Debes estar logueado
-
WróćX
-
Componentes
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductores
- Diodos
- Tiristores
-
Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | VISHAY (IR)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | Semikron
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POWEREX
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | IXYS
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POSEICO
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | ABB
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | TECHSEM
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Rectificadores de puente
-
Transistores
- Transistores | GeneSiC
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | Mitsubishi
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | STARPOWER
- Módulos ABB SiC MOSFET
- Módulos IGBT | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos MOSFET | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | ABB
- Módulos IGBT | POWEREX
- Módulos IGBT | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elementos semiconductores de carburo de silicio (SiC)
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Controladores de puerta
- Bloques de energía
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Convertidores de corriente y tensión LEM
-
Componentes pasivos (condensadores, resistencias, fusibles, filtros)
- Resistencias
-
Fusibles
- Fusibles miniatura para circuitos electrónicos, serie ABC y AGC
- Fusibles tubulares de acción rápida
- Eslabones fusibles de retardo de tiempo con características GL / GG y AM
- Eslabones fusibles ultrarrápidos
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar británico y estadounidense)
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar europeo)
- Fusibles de tracción
- Eslabones fusibles de alto voltaje
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Condensadores
- Condensadores de motor
- Condensadores electrolíticos
- Condensadores de película
- Condensadores de potencia
- Condensadores para circuitos de CC
- Condensadores de corrección del factor de potencia
- Condensadores de alto voltaje
- Condensadores de calentamiento por inducción
- Condensadores de almacenamiento de energía y pulsos
- Condensadores de ENLACE CC
- Condensadores para circuitos AC/DC
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Filtros EMI
- Supercondensadores
-
Protección contra sobretensiones
- Protección contra sobretensiones para aplicaciones coaxiales
- Protección contra sobretensiones para sistemas de videovigilancia
- Protección contra sobretensiones para cableado de potencia
- Pararrayos para LED
- Descargadores de sobretensiones para energía fotovoltaica
- Protección del sistema de pesaje
- Protección contra sobretensiones para Fieldbus
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Filtros para detección de emisiones TEMPEST
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Relés y contactores
- Teoría de relés y contactores
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Reguladores, controles y accesorios
- Arranques suaves y contactores de inversión
- Relés electromecánicos
- Contactores
- Interruptores giratorios
-
Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, serie 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, series CWA y CWD
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos de las series CMRA y CMRD
- Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos, serie PS
- Relés semiconductores de CA dobles y cuádruples, serie D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relés de estado sólido monofásicos, serie gn
- Relés semiconductores de ca monofásicos, serie ckr
- Relés AC monofásicos SERIE ERDA Y ERAA para carril DIN
- Relés AC monofásicos para corriente 150A
- Relés dobles de estado sólido integrados con disipador de calor para carril DIN
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos para PCB
- Relés de interfaz
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Núcleos y otros componentes inductivos
- Radiadores, varistores, protecciones térmicas
- Aficionados
- Aire Acondicionado, Accesorios para Armarios Eléctricos, Neveras
-
Baterías, cargadores, fuentes de alimentación de búfer e inversores
- Baterías, cargadores - descripción teórica
- Baterías de iones de litio. Baterías personalizadas. Sistema de gestión de batería (BMS)
- Pilas
- Cargadores de baterías y accesorios
- Fuente de alimentación de respaldo de UPS y fuentes de alimentación de búfer
- Convertidores y accesorios para fotovoltaica
- Almacen de energia
- Celdas de combustible
- Baterías de iones de litio
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Automaticas
- Elevadores Spiralift
- Piezas para drones Futaba
- Finales de carrera, microinterruptores
- Sensores, transductores
- Pirometría
- Contadores, temporizadores, medidores de panel
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Señalización luminosa y sonora
