Debes estar logueado
-
moreX
-
Componentes
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductores
- Diodos
- Tiristores
-
Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | VISHAY (IR)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | Semikron
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POWEREX
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | IXYS
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | POSEICO
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | ABB
- Módulos con aislamiento eléctrico | TECHSEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Rectificadores de puente
-
Transistores
- Transistores | GeneSiC
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | Mitsubishi
- Módulos SiC MOSFET | STARPOWER
- Módulos ABB SiC MOSFET
- Módulos IGBT | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos MOSFET | MITSUBISHI
- Módulos de transistores | ABB
- Módulos IGBT | POWEREX
- Módulos IGBT | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elementos semiconductores de carburo de silicio (SiC)
- Go to the subcategory
- Controladores de puerta
- Bloques de energía
- Go to the subcategory
- Convertidores de corriente y tensión LEM
-
Componentes pasivos (condensadores, resistencias, fusibles, filtros)
- Resistencias
-
Fusibles
- Fusibles miniatura para circuitos electrónicos, serie ABC y AGC
- Fusibles tubulares de acción rápida
- Eslabones fusibles de retardo de tiempo con características GL / GG y AM
- Eslabones fusibles ultrarrápidos
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar británico y estadounidense)
- Fusibles de acción rápida (estándar europeo)
- Fusibles de tracción
- Eslabones fusibles de alto voltaje
- Go to the subcategory
-
Condensadores
- Condensadores de motor
- Condensadores electrolíticos
- Condensadores de película
- Condensadores de potencia
- Condensadores para circuitos de CC
- Condensadores de corrección del factor de potencia
- Condensadores de alto voltaje
- Condensadores de calentamiento por inducción
- Condensadores de almacenamiento de energía y pulsos
- Condensadores de ENLACE CC
- Condensadores para circuitos AC/DC
- Go to the subcategory
- Filtros EMI
- Supercondensadores
-
Protección contra sobretensiones
- Protección contra sobretensiones para aplicaciones coaxiales
- Protección contra sobretensiones para sistemas de videovigilancia
- Protección contra sobretensiones para cableado de potencia
- Pararrayos para LED
- Descargadores de sobretensiones para energía fotovoltaica
- Protección del sistema de pesaje
- Protección contra sobretensiones para Fieldbus
- Go to the subcategory
- Go to the subcategory
-
Relés y contactores
- Teoría de relés y contactores
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Relés semiconductores de CA trifásicos
- Reguladores, controles y accesorios
- Arranques suaves y contactores de inversión
- Relés electromecánicos
- Contactores
- Interruptores giratorios
-
Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, serie 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos, series CWA y CWD
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos de las series CMRA y CMRD
- Relés semiconductores de CA monofásicos, serie PS
- Relés semiconductores de CA dobles y cuádruples, serie D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relés de estado sólido monofásicos, serie gn
- Relés semiconductores de ca monofásicos, serie ckr
- Relés AC monofásicos SERIE ERDA Y ERAA para carril DIN
- Relés AC monofásicos para corriente 150A
- Relés dobles de estado sólido integrados con disipador de calor para carril DIN
- Go to the subcategory
- Relés semiconductores CA monofásicos para PCB
- Relés de interfaz
- Go to the subcategory
- Núcleos y otros componentes inductivos
- Radiadores, varistores, protecciones térmicas
- Aficionados
- Aire Acondicionado, Accesorios para Armarios Eléctricos, Neveras
-
Baterías, cargadores, fuentes de alimentación de búfer e inversores
- Baterías, cargadores - descripción teórica
- Baterías de iones de litio. Baterías personalizadas. Sistema de gestión de batería (BMS)
- Pilas
- Cargadores de baterías y accesorios
- Fuente de alimentación de respaldo de UPS y fuentes de alimentación de búfer
- Convertidores y accesorios para fotovoltaica
- Almacen de energia
- Celdas de combustible
- Baterías de iones de litio
- Go to the subcategory
-
Automaticas
