
Debes estar logueado
Category


Las fotos son solo para fines informativos. Ver especificaciones de producto
please use latin characters
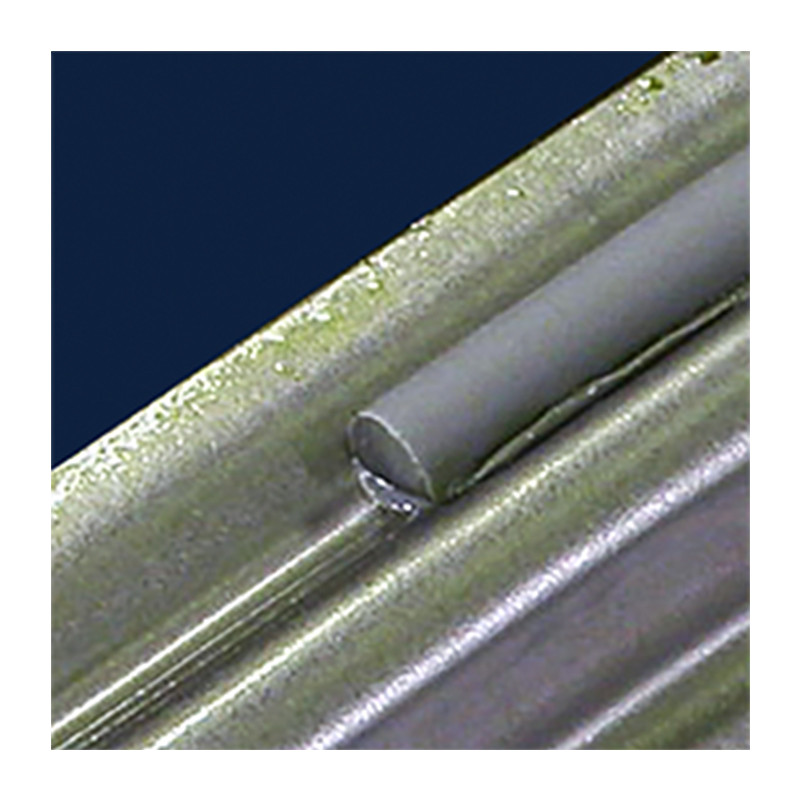
Bonding is the process of joining a metal or conductive material to a rubber or plastic material without a third bonding agent. This category includes applications where gaskets are bonded to metal casings, thermoplastic composite bonding, and rubber washer/bumper assemblies. Bonding requires accurate heat control while still reaching temperatures that cause the bonds to form (see also metal-to-plastic insertion.
Modern induction heating provides many advantages over other heating methods and is commonly used for bonding applications. Heating through induction provides reliable, repeatable, non-contact and energy-efficient heat in a minimal amount of time. Solid state systems are capable of heating very small areas within precise production tolerances, without disturbing individual metallurgical characteristics.
Closed loop control, through the use of an optical pyrometer or other temperature sensing device, can provide constant heat with a tolerance as low as 3°C at 700°C. Induction heating also ideal for in-line production processes because of its ability to produce repeatable, rapid and accurate heating cycles.
Typical RF power supplies for induction bonding range from 1 to 20kW, depending on the parts and application requirements.
| Bonding Steel Tubes to Plastic Tubes | Bonding a stainless steel sheet to a soundproofing mat | Debonding Rubber Gaskets with Metal End Rings | Bonding adhesive onto a steel washer for an automotive application | Bonding plastic with a steel gasket for an automotive application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |
| De-bonding a magnetic steel paint can lid | De-bonding urethane from a steel insert (doffer pad) | Bonding Metal to Plastic for Dental Tools | Bonding plastic sleeve to stainless steel handle for food industry | Debonding rubber coating from a steel casted water valve |
 |  |  |  |  |
¿Estás interesado en este producto? ¿Necesita información adicional o precios individuales?
Usted debe estar conectado
Bonding is the process of joining a metal or conductive material to a rubber or plastic material without a third bonding agent. This category includes applications where gaskets are bonded to metal casings, thermoplastic composite bonding, and rubber washer/bumper assemblies. Bonding requires accurate heat control while still reaching temperatures that cause the bonds to form (see also metal-to-plastic insertion.
Modern induction heating provides many advantages over other heating methods and is commonly used for bonding applications. Heating through induction provides reliable, repeatable, non-contact and energy-efficient heat in a minimal amount of time. Solid state systems are capable of heating very small areas within precise production tolerances, without disturbing individual metallurgical characteristics.
Closed loop control, through the use of an optical pyrometer or other temperature sensing device, can provide constant heat with a tolerance as low as 3°C at 700°C. Induction heating also ideal for in-line production processes because of its ability to produce repeatable, rapid and accurate heating cycles.
Typical RF power supplies for induction bonding range from 1 to 20kW, depending on the parts and application requirements.
| Bonding Steel Tubes to Plastic Tubes | Bonding a stainless steel sheet to a soundproofing mat | Debonding Rubber Gaskets with Metal End Rings | Bonding adhesive onto a steel washer for an automotive application | Bonding plastic with a steel gasket for an automotive application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |
| De-bonding a magnetic steel paint can lid | De-bonding urethane from a steel insert (doffer pad) | Bonding Metal to Plastic for Dental Tools | Bonding plastic sleeve to stainless steel handle for food industry | Debonding rubber coating from a steel casted water valve |
 |  |  |  |  |
Su agradecimiento a la reseña no pudo ser enviado
Reportar comentario
Reporte enviado
Su reporte no pudo ser enviado
Escriba su propia reseña
Reseña enviada
Su reseña no pudo ser enviada
