Debes estar logueado
-
WróćX
-
Componentes
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductores
- Diodos
- Tiristores
-
Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | VISHAY (IR)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | Semikron
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POWEREX
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | IXYS
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POSEICO
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | ABB
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | TECHSEM
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Rectificadores de puente
-
Transistores
- Transistores | GeneSiC
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | Mitsubishi
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | STARPOWER
- Módulos ABB SiC MOSFET
- Módulos IGBT | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos MOSFET | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | ABB
- Módulos IGBT | POWEREX
- Módulos IGBT | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elementos semiconductores de carburo de silicio (SiC)
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Controladores de puerta
- Bloques de energía
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Convertidores de corriente y tensión LEM
-
Componentes pasivos (condensadores, resistencias, fusibles, filtros)
- Resistencias
-
Fusibles
- Fusibles miniatura para circuitos electrónicos, serie ABC y AGC
- Fusibles tubulares de acción rápida
- Eslabones fusibles de retardo de tiempo con características GL / GG y AM
- Eslabones fusibles ultrarrápidos
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar británico y estadounidense)
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar europeo)
- Fusibles de tracción
- Eslabones fusibles de alto voltaje
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Condensadores
- Condensadores de motor
- Condensadores electrolíticos
- Condensadores de película
- Condensadores de potencia
- Condensadores para circuitos de CC
- Condensadores de corrección del factor de potencia
- Condensadores de alto voltaje
- Condensadores de calentamiento por inducción
- Condensadores de almacenamiento de energía y pulsos
- Condensadores de ENLACE CC
- Condensadores para circuitos AC/DC
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Filtros EMI
- Supercondensadores
- Protección contra sobretensiones
- Filtros para detección de emisiones TEMPEST
- Pararrayos
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Relés y contactores
- Teoría de relés y contactores
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Reguladores, controles y accesorios
- Arranques suaves y contactores de inversión
- Relés electromecánicos
- Contactores
- Interruptores giratorios
-
Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, serie 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, series CWA y CWD
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos de las series CMRA y CMRD
- Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos, serie PS
- Relés semiconductores de CA dobles y cuádruples, serie D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relés de estado sólido monofásicos, serie gn
- Relés semiconductores de ca monofásicos, serie ckr
- Relés AC monofásicos SERIE ERDA Y ERAA para carril DIN
- Relés AC monofásicos para corriente 150A
- Relés dobles de estado sólido integrados con disipador de calor para carril DIN