- Futaba Drone Parts
- Finales de carrera, microinterruptores
- Sensores, transductores
- Pirometría
- Contadores, temporizadores, medidores de panel
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Señalización luminosa y sonora
- Cámara termográfica
- Pantallas LED
- Botones e interruptores
-
Grabadores
- Grabadora AL3000
- Grabadora KR2000
- Grabadora KR5000
- Medidor HN-CH con función de registro de humedad y temperatura
- Consumibles para registradores
- Grabadora 71VR1
- Grabadora KR 3000
- Grabadores de PC de la serie R1M
- Grabadores de PC de la serie R2M
- Grabador de PC, 12 entradas aisladas - RZMS-U9
- Grabador de PC, USB, 12 entradas aisladas - RZUS
- Go to the subcategory
- Go to the subcategory
-
Cables, alambres Litz, conductos, conexiones flexibles
- alambres
- cables Litz
-
Cables para aplicaciones especiales
- Los cables de extensión y compensación
- Cables para termopares
- Los cables de conexión a PT czyjnków
- Multicore cables temp. -60 ° C a + 1400 ° C
- cables de media tensión SILICOUL
- ignición alambres
- Los cables calefactores
- temp núcleo único. -60 ° C a + 450 ° C
- conductores de trenes
- El calentamiento de los cables en el Ex
- Go to the subcategory
- camisas
-
trenzas
- trenzas planas
- trenzas ronda
- trenza muy flexible - plana
- trenza muy flexible - Ronda
- Copper cilíndrico trenzado
- Copper protector de la trenza y cilíndrica
- cintas de conexión flexibles
- Trenzas cilíndrico galvanizado y acero inoxidable
- Aislamiento de PVC trenzas de cobre - Temperatura 85 ° C
- aluminio trenzado plano
- Kit de conexión - trenzas y tubos
- Go to the subcategory
- Accesorios para la tracción
- Terminales de cable
- barras flexibles aisladas
- carril flexible multicapa
- sistemas de gestión de cables
- Conductos, tuberías
- Go to the subcategory
- View all categories
-
Semiconductores
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- Accionamientos de CA y CC (inversores)
- Automatización HVAC
- Automatización industrial
- Automatización industrial
- Calentamiento por inducción
- Componentes para atmósferas potencialmente explosivas (EX)
- Dispositivos de protección industrial
- Energy bank
- Equipos para Armarios de Distribución, Control y Telecomunicaciones
- Fuentes de alimentación (UPS) y sistemas rectificadores
- Impresión
- Máquinas de soldar y máquinas de soldar
- Máquinas herramientas CNC
- Máquinas para secar y procesar madera
- Máquinas para termoformado de plásticos
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Medición y regulación de temperatura
- Minería, metalurgia y fundación
- Motores y transformadores
- Tracción de tranvía y ferrocarril
-
Instalación
-
-
Inductores
-
-
Dispositivos de inducción
-
-
https://www.dacpol.eu/pl/naprawy-i-modernizacje
-
-
Servicio
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Advanced Si-IGBT Chip Design for Maximum Overall System Performance

Advanced Si-IGBT Chip Design for Maximum Overall System Performance
The overall system performance is undoubtedly influenced to a significant extent by the choice of the power semiconductor technology employed. For conventional IGBT modules, the recent improvements in the VCEsat vs. Eoff trade-off shows a tendency towards saturation and hence the performance improvement of upcoming IGBT chip generations do not indicate a significant step in efficiency improvements anymore. With the new G1- IPM series it is possible to obtain substantial system efficiency improvement by utilizing an advanced Si-IGBT chip and implementing an adaptive gate control.
By Narender Lakshmanan and Thomas Radke, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Introduction:
Mitsubishi Electric has introduced the new G1 series Intelligent Power Modules (IPM) with an advanced Si-IGBT design to address several key performance parameters and enable the end-user to achieve high system performance. The advancements in the G1 IPM chip technology are aimed at resolving some inherent drawback of the Si-IGBT especially when it is employed for motor control applications. The G1 IPM device has been developed by implementing some key advancements in the latest 7th generation IGBT. It can be noticed (refer Figure 1) that in comparison to the 7th generation conventional Si-IGBT, the advanced G1 IPM chip technology offers significant benefits although it belongs to the same chip generation.
