Debes estar logueado
-
WróćX
-
Componentes
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductores
- Diodos
- Tiristores
-
Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | VISHAY (IR)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | Semikron
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POWEREX
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | IXYS
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POSEICO
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | ABB
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | TECHSEM
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Rectificadores de puente
-
Transistores
- Transistores | GeneSiC
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | Mitsubishi
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | STARPOWER
- Módulos ABB SiC MOSFET
- Módulos IGBT | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos MOSFET | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | ABB
- Módulos IGBT | POWEREX
- Módulos IGBT | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elementos semiconductores de carburo de silicio (SiC)
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Controladores de puerta
- Bloques de energía
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Convertidores de corriente y tensión LEM
-
Componentes pasivos (condensadores, resistencias, fusibles, filtros)
- Resistencias
-
Fusibles
- Fusibles miniatura para circuitos electrónicos, serie ABC y AGC
- Fusibles tubulares de acción rápida
- Eslabones fusibles de retardo de tiempo con características GL / GG y AM
- Eslabones fusibles ultrarrápidos
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar británico y estadounidense)
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar europeo)
- Fusibles de tracción
- Eslabones fusibles de alto voltaje
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Condensadores
- Condensadores de motor
- Condensadores electrolíticos
- Condensadores de película
- Condensadores de potencia
- Condensadores para circuitos de CC
- Condensadores de corrección del factor de potencia
- Condensadores de alto voltaje
- Condensadores de calentamiento por inducción
- Condensadores de almacenamiento de energía y pulsos
- Condensadores de ENLACE CC
- Condensadores para circuitos AC/DC
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Filtros EMI
- Supercondensadores
- Protección contra sobretensiones
- Filtros para detección de emisiones TEMPEST
- Pararrayos
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Relés y contactores
- Teoría de relés y contactores
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Reguladores, controles y accesorios
- Arranques suaves y contactores de inversión
- Relés electromecánicos
- Contactores
- Interruptores giratorios
-
Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, serie 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, series CWA y CWD
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos de las series CMRA y CMRD
- Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos, serie PS
- Relés semiconductores de CA dobles y cuádruples, serie D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relés de estado sólido monofásicos, serie gn
- Relés semiconductores de ca monofásicos, serie ckr
- Relés AC monofásicos SERIE ERDA Y ERAA para carril DIN
- Relés AC monofásicos para corriente 150A
- Relés dobles de estado sólido integrados con disipador de calor para carril DIN
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos para PCB
- Relés de interfaz
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Núcleos y otros componentes inductivos
- Radiadores, varistores, protecciones térmicas
- Aficionados
- Aire Acondicionado, Accesorios para Armarios Eléctricos, Neveras
-
Baterías, cargadores, fuentes de alimentación de búfer e inversores
- Baterías, cargadores - descripción teórica
- Baterías de iones de litio. Baterías personalizadas. Sistema de gestión de batería (BMS)
- Pilas
- Cargadores de baterías y accesorios
- Fuente de alimentación de respaldo de UPS y fuentes de alimentación de búfer
- Convertidores y accesorios para fotovoltaica
- Almacen de energia
- Celdas de combustible
- Baterías de iones de litio
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Automaticas
- Elevadores Spiralift
- Piezas para drones Futaba
- Finales de carrera, microinterruptores
- Sensores, transductores
- Pirometría
- Contadores, temporizadores, medidores de panel
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Señalización luminosa y sonora
- Cámara termográfica
- Pantallas LED
- Botones e interruptores
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Cables, alambres Litz, conductos, conexiones flexibles
- alambres
- Pasamuros y acopladores de cables
- cables Litz
-
Cables para aplicaciones especiales
- Los cables de extensión y compensación
- Cables para termopares
- Los cables de conexión a PT czyjnków
- Multicore cables temp. -60 ° C a + 1400 ° C
- cables de media tensión SILICOUL
- ignición alambres
- Los cables calefactores
- temp núcleo único. -60 ° C a + 450 ° C
- conductores de trenes