- Cámara termográfica
- Pantallas LED
- Botones e interruptores
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Cables, alambres Litz, conductos, conexiones flexibles
- alambres
- cables Litz
-
Cables para aplicaciones especiales
- Los cables de extensión y compensación
- Cables para termopares
- Los cables de conexión a PT czyjnków
- Multicore cables temp. -60 ° C a + 1400 ° C
- cables de media tensión SILICOUL
- ignición alambres
- Los cables calefactores
- temp núcleo único. -60 ° C a + 450 ° C
- conductores de trenes
- El calentamiento de los cables en el Ex
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- camisas
-
trenzas
- trenzas planas
- trenzas ronda
- trenza muy flexible - plana
- trenza muy flexible - Ronda
- Copper cilíndrico trenzado
- Copper protector de la trenza y cilíndrica
- cintas de conexión flexibles
- Trenzas cilíndrico galvanizado y acero inoxidable
- Aislamiento de PVC trenzas de cobre - Temperatura 85 ° C
- aluminio trenzado plano
- Kit de conexión - trenzas y tubos
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Accesorios para la tracción
- Terminales de cable
- barras flexibles aisladas
- carril flexible multicapa
- sistemas de gestión de cables
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
-
Semiconductores
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- Accionamientos de CA y CC (inversores)
- Automatización HVAC
- Automatización industrial
- Automatización industrial
- Calentamiento por inducción
- Componentes para atmósferas potencialmente explosivas (EX)
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Energy bank
- Equipos para Armarios de Distribución, Control y Telecomunicaciones
- Fuentes de alimentación (UPS) y sistemas rectificadores
- Impresión
- Máquinas de soldar y máquinas de soldar
- Máquinas herramientas CNC
- Máquinas para secar y procesar madera
- Máquinas para termoformado de plásticos
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Minería, metalurgia y fundación
- Motores y transformadores
- Tracción de tranvía y ferrocarril
-
Instalación
-
-
Inductores
-
-
Dispositivos de inducción
-
-
Servicio
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Power Modules for Combining Innovation, Flexibility and Power Capability in the Various 3-Level Topologies

Power Modules for Combining Innovation, Flexibility and Power Capability in the Various 3-Level Topologies
Three level topologies have demonstrated higher efficiencies, filter optimization potential and the capability of handling high DC-link voltages. To maximize the advantages offered by the 3-level topologies, Mitsubishi Electric offers new power modules which unlock the potential to realize innovative solutions for different power segments.
By Narender Lakshmanan and Thomas Radke, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V. and Satoshi Kawabata, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Japan Power Device Works
Power conversion applications have always had to deliver high performance while maintaining the required quality of power. The harmonic profile of the output power can be improved by increasing the switching frequency. However, an increase in switching frequency compromises the inverter efficiency. Historically, the conventional 2-level inverters have served the industry with its seemingly uncomplicated topology where developers have always had to strike a balance between efficiency and filter optimization. With the invention of the 3-level topologies, many new avenues are now open for improving the output harmonic profile without compromising on the system efficiency. With the option of being able to apply the ‘zero’ level, this topology brings with it the following inherent benefits:
- Efficiency and output power capability [1]: The superior switching loss profile of a 3-level inverter ensures that better efficiencies can be achieved. Thus, for the same dc-link, a 3-level based inverter can deliver a higher output power compared to the corresponding 2-level inverter.
- AC filtering [5]: For the same switching frequency, the 3-level topology utilizes the availability of the ‘zero’ level to deliver an AC output of higher power quality than the corresponding 2-level inverter. This naturally allows a significant reduction of the output filter inductance.
- dv/dt Filter [5]: Since the phase to neutral output of a 3-level inverter shifts between 0V and (+/- Vdc)/2 (unlike the 2-level output), the corresponding dv/dt across the load is naturally reduced by about 50%.
- Common mode voltage reduction [5][6]: In comparison with 2-level, significant reduction (about 25%) of common mode voltage is possible in the 3-level topology.
While every segment of the inverter industry can avail the benefits associated with the 3-level topologies, grid connected inverters (Solar, Wind, HVDC), UPS and medium-tohigh power drives stand to benefit significantly by employing this innovative approach [3][4].