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos para PCB
- Relés de interfaz
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Núcleos y otros componentes inductivos
- Radiadores, varistores, protecciones térmicas
- Aficionados
- Aire Acondicionado, Accesorios para Armarios Eléctricos, Neveras
-
Baterías, cargadores, fuentes de alimentación de búfer e inversores
- Baterías, cargadores - descripción teórica
- Baterías de iones de litio. Baterías personalizadas. Sistema de gestión de batería (BMS)
- Pilas
- Cargadores de baterías y accesorios
- Fuente de alimentación de respaldo de UPS y fuentes de alimentación de búfer
- Convertidores y accesorios para fotovoltaica
- Almacen de energia
- Celdas de combustible
- Baterías de iones de litio
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Automaticas
- Elevadores Spiralift
- Piezas para drones Futaba
- Finales de carrera, microinterruptores
- Sensores, transductores
- Pirometría
- Contadores, temporizadores, medidores de panel
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Señalización luminosa y sonora
- Cámara termográfica
- Pantallas LED
- Botones e interruptores
- Przejdź do podkategorii
-
Cables, alambres Litz, conductos, conexiones flexibles
- alambres
- Pasamuros y acopladores de cables
- cables Litz
-
Cables para aplicaciones especiales
- Los cables de extensión y compensación
- Cables para termopares
- Los cables de conexión a PT czyjnków
- Multicore cables temp. -60 ° C a + 1400 ° C
- cables de media tensión SILICOUL
- ignición alambres
- Los cables calefactores
- temp núcleo único. -60 ° C a + 450 ° C
- conductores de trenes
- El calentamiento de los cables en el Ex
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- camisas
-
trenzas
- trenzas planas
- trenzas ronda
- trenza muy flexible - plana
- trenza muy flexible - Ronda
- Copper cilíndrico trenzado
- Copper protector de la trenza y cilíndrica
- cintas de conexión flexibles
- Trenzas cilíndrico galvanizado y acero inoxidable
- Aislamiento de PVC trenzas de cobre - Temperatura 85 ° C
- aluminio trenzado plano
- Kit de conexión - trenzas y tubos
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Accesorios para la tracción
- Terminales de cable
- barras flexibles aisladas
- carril flexible multicapa
- sistemas de gestión de cables
- Przejdź do podkategorii
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
-
Semiconductores
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- Accionamientos de CA y CC (inversores)
- Automatización HVAC
- Automatización industrial
- Automatización industrial
- Calentamiento por inducción
- Componentes para atmósferas potencialmente explosivas (EX)
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Energy bank
- Equipos para Armarios de Distribución, Control y Telecomunicaciones
- Fuentes de alimentación (UPS) y sistemas rectificadores
- Impresión
- Máquinas de soldar y máquinas de soldar
- Máquinas herramientas CNC
- Máquinas para secar y procesar madera
- Máquinas para termoformado de plásticos
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Minería, metalurgia y fundación
- Motores y transformadores
- Tracción de tranvía y ferrocarril
-
Instalación
-
-
Inductores
-
-
Dispositivos de inducción
-
-
Servicio
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
The Next Generation of High Power IGBT Module

The Next Generation of High Power IGBT Modules
LV100 dla przekształtników wiatrowych, falowników fotowoltaicznych i napędów silników