- El calentamiento de los cables en el Ex
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- camisas
-
trenzas
- trenzas planas
- trenzas ronda
- trenza muy flexible - plana
- trenza muy flexible - Ronda
- Copper cilíndrico trenzado
- Copper protector de la trenza y cilíndrica
- cintas de conexión flexibles
- Trenzas cilíndrico galvanizado y acero inoxidable
- Aislamiento de PVC trenzas de cobre - Temperatura 85 ° C
- aluminio trenzado plano
- Kit de conexión - trenzas y tubos
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Accesorios para la tracción
- Terminales de cable
- barras flexibles aisladas
- carril flexible multicapa
- sistemas de gestión de cables
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
-
Semiconductores
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- Accionamientos de CA y CC (inversores)
- Automatización HVAC
- Automatización industrial
- Automatización industrial
- Calentamiento por inducción
- Componentes para atmósferas potencialmente explosivas (EX)
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Energy bank
- Equipos para Armarios de Distribución, Control y Telecomunicaciones
- Fuentes de alimentación (UPS) y sistemas rectificadores
- Impresión
- Máquinas de soldar y máquinas de soldar
- Máquinas herramientas CNC
- Máquinas para secar y procesar madera
- Máquinas para termoformado de plásticos
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Minería, metalurgia y fundación
- Motores y transformadores
- Tracción de tranvía y ferrocarril
-
Instalación
-
-
Inductores
-
-
Dispositivos de inducción
-
-
Servicio
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
7th Generation 1700 V IGBT Modules: Loss Reduction and Excellent System Performance

7th Generation 1700 V IGBT Modules: Loss Reduction and Excellent System Performance
For power electronic systems like industrial drives and converters for renewable energy applications, the major system requirements are: high reliability, high efficiency, high power density and competitive costs. In order to meet these requirements, power loss reduction is a key factor. Power loss reduction enables designs with higher power densities and lower IGBT junction temperatures. As a result, higher reliability can be achieved and the cooling system can be accordingly optimized. Therefore, Mitsubishi Electric has developed the new 1.7 kV 7th generation IGBT modules with improved performance.
By Masaomi Miyazawa, Thomas Radke and Narender Lakshmanan, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
1. Introduction
Power module performance affects the overall efficiency of the power electronic system. Accordingly, power modules have to be carefully chosen for a given application depending on various electrical and thermal performance parameters. Mitsubishi Electric had launched the latest 7th generation industrial IGBT modules in the 650 V and 1200 V classes [1]. These modules have already been well accepted by the market due to the advantages with regards to the key system requirements: high power density, high efficiency and high reliability. Subsequently, the 1700 V IGBT modules were developed to support applications with system voltages of 690 Vac.
For renewable applications, the AC-grid filter size can be reduced by increasing the IGBT switching frequency. In case of motor drives, higher switching frequencies are considered beneficial especially for operation at high output frequencies. Unfortunately, the switching loss behavior of the existing 1700 V modules available at the market has not encouraged the designers to explore the possibility of increasing the switching frequency for availing system level benefits. In order to enable operation at reasonable switching frequencies (above 1000 Hz) with the 1.7 kV IGBT modules, the 7th generation IGBT chips and the RFC (Relaxed Field of Cathode) diode chips [2] were developed and optimized for achieving a significant reduction in power loss.
An optimized line-up from 100 A to 600 A current rating has been developed. Further module developments with higher rated currents (up to 1200A) are ongoing.
2. 7th generation chip performance
In order to offer the best electrical characteristics, the latest 7th generation CSTBT™ chip [4] and RFC diode have been used in the 1.7 kV IGBT modules. These chips possess an optimized structure and are thinner than previous generation devices. Additionally, the devices have been designed by selecting an appropriate trade-off between the DC performance and the switching performance.
2.1 IGBT chip
The IGBT power loss and the EMI profile has been optimized by designing an optimized MOS structure, advanced termination, and a reduction of the wafer thickness. Figure 1 shows the comparison of the trade-off between VCEsat and Eoff of the 7th generation IGBT with a standard IGBT chip available in the market today. The Eoff of the 7th generation IGBT is approximately 30 percent lower in spite of the same on-sate voltage drop.
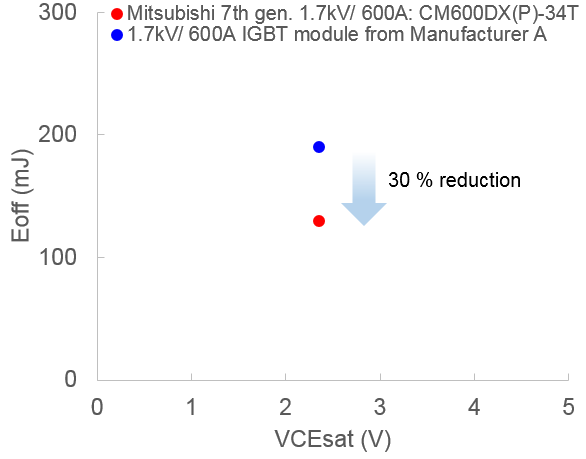
Figure 1: Comparison of the trade-off between VCEsat and Eoff Conditions: VCC=1000 V, IC=600 A, Tj=125 °C, RG min.
