHz. However, the most common devices in the industry work with a frequency of about 400kHz. By modernizing lamp generators, it is important to exchange essential components of the device. The replacement of these components is aimed at repairing or improving the functioning of the device in a technical sense as well as achieving better technological effects by these devices. Generators subject to modernization are usually devices designed and constructed by both domestic and foreign producers in the 50's, 60's, 70's and 80's of the last century. Tube generators are now often (due to the fact that high-speed semiconductor switches have appeared on the market) replaced by transistor generators (with IGBT or MOSFET type transistors).
The advantages of transistor generators
Transistor generators have the following advantages:
The advantages of tube generators
Tube generators have the following advantages:
The construction of tube generators
Tube generator consists essentially of two blocks:
The process of modernisation of generators
Modernization of generator should be considered in several aspects:
Conducting the modernization activities, means that tube generators produced several decades ago can still be very useful for applications even in technologically demanding heat treatment processes and with much smaller financial outlays than would be required by investments in modern transistor generators.
The DACPOL company offers a comprehensive selection of replacements for the non-manufactured LAMINA lamps: T-25W, T-25P, T26W/22, T26W/23, T-26P/22, T-26P/23, T-10P/22, T-12W/21, T-60W/12, T-60W/22, T-60V/12. We select the lamp, make a replacement and comprehensive service and start the generator.

The attached drawing shows the basic schematic diagram of the modernized GIS-10 generator; after modernization the generator was named GIS-10RT (RT - thyristor controller). Numerals (in a circle) 1, 3 indicate the high voltage power circuit of the high voltage power supply. The number 4 indicates the correct block of the induction generator. Figures 2 and 5 indicate the control, measuring, protecting and supplying cathodes of the triodes. GIS generators were produced in the 1960s and early 1970s at WAREL plants and after modernization they have been working successfully in small factories to this day. Prior to the modernization, the thyratron rectifier on the side of the 3TM1 high voltage transformer was used to regulate the power (3V1 diode rectifier is now in place). Modernization consisted in removing the thyratron controller and installing a 2U1 thyristor regulator with the 2U2 control panel and the diode rectifier (diode stacks) on the high voltage side 3V1. If necessary, the resonance system 4V1, 4T3, 4T4, 4T2 shall be modernized.
An example description of the modernisation
The modernization of the HFG / J40 generator was carried out in 2017 in FAMUR S.A. company that produce equipment for mining. Generator HFG/J40 was produced in 1962 in the austrian company ELIN. Its operating frequency: 400kHz, and power (guaranted by the manufacturer) on output terminal: 40kW. At the beginning of the 90s of the last century, the ELCAL company modernized the generator, which consisted of replacing the BBC triode, the triode of national production type T26W, and replacing the thyratron regulator with the thyristor regulator type: PRW 210/440 and rectifying diode stacks. Selected photos showing the device before modernization are presented below.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Modernization consisted of:
After modernization, the output power of the generator increased by approx. 20%.
Selected photos showing the device after modernization are presented below.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Modernization of the Induction Generator REL30Tr - A New Era of Efficiency
Modernization of the Induction Generator REL30Tr - A New Era of Efficiency
Your review appreciation cannot be sent
Report comment
Report sent
Your report cannot be sent
Write your review
Review sent
Your review cannot be sent