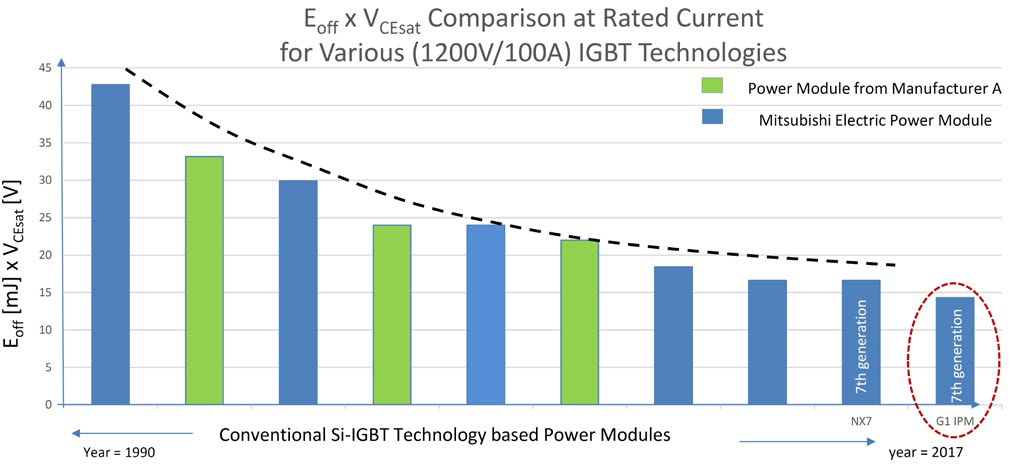
Figure 1 : A comparison of the VCEsat x EOFF index for different Si-IGBT technologies
Short Circuit Capability and Electrical Performance:
Short circuit protection for a conventional Si-IGBT has been implemented using a ‘desaturation detection’ based system where the VCE across the IGBT is observed to ascertain the occurrence of a short circuit event. To facilitate a successful detection, the conventional Si-IGBT devices are designed such that several gate cells in the chip are left unconnected [6][2]. While this ensures that the IGBT enters into the desaturation mode beyond a particular value of IC, it also means that several electrical parameters are compromised to a certain extent [6][2][3]. The G1 IPM possess a Si-IGBT chip with a monolithically integrated current sense emitter (refer figure 2). The sense emitter feature facilitates an assessment of the IGBT collector current via direct measurement. Based on the input from the sense emitter, trip levels can be assigned and an SC turn-off can be initiated before the chip desaturates. This approach to directly determine the instantaneous IC renders the VCE based desaturation detection system obsolete. Thus, it is no longer necessary to ensure that the IGBT enters into the desaturation mode. As a direct consequence, all available gate cells in the Si-IGBT chip can be connected transforming the chip into a ‘full gate IGBT’ and the subsequent electrical benefits can be harvested due to the enhanced utilization of the Si-IGBT chip [1]. Additionally, the IGBT chip is provided with an on-chip temperature sensing diode in the center of the chip in order to ascertain the IGBT junction temperature with maximum effectiveness (refer figure 2).