2.2 Diode chip
The 7th generation 1.7kV IGBT module is equipped with the RFC diode in order to reduce power loss without generating unnecessary oscillations during switching. The RFC diode has a unique structure in which the P layer is partially added on the cathode side and holes are injected during the recovery period to soften the recovery waveform. Using the RFC structure, it was possible to develop a diode with a reduced wafer thickness and one which does not exhibit snappy behavior. Thus, it was possible to improve the diode trade-off (DC performance versus switching loss). Figure 2 shows the comparison of the trade-off between VF and Err. A significant reduction (about 50%) of recovery losses has been achieved. Additionally, the lower recovery charge Qrr results in a reduction of IGBT turn-on switching losses.
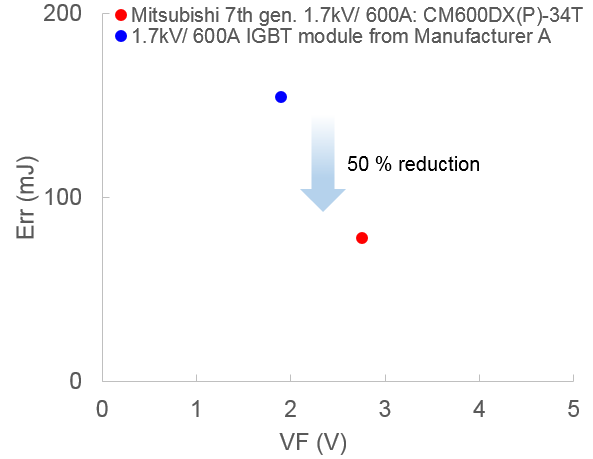
Figure 2: Comparison of the trade-off between VF and Err Conditions: VCC=1000 V, IC=600 A, Tj=125 °C, RG min.
3. Power loss comparison
A loss simulation for several application conditions has been performed by using the free simulation software Melcosim [5]. Figure 3 shows the overall power loss comparison of 600A/1700V IGBT module CM600DX(P)-34T [6] with the IGBT module from Manufacturer A. As evident from Fig. 3, the power loss of the 7th generation IGBT module is approximately 30 percent lower under typical application conditions (considering a switching frequency of 2 kHz). It is clear that a major contributor to the loss improvement is the reduction of diode switching losses and the IGBT switching losses. For a heatsink with Rth(s-a)=90 K/kW, the resulting IGBT-chip temperature Tj is 22 K lower at the given application conditions. However, if the junction temperature Tj is to be maintained the same, the output current can be increased by approximately 30%. Figure 4 shows the comparison of power loss in the 600A/1700V IGBT module as function of switching frequency. As evident from Fig. 4, the improvement rate is getting higher at a higher frequency. For example the power loss of the IGBT module from Manufacturer A at 2 kHz is almost the same as the overall power loss considering the 7th generation technology’s performance at 4 kHz switching frequency. As a result, by maintaining the same efficiency, the switching frequency could be doubled from 2 kHz to 4 kHz. This increase in the switching frequency enables a remarkable size and cost reduction of passive components like filter chokes.
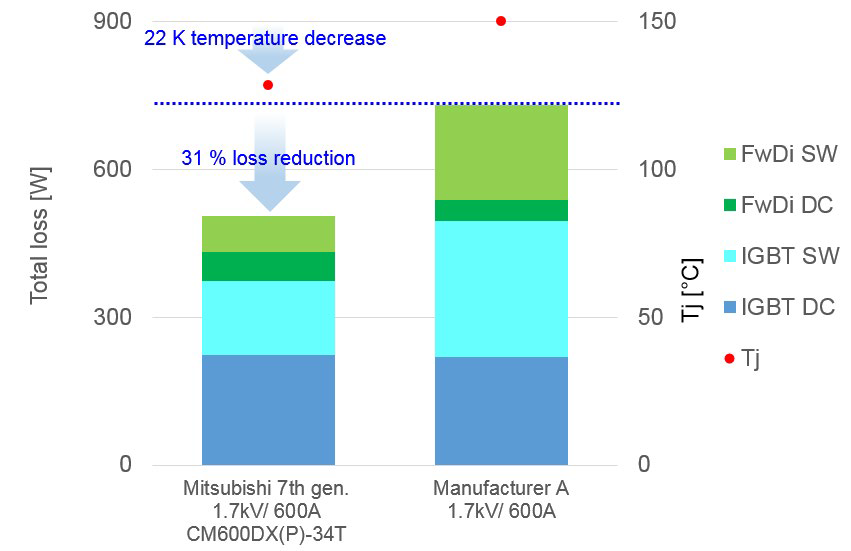
Figure 3: The Power loss comparison of the 600A/1700V IGBT module at 2 kHz Conditions: VCC=1000 V, IO=270 A peak, fc=2 kHz, cos(φ)=0.8, M=1, Ta=40 °C, Rth(s-a)=90 K/kW, RG min.