High power applications in the fields such as renewable energy and industrial drives require reliable and scalable power modules with high power density and low stray inductances. In order to fulfill these requirements, the concept of the well-known and successful HVIGBT LV100 package has been transferred and adapted to the needs of renewable and industrial applications.
By Thomas Radke and Narender Lakshmanan, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V
LV100 Concept
Applications like wind energy converters, central photovoltaic inverters and industrial drives require power modules with the highest power density, high reliability, and scalable power ranges with a standardized outline in the voltage classes of 1200V and 1700V. To fulfill such requirements, the LV100 power module is based on same outline and internal layout concept as the well-known HVIGBT LV100 module. This concept is convincing because it is based on a standardized package outline while also capable of delivering the highest power density, scalability by easy paralleling, low stray inductance, capability to operate with fast switching devices like SiC MOSFETs and having excellent current sharing balance. In combination with the latest 7th generation IGBT and Diode efficient chips and the thermal cycle failure free SLC-package-technology, the LV100 module provide the best overall performance. In the 1700V, a current rating of 1200A has been realized which represents an outstanding current density considering the compact package footprint of only 144x100mm2.
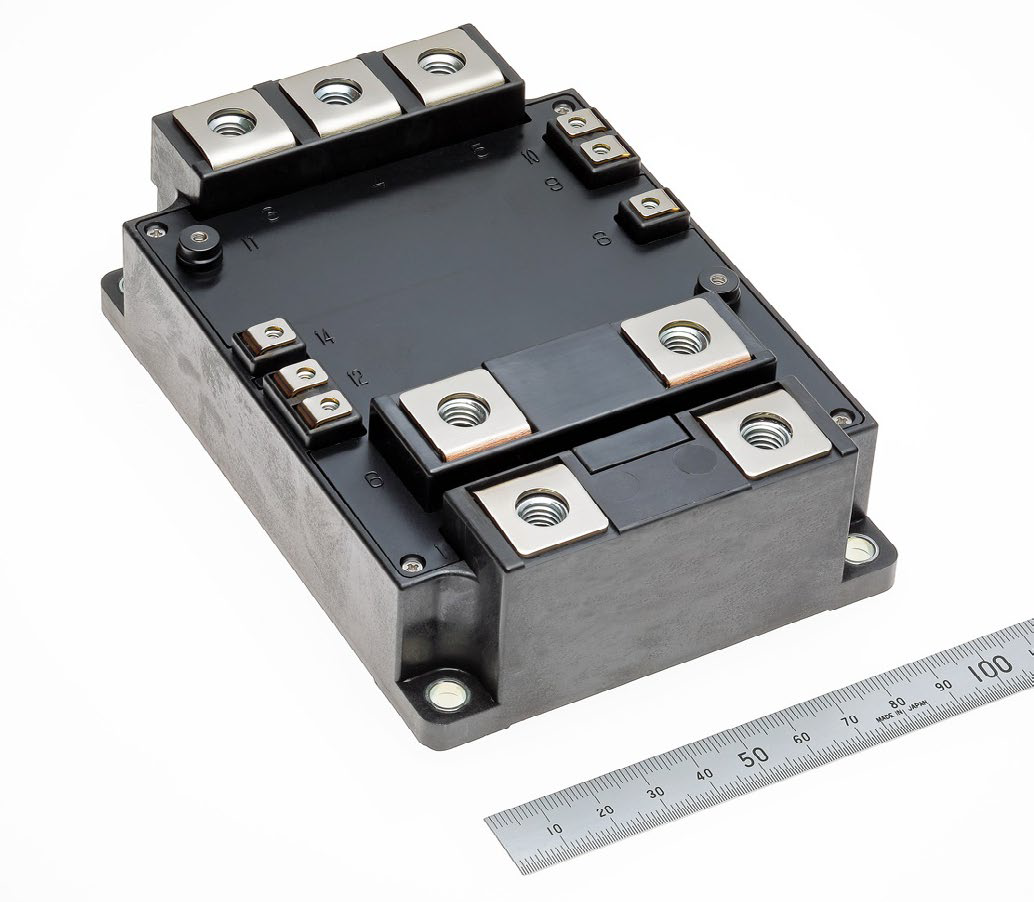

Figure 1: New LV100 Power Module for industrial application
LV100 Internal Layout
In high power IGBT modules, multiple chips are connected in a parallel configuration because IGBT chips sizes are limited and usually the rating maximum current is in a range of ~200A for IGBT chips with blocking voltages of 1200V or 1700V. Therefore, for the realization of an IGBT module with a current rating of 1200A or more, paralleling of at least six or more IGBT chips is required. While designing the layout, the current balancing between the chips connected in parallel has to be considered. Equally shared chip currents are required for achieving homogeneous loss and heat distribution. A non-homogeneous current distribution causes a certain chip to carry the highest current and this chip will experience the highest temperature which ultimately limits the performance and life-time of the total system. The parasitic impedances of the connection to the individual chips significantly influence the current sharing between the chips operated in parallel. In case the parasitic inductances are not equally designed for all chips, a dynamic current imbalance during IGBT switching will occur. The module terminal arrangements and the chip positions are the major influencing factors for the parasitic impedances. To realize an equal impedance, the distances from the power terminals to all the chips have to be ideally the same. This can be achieved by optimizing the terminal and chip arrangement so that it is perpendicular to
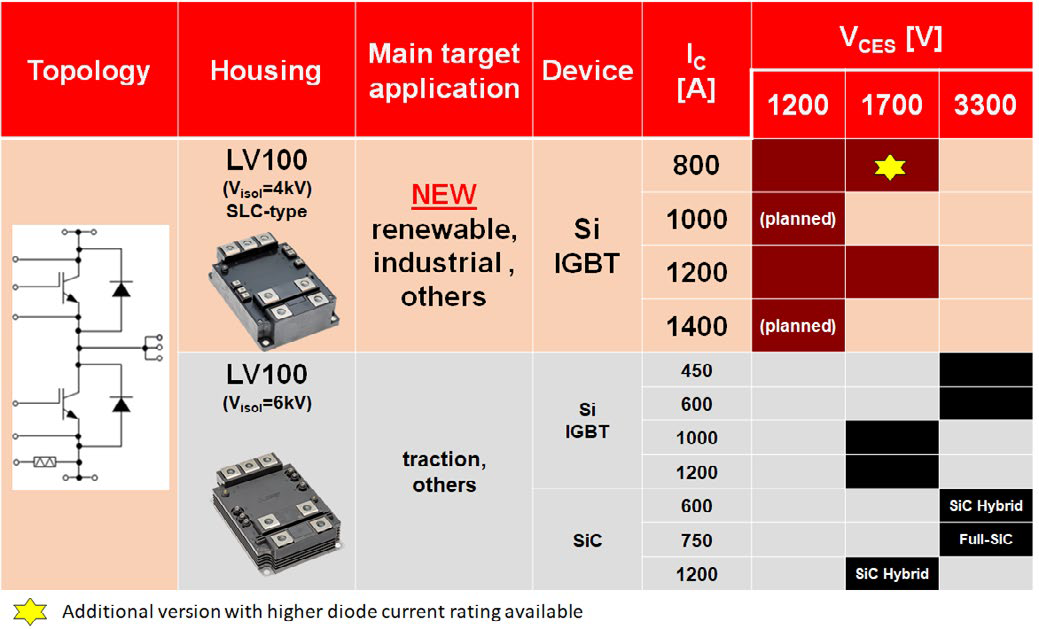
Figure 2: LV100 product line-up plan
the current flow as shown in figure 3 [6]. In the ideal module concept, the commutation (indicated by the blue and red arrows) is only in Y-direction whereas the terminals and chips are orientated perpendicular in x-direction.