Power Modules from Mitsubishi Electric for 3-level NPC inverters
The CM400ST-24S1 module has already been introduced and presented in good detail ([2] Bodos article Feb’2015). A new series of power modules with innovative packaging optimized for 3-level applications has been developed. The comprehensive line-up is shown in Figure 1. The CM500C2Y-24S is provided as a dedicated neutral clamp switch for efficiently realizing the T type 3-level topology.
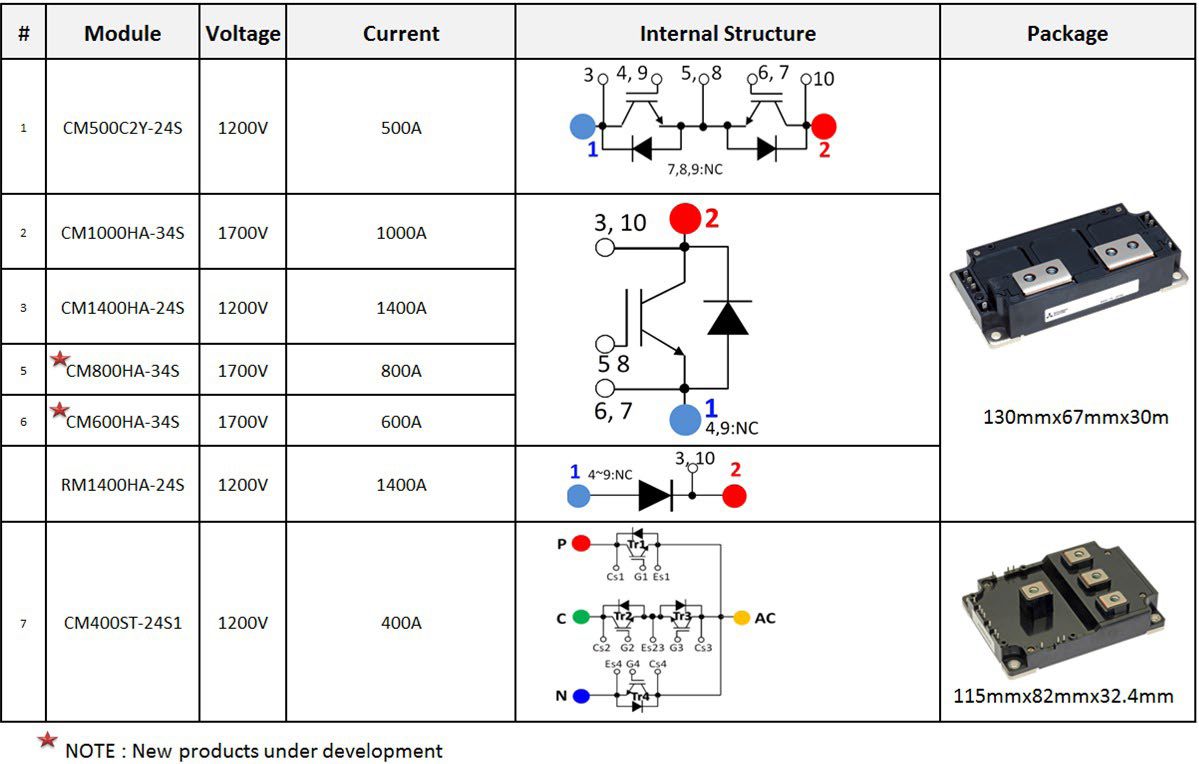
Figure 1: Line-up of the products dedicated for 3-level solutions
These power modules from Mitsubishi Electric are optimized for 3-level topologies with regards to the following parameters:
- Compact package size: For realizing an I type topology, in comparison with its counterparts from other manufacturers, the 1 in 1 modules (each 130 mm x 67 mm x 30 mm in size) offer about 20% reduction in mounting area. This was achieved by taking advantage of the superior thermal behavior of the Aluminium nitride (AlN) substrate and combining it with the CSTBT™ chip technology.