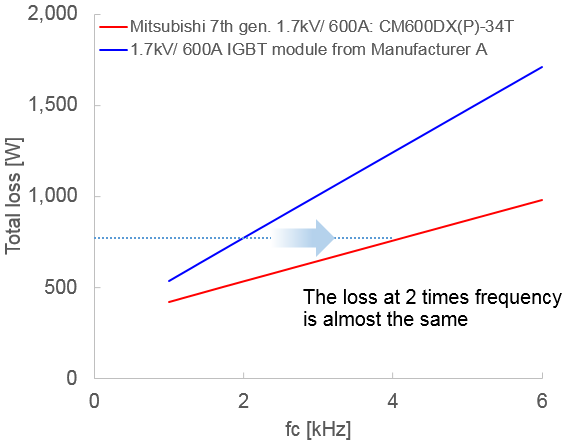
Figure 4: The power loss comparison considering the 600A/1700V IGBT module for several switching frequencies Conditions: VCC=1000 V, IO=270 Apeak, cos(φ)=0.8, M=1, Tj=125 °C, RG min.
4. Expanded line-up
In order to meet various applications requirements, Mitsubishi Electric has developed a comprehensive modules line-up in 1.7 kV class. Table 1 shows the line-up which includes 12 module types in the NX-package ranging from 100 A to 600 A and 6 module types in the standard package ranging from 75 A to 400 A. In the NX-type package, both solder-pin and press-fit-pin options have been developed for each current rating. They have different terminals. The press-fit-pin package can be assembled by solderless press process to the PCB board. Furthermore, in the NX-type module, the SLC (Solid Cover) technology delivers an improved thermal cycle capability by combining a resininsulated metal baseplate and direct potting resin [3]. The advanced SLC technology enables the elimination of the internal bond wires between multiple ceramic substrates which resulting in lower parasitic inductance and higher reliability. In the standard-type module (refer to Table 1), the TMS (Thick Metal Substrate) technology eliminates the solder layer under the substrate and increases the thermal cycle capability [1]. The parasitic inductance has been reduced by improving the internal layout. In addition, the main terminal pitch for the 62× 108 mm package is 28 mm, which is compatible to the existing package in Europe. The 7th generation IGBT modules are available with the pre-applied PC-TIM (Phase Change Thermal Interface Material) optionally. It contributes to the simplification of the assembly process and improves the thermal contact between module base and heatsink.
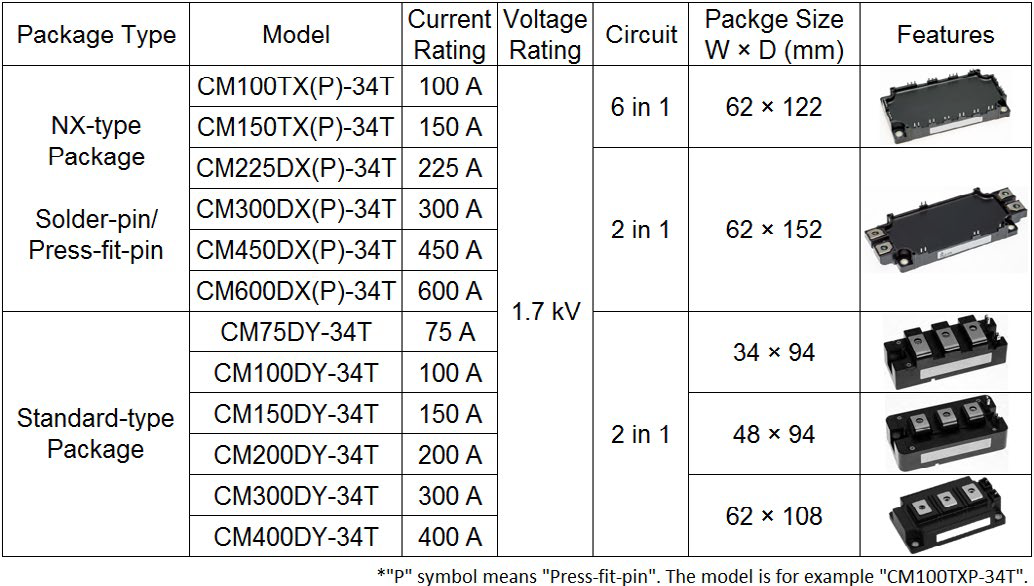
Table 1: Expanded line-up in 1.7 kV class. In the NX-type package, there are two pin types (solder and press-fit) in the each current rating.