By this approach, equal parasitic impedances are achievable. This ideal concept was considered in the development of the LV100 layout and a homogenous current sharing, as shown in the simulation result in figure 4 was realized. The conventional modules available today in the field of high power industrial drives or converters for renewable energy usually have a terminal arrangement which is parallel to the chip arrangement and current flow. As a result of this conventional design, equal parasitic impedances was not be realizable and the resulting imbalance in the current sharing was an accepted feature of the conventional modules. For events such as load short circuits, due to the absence of the inductive coupling in the laminated busbars, the impact of the unequal stray inductances between different chips becomes significant for such conventional modules.
In case of fast switching semiconductor devices with high di/dt, the differences in parasitic stray inductances between the chips will influence the current sharing enormously. Therefore, if an inverter designer considers changing to SiC devices in future, the LV100 package is the right choice since the layout concept is ready for SiC [8]. As result, a potential future change from Si-IGBT to SiC-MOSFET [9] devices is feasible with less changes and redesign efforts.
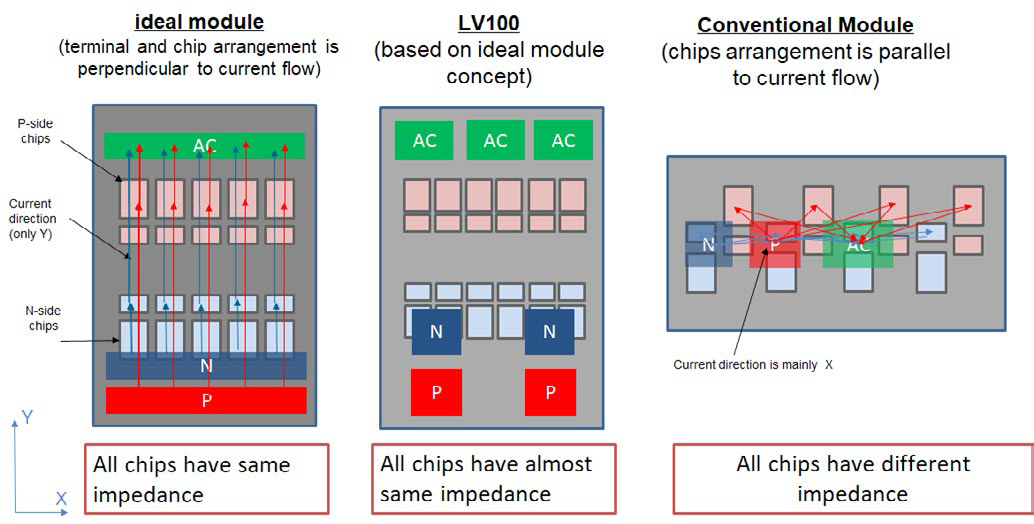
Figure 3: Comparison of power module layout concepts
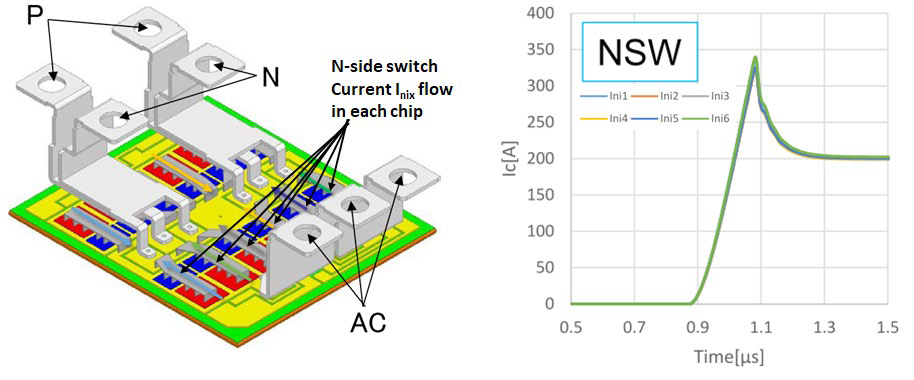
Figure 4: Simulation result of current sharing at turn-on event in LV100 package concept.