- Reduced internal inductance: The 1 in 1 modules have an internal inductance of only 8 nH. Internal stray inductance plays an important role in 3-level topologies as several elements are connected in series unlike the traditional 2-level topologies.
- Reduced overall inductance: The combination of a low internal inductance, a reduced mounting area and the location of terminals for easy connections ensure a reduced overall inductance for the set-up.
- Access to auxiliary terminals: The module provides access to the auxiliary terminals on two sides for the connecting the gate driver (without having the need to disturb the bus bar arrangement).
An example of how low inductance I-type and T-type 3-level topology bus bar designs can be realized is represented in Figure 2. As shown in this example, it is obvious that these modules are specifically optimized for 3-level topologies, thereby addressing the challenges associated with DC bus bar inductance, power density and flexibility.
Figure 3 shows the different power levels achievable by developing various 3-level topologies employing power modules from Mitsubishi Electric. The power levels are based on a conservative dimensioning of junction-case temperature rise of 25K considering a switching frequency of 2 kHz. Depending on the cooling system and the switching frequency, the output can obviously be further maximized.
Power levels
- 125 kW to 500 kW range: For a DC link voltage of 850 V, the CM400ST-24S1 with its inbuilt T type topology can deliver up to 250 kW in stand-alone mode. When used in parallel, about 500 kW output can be delivered.
- 500 kW to 2 MW range: When a DC link voltage of 1200V is utilized, two CM1000HA-34S (1000A/1700V) together with two CM500C2Y-24S (500A /1200V) in parallel can be employed to achieve more than 1 MW output. On the other hand, when an 850V DC link is considered, two CM1400HA-24S (1400A/1200V) can be employed together with two CM500C2Y in parallel to achieve more than 1 MW output power. With a DC link of 2400V, six CM1000HA-34S can be employed to develop a 1.8 MW inverter. Remarkably, utilizing a 1700V DC link, more than 2 MW output can be achieved by employing four CM1400HA-24S modules along with two RM1400HA-24S (neutral clamp diodes).