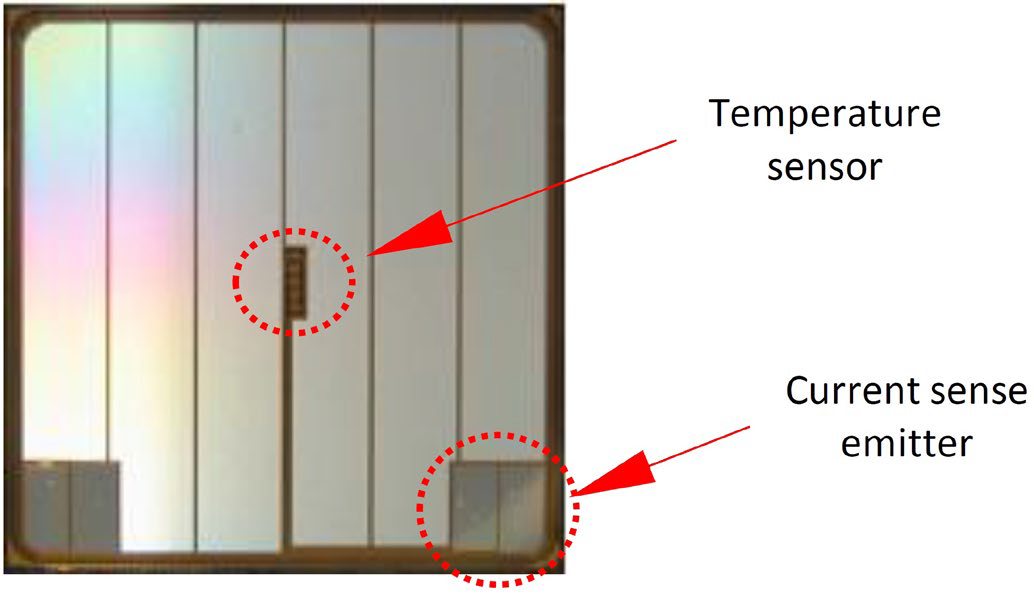
Figure 2 : The temperature sensor and the current sense emitter components of the IGBT chip in the G1-IPM
Switching dv/dt as a Performance Limiting Factor:
One factor that negatively influences the lifetime of the insulation layers in the system (motor winding insulation or cable insulation) is the exposure to high speed transient voltages (dv/dt). The IGBT switching event is capable of generating high dv/dt at the terminals of the power module (especially during a turn-on event). A conventional solution to address this issue is to restrict the switching speed of the IGBT by employing a gate impedance such that the switching dv/dt is maintained below a particular level. The dv/dt versus IC characteristics is such that the highest dv/dt (worst case dv/dt) is experienced during turn-on of low IC and the turn-on dv/dt reduces with an increase in IC. Although the worst case dv/dt would be generated only during turn-on of low IC, a conventional gate driver with fixed turn-on gate resistances will force a restriction of switching speed for all values of IC. This approach will generate significant turn-on losses while operating at high IC even though the switching dv/dt is not the worst case during high IC operation. It is therefore clear that for conventional Si-IGBT technology, there is a trade-off between controlling the worst-case dv/ dt and efficiency.
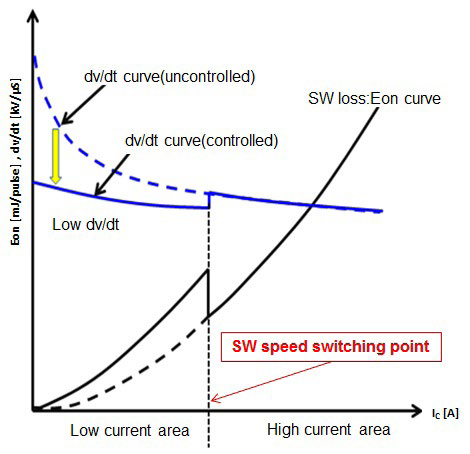
Figure 3 : Utilization of the sense emitter to implement a switching speed control in the G1 IPM
Utilizing Sense Emitter to Control dv/dt Without Sacrificing Efficiency:
The sense emitter provision in the advanced full gate Si-IGBT open up the possibility to ascertain the IC. Based on the dv/dt vs IC dependency, it is clear that to address the worst case dv/dt, it is appropriate to implement a switching speed restriction only during the switching of low IC. Considering this key point, a switching technique has been implement in the G1 IPM Si-IGBT devices where the turn-on switching speed in regulated based on the IC. If the IC (from the sense emitter data) is ascertained to be below a particular threshold, the gate drive unit will be informed to apply a switching speed restriction such that the worst case dv/dt is avoided. When the switching IC exceeds the pre-set threshold value, the gate drive unit will be informed to turn the IGBT ON with a higher switching speed, such that the turn-on losses can be optimized. With this approach, the worst case dv/dt is avoided during switching, while simultaneously ensuring that the system efficiency is not compromised (refer Figure 3).