Thermal cycle failure free package
IGBT modules in high power industrial drive applications experience thermal cycling [1] in case of fluctuating (or non-continuous) loads. Wind power converters are usually liquid-cooled with the cooler having a thermal time constant of a couple of seconds. As a result, the IGBT case temperature will respond rapidly to a temperature swing by changing of load conditions. That means on days with fluctuating wind conditions the IGBT module baseplate will experience many thermal cycles. Also photovoltaic inverters experience at minimum one huge thermal cycle per day. Considering an inverter life-time of 25 years, the IGBT module have to be capable to resist several thousand thermal cycles. The thermal cycle capability of conventional industrial IGBT modules with conventional package structure (with several pieces of ceramicling substrates solder to copper baseplates), is limited. Hence thermal cycles have to be considered as lifetime limiting parameter during the converter design. To eliminate thermal cycling as lifetime limiting parameter, the SLC-Technology [2] [3] has been selected for the LV100 development for industrial application. As shown in figure 5, the conventional power module package structure is replaced by an IMB (Insulated Metal Baseplate) in combination with a direct potting resin. The thermal expansion coefficient of the insulator and the potting resin are matched with each other [4] (considering the thermal expansion of copper base- and pattern-layer. Due to this matching thermal expansion and the elimination of system solder layer, a thermal cycling failure free package structure has been realized [5].
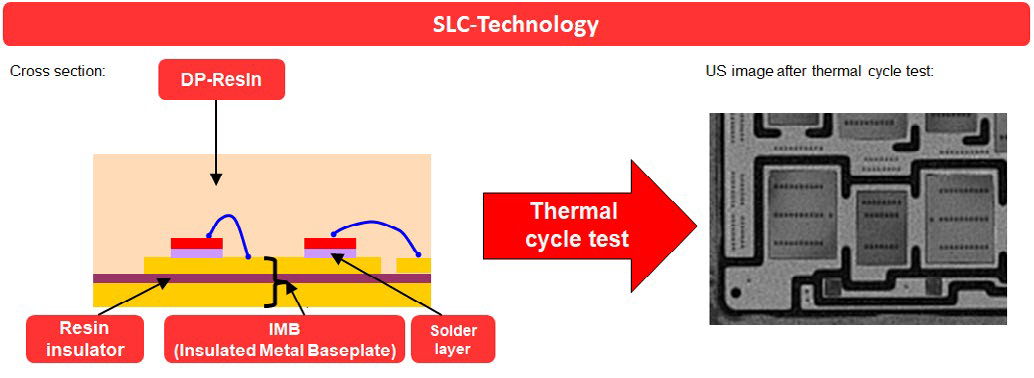
Figure 5: SLC-Technology and thermal cycle test result
7th gen 1700V IGBT chip-set
The 7th gen IGBT and diode chips possess an optimized structure and are thinner than its predecessors. Additionally, the devices have been designed by selecting an appropriate trade-off between the DC performance and the switching performance [5]. The inverter losses under typical application conditions for high power converters has been performed by Mitsubishi Electric Melcosim [7] simulation software. In figure 6 the result and comparison of 1200A/1700V LV100 vs a conventional 1400A/1700V module from company A. It is noticeable that for a switching frequency of 500Hz the total losses are comparable. However due to the appropriately selected trade-off in combination with the optimized chip structure, the diodes and the IGBTs indicate switching losses are significantly reduced. The result is that for switching frequencies higher than 500Hz, the LV100 has significantly higher efficiency. For example, at a switching frequency