- Extended Megawatt range: It is obvious that by paralleling the options provided above, extended megawatt range inverters can be realized. An alternative solution for this class is to employ multi-level topologies.
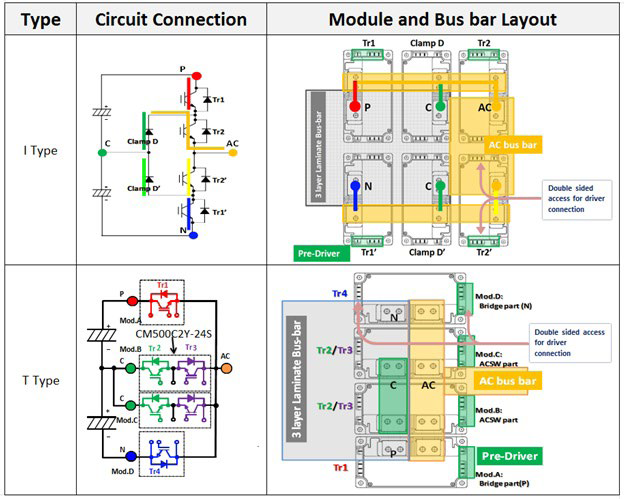
Figure 2: Sample 3-level constructions which can be realized for using Mitsubishi Electric power modules
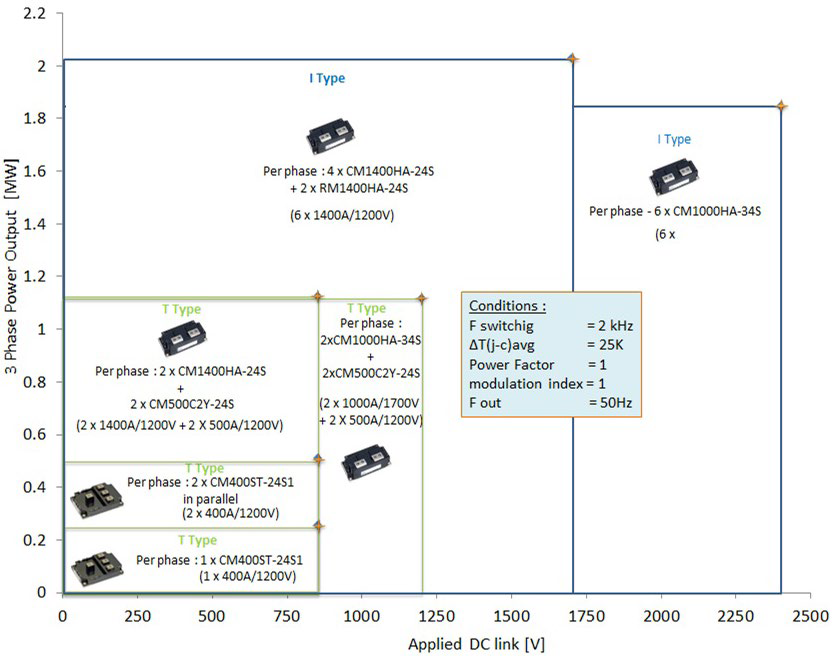
Figure 3: Power capability matrix for different 3-level solutions
As a result of these new products being available, the designer can choose the best fitting solution considering the power and DC voltage requirements. The designer is thus able to evaluate and accordingly select a suitable system voltage to achieve significant system level benefits and thereby maximize overall efficiency.
Employing the appropriate solution
Figure 4 shows that for an inverter with 1200V dc-link voltage, the maximum output current achievable for different switching frequencies for a maximum allowable ΔT(j-c) avg = 25K (imposed on the first element in any module to reach this limit) depends on the topology employed. The T type topology has advantages with respect to a lower part count and the corresponding volume reduction. However, the equivalent I type topology brings forth interesting system level benefits. Considering a fixed switching frequency of 3 kHz, it can be seen that the I type inverter is capable of delivering 1.41 times more current than the equivalent T type topology. Such benefit in power capability can also be used to allow an increase in the switching frequency (a factor of 2.66 for the 800A range) bringing significant benefits in passive component reduction. Depending on the weightage allocated to passives dimensioning and device count, an appropriate decision can be made.
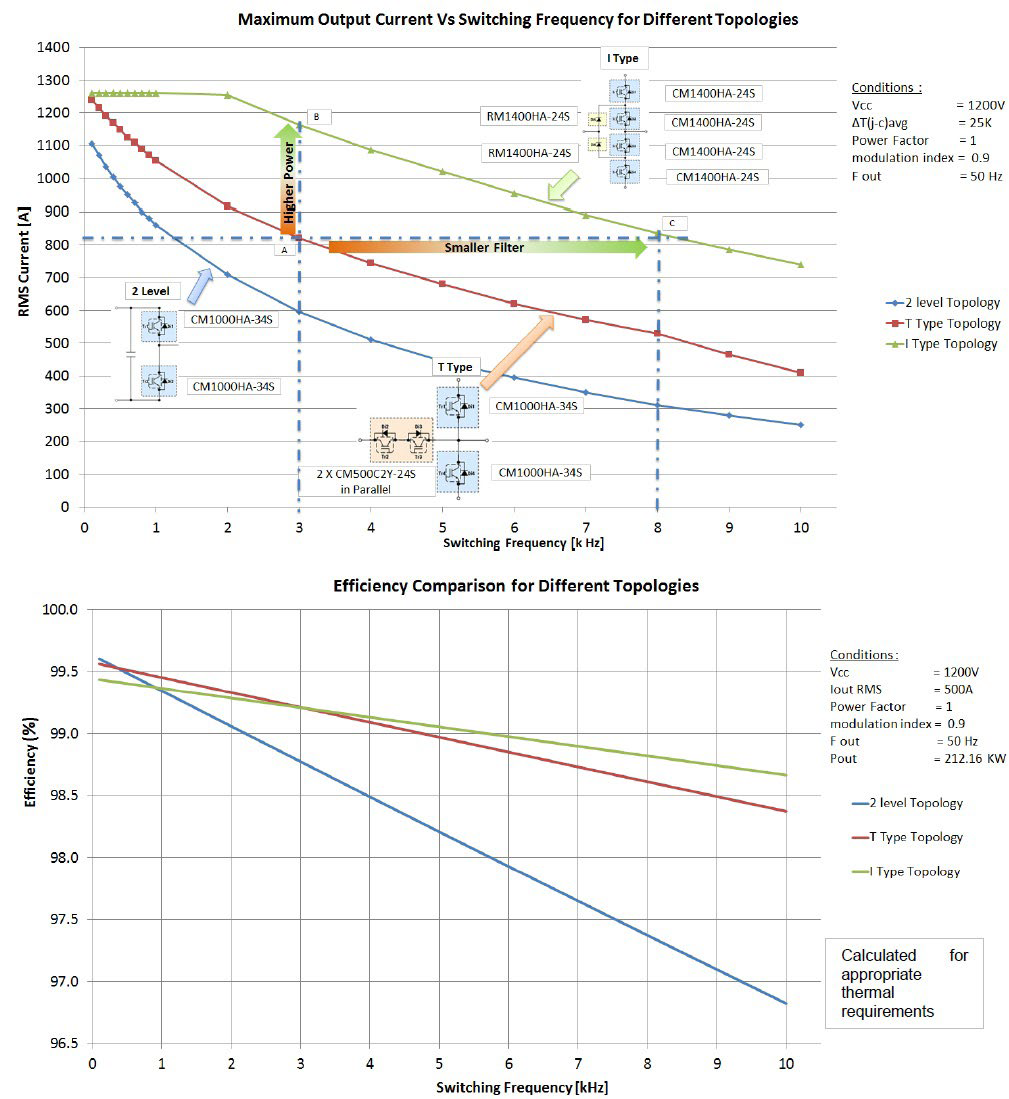
Figure 4: Analysis and comparison of performance using 3-level and 2-level topologies