Full Gate IGBT with Sense Emitter - Analysis of Overall Performance:
The G1 IPM module utilizes the full gate 7th generation Si-IGBT which is equipped with the monolithically integrated sense emitter. This approach is aimed at combining the benefits of the full gate Si-IGBT along with the advantages of the sense emitter component. The target is to ensure maximum efficiency, high reliability (instantaneous IC based SC protection) and an acceptable EMI profile (dv/dt control). Figure 4 shows a comparison of the overall power loss performance of the full gate device with the conventional Si-IGBT (under same turn-on dv/dt condition). As evident from Figure 4, the full gate IGBT device generates approximately 18% less overall losses than the conventional Si-IGBT device under the mentioned working conditions.
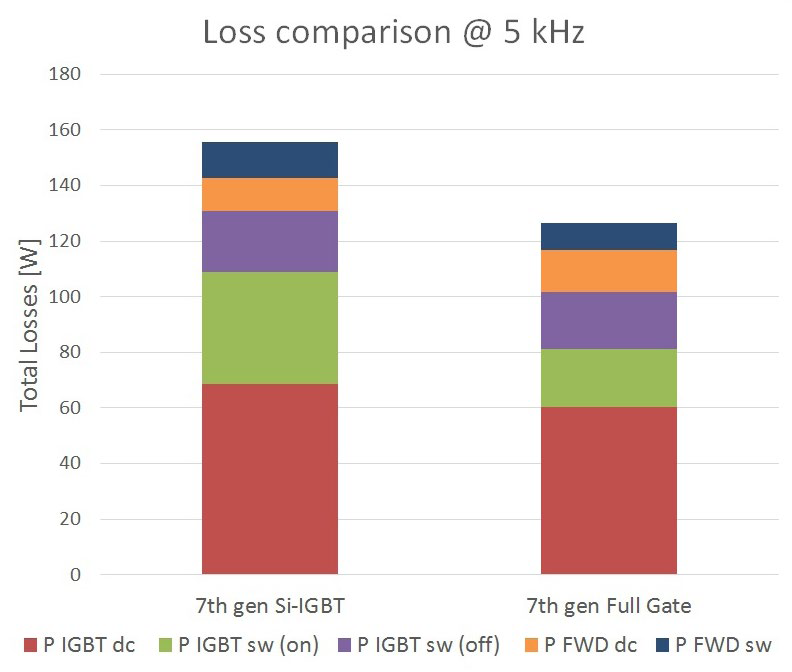
Figure 4 : The comparison of the total power loss generated by a single IGBT + Diode combination in the 100A/1200V 7th gen Full Gate device and the 7th gen Si-IGBT (100A/1200V) for the conditions: VCC = 600V, Iout = 100 A rms, fC = 5 kHz, m = 1, cos(φ) = 0.8, TS = 80°C, fo = 50 Hz
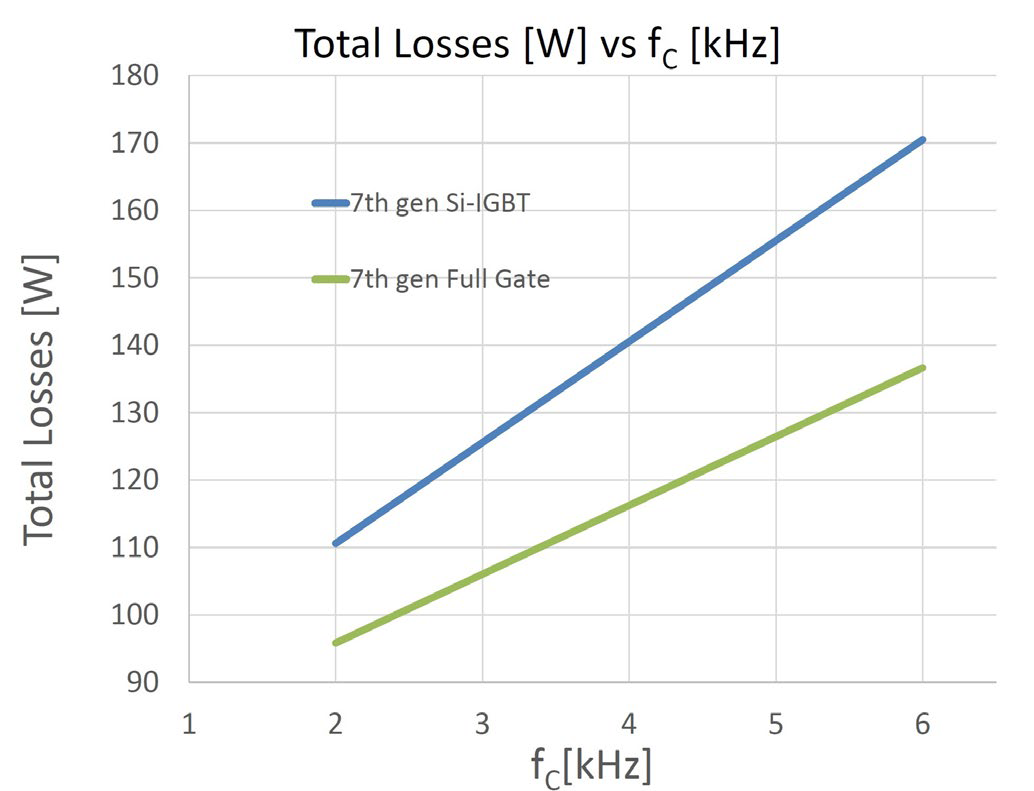
Figure 5: The Comparison of total losses generated in a single IGBT + Diode combination in the 100A/1200V 7th gen Full Gate device and the 7th gen Si-IGBT (100A/1200V) for several switching frequencies. Conditions: VCC= 600V, Iout = 100 Arms, m = 1, cos (φ) = 0.8, Ts = 80°C, fo = 50 Hz
Under the conditions mentioned in Figure 4, the switching speed control technique allows for a 48% reduction in the turn-on losses. The full gate IGBT (with sense emitter) clearly generates significantly lower switching loss versus its convention counterpart. Figure 5 shows the overall power loss versus fC (switching frequency) of the full gate (with sense emitter) IGBT and the conventional Si-IGBT device. The gap in performance between the full gate IGBT (with sense emitter) and the conventional Si-IGBT increases with an increase in the fC.