To support applications requiring higher power ratings, a new industrial IGBT module with a half bridge configuration is under development. This new power module package which is shown in Figure 5 has a dimension of 100x144x40 mm³. IGBT modules based on the 7th generation chip technology, with a current ratings up to 1200 A in the 1700 V category are under consideration. In case an application requires higher current (more than 1200A) this module is an ideal solution since it is optimized for parallel operation thereby providing a scalable and an efficient solution for high power applications.
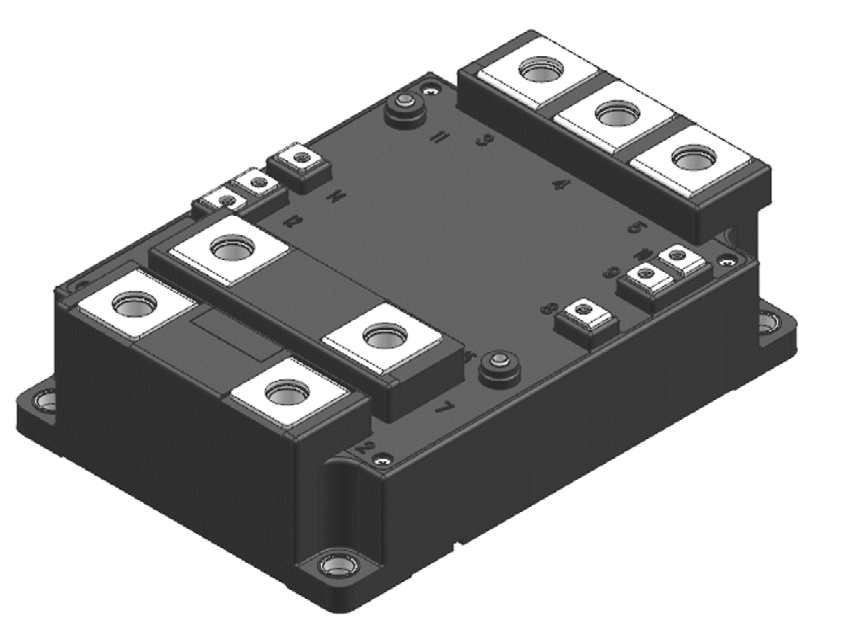
Figure 5: New industrial IGBT module
5. Summary
In the analysis presented here, the IGBT chip performance exhibits approximately 30% improved trade-off between the VCEsat and Eoff. The diode chip performance exhibits 50% lower Err. By utilizing these devices, the overall power loss is approximately 30% lower and Tj is 22 K lower than the performance of the IGBT module from Manufacturer A at 2 kHz and even more significant in case of higher switching frequencies. This enables either 30% higher output power or doubling the switching frequency (cost saving of passive components).
It is evident that Mitsubishi Electric offers several different types of power semiconductor modules (18 types of module designs) utilizing latest technologies in order to deliver the best system performance and the highest system reliability in the 1700 V category.
References:
[1] M. Miyazawa et al., “7th Generation IGBT Module for Industrial Applications“, PCIM Europe 2014, Nuremberg, Germany, pp. 34-38.
[2] K. Nakamura et al., “Evaluation of Oscillatory Phenomena in Reverse Operation for High Voltage Diodes”, ISPSD 2009, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 156-159.
[3] T. Radke et al., “Enhanced Power Density and Expanded Line-up of the 7th Gen. Industrial IGBT Modules Utilizing the Improved Thermal Conductivity of the Highly Reliable SLC-Technology”, Bodo’s Power Systems, June 2016, pp. 16-22.
[4] H. Takahashi et al., ”Carrier Stored Trench-Gate Bipolar Transistor (CSTBT) – A Novel Power Device for High Voltage Application”, ISPSD 1996, Maui, USA, pp. 349-352.
[5] Melcosim Simulation software “www.mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/simulator/index.html”
[6] DatasheetCM600DX(P)-34T www.mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/php/oPartProfile.php?FILENAME=cm600dx-34t_e.pdf&FOLDER=/product/powermodule/igbt/t_series
Publicaciones relacionadas
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Deja un comentario