Conclusion
While each module is designed to deliver the best electrical performance, the module packaging itself and the layout as well is optimized for 3-level inverter design. Combining these aspects with the variety of combinations possible using these different modules, designers now are allowed greater flexibility in realizing solutions which cater to their specific needs. To sum things up - it is clear, that there is flexibility in mechanical layout and flexibility in system level design parameters (choice of DC-link, filter). By addressing the specific needs of individual applications, it is obvious that solutions based on Mitsubishi Electric 3-level modules help achieve the maximum possible overall efficiency along with the best possible performance.
References
[1] MELCOSIM: IGBT thermal and loss simulation software, available at www. mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/ simulator/
[2] Marco Honsberg and Thomas Radke : “4in1 400A/1200V Module with T-type Topology for 3-Level Applications” Bodos Power Feb’2015, pages 26-28.
[3] Marco Honsberg, Thomas Radke : “3-level IGBT modules with Trench Gate IGBT and their thermal analysis in UPS, PFC and PV operation modes” - EPE 2009 – Barcelona - ISBN: 9789075815009
[4] Marco Honsberg and Thomas Radke : “A family of 3-level IGBT modules from 10A to 600A equipped with Trench Gate IGBT and their thermal performance under typical conditions for UPS and PV inverter operation” PCIM 2009 ISBN: 978-3-8007-3158-9
[5] L. Caballero, S. Ratés, O. Caubet, S. Busquets-Monge: Advantages of ac-ac power converters based on ANPC topology for wind applications”
[6] International Journal of Conceptions on Electrical & Electronics Engineering Vol. 1, Issue. 2, December 2013; ISSN: 2345 – 9603 : “Reduction of common mode voltage in three level neutral point diode clamped multilevel inverter using space vector pulse width modulation”
[7] Application note : 3-level application using 1 in 1, 2 in 1 and the 4 in 1 modules.
Publicaciones relacionadas
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Deja un comentario