For applications which require an operation at low levels of audible noise (high switching frequencies are necessary), the 7th generation full gate IGBT (with sense emitter) promises enormous system level benefits. Certain overload operation points exist for motor control applications. During the stand-still (locked rotor) condition - the load current is not symmetrically distributed among the inverter IGBTs, and during extremely low output frequencies - the inverter IGBTs can experience a high current ripple. Under such overload conditions, it is crucial to determine the IGBT junction temperatures of each chip to avoid an over-temperature failure event. The IGBT junction temperature can be effectively monitored using the on-chip temperature sensor integrated on each chip.
It can thus be concluded that the full gate Si-IGBT equipped with the sense emitter feature and the on-chip temperature sensor address several key challenges which were inherent to the conventional Si- IGBT approach thereby allowing the inverter developer to achieve significantly higher system performance.
References:
[1] An Advanced Si-IGBT Chip for Delivering Maximum Overall System Performance, Narender Lakshmanan and Thomas Radke, Proc. PCIM 2017
[2] USING F-SERIES IGBT MODULES, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC. Application Note. Feb 2000
[3] New chip design technology for next generation power module. Katsumi Satoh et al., Proc. PCIM 2008
[4] A 6-in-1 IGBT module performance evaluation platform determining the trade-off between dV/dt and turn-on loss of different IGBT/ FwDi chip setups, Marco Honsberg, et al., Proc. EPE 2011
[5] Datasheet – CM100TX-24T
[6] A Novel Series of Intelligent Power Modules “V1” with Internally Paralleled FULL GATE CSTBTTM and mirror Emitter technology for short circuit sensing, Nishida Nobuya et al., Proc. PCIM 2010
Publicaciones relacionadas
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Deja un comentario