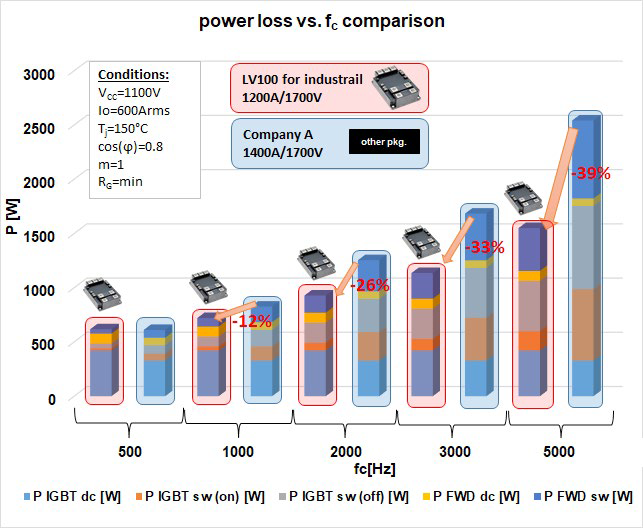
Figure 6: Power loss comparison of 7th gen. IGBT chip in LV100 1200A/1700V module vs. Company A 1400A/1700V conventional module.
of 5kHz the loss reduction is 39%. This loss reduction contributes to reduce the cost of total inverter by reducing efforts for cooling and enabling to achieve higher power density of the system.
Conclusion
A new high power IGBT module (LV100 for industrial) is under development, which has been optimized for the requirements of high power applications in the field of renewable energy converters, and industrial drives. The outline of the module housing is same as HVIGBT LV100 and in line with the new market defacto standard. The SLC-packagetechnology is thermal cycling failure free and improves the reliability of the system. The 7th gen IGBT chip technology provides a significant reduction of switching losses and is beneficial considering a switching frequency from 500Hz onwards. The internal layout has a minimized stray inductance and ensures a homogenous current sharing between the chips. Therefore, it is feasible to use this layout with fast switching semiconductor.
References
[1] “Power Module Reliabilty” Mitsubishi Electric Application note www.mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/products/pdf/ reliability/0512_e.pdf
[2] T. Takahashi, et al: “A 1700V-IGBT module and IPM with new insulated metal baseplate (IMB) featuring enhanced isolation properties and thermal conductivity”, PCIM Europe 2016
[3] S. Asada, et al: “Resin Encapsulation Combined with Insulated Metal Baseplate for Improving Power Module Reliability”, PCIM Europe 2016,
[4] J. Yamada, et al: ”Pumping out failure free package structure”, PCIM Europe 2016,
[5] Thomas Radke et. al., “More Power and Higher Reliability by 7th Gen. IGBT Module with New SLC-Technology”, Bodo’s Power Systems June 2015
[5] M. Miyazawa, et al: “Mitsubishi 7th generation 1700 V IGBT Modules: Loss Reduction and Excellent System Performance”, Bodo’s Power Systems March 2018
[6] Georg Borghoff, “Implementation of low inductive strip line concept for symmetric switching in a new high power module”, PCIM Europe 2013, p. 185
[7] Melcosim simulation software for Mitsubishi Electric power modules http://www.mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/simulator/ index.html
[8] N. Soltau, et al: “3.3 kV Full SiC MOSFETs - Towards High-Performance Traction Inverters,” Bodo’s Power Systems, pp. 22-24, Jan. 2018
[9] N. Soltau, et al: “Switching Performance of 750A/3300V Dual SiCModules”, Bodo’s Power Systems, pp. 26-28, Feb. 2019
Publicaciones relacionadas
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Deja un comentario