Vous devez être connecté
-
revenirX
-
Composants
-
-
Category
-
Semi-conducteurs
- La diode
- Les thyristors
- Modules de puissance isolés
- Ponts redresseurs
-
Transistors
- Transistors | GeneSiC
- Modules MOSFET SiC | Mitsubishi
- Modules MOSFET SiC | STARPOWER
- Modules MOSFET SiC ABB
- Modules IGBT | MITSUBISHI
- Modules de transistors | MITSUBISHI
- Modules MOSFET | MITSUBISHI
- Modules de transistors | ABB
- Modules IGBT | POWEREX
- Modules IGBT | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Composants semiconducteurs en carbure de silicium
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Circuits de commande
- Blocs de puissance
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Transducteurs électriques
-
Composants passifs (condensateurs, résistances, fusibles, filtres)
- Résistances
-
Fusibles
- Fusibles miniatures pour c.imp. série ABC et AGC
- Fusible rapides tubulaires
- Cartouches de courbe GL/GG et AM
- Cartouches ultrarapides
- Fusibles à action rapide (norme britannique et américaine)
- Fusibles à action rapide (norme européenne)
- Fusibles de traction
- Cartouche de haute tension
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
-
Condensateurs
- Condensateurs pour moteurs
- Condensateurs électrolitiques
- Condensateurs de type snubbers
- Condensateurs de puissance
- Condensateurs pour circuits continus
- Condensateurs de compensation de puissance
- Condensateurs de haute tension
- Condensateurs pour chauffage par induction
- Condensateurs pour impulsions
- Condensateurs DC LINK
- Condensateurs pour circuits AC/DC
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Filtres anti-interférences
- Supercondensateurs
-
Protection contre les surtensions
- Protection contre les surtensions pour les applications coaxiales
- Protection contre les surtensions pour les systèmes de vidéosurveillance
- Parafoudres de ligne électrique
- Protection contre surtensions pour LED
- Parafoudres pour le photovoltaïque
- Protection du système de pesage
- Protection contre les surtensions pour bus de terrain
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
-
Relais et contacteurs
- Théorie relais et contacteurs
- Relais statiques triphasés
- Relais statiques CC
- Régulateurs, circuits de commande et accessoires
- Démarrages progressifs et contacteurs inverseurs
- Relais electromécaniques
- Contacteurs
- Commutateurs rotatifs
-
Relais statiques monophasés
- Relais semi-conducteurs AC monophasés, série 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relais à semi-conducteurs CA monophasés, séries CWA et CWD
- Relais à semi-conducteurs CA monophasés des séries CMRA et CMRD
- Relais à semi-conducteurs CA monophasés, série PS
- Relais semi-conducteurs AC double et quadruple, série D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relais statiques monophasés, série GN
- Relais à semi-conducteurs CA monophasés, série CKR
- Relais AC monophasés SÉRIES ERDA ET ERAA pour rail DIN
- Relais CA monophasés pour courant 150A
- Relais à semi-conducteurs doubles intégrés à un dissipateur thermique pour un rail DIN
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Relais statiques monophasé pour c.imp.
- Relais d'interface
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Composants inductifs
- Radiateurs, varistances, protections thermiques
- Ventilateurs
- Climatiseurs et accessoires d'armoires électriques
-
Batteries, chargeurs, blocs d'alimentation tampon et onduleurs
- Batteries et Chargeurs - théorie
- Batteries Li-ion et non-standards. Systèmes de gestion des batteries (BMS)
- Batteries
- Chargeurs de batteries et accessoires
- Alimentation de secours UPS et alimentation tampon
- Convertisseurs de tension et accessoires pour photovoltaïque
- Stockage d'Energie
- Réservoirs de carburant
- Batteries lithium-ion
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
-
Automatique industrielle
- Futaba Drone Parts
- Interrupteurs de fin de course, micro-rupteurs
- Capteurs et convertisseurs
- Pyromètres
- Compteurs, Relais temporisés, Indicateurs de tableau
- Appareils industriels de protection
- Signalisation lumineuse et sonore
- Caméra thermique
- Afficheurs à LED
- Boutons et commutateurs
-
Enregistreurs
- Enregistreur de température à bande et afficheur numérique - AL3000
- Enregistreurs à microprocesseur avec ecran LCD série KR2000
- Enregistreur KR5000
- Indicateur avec fonction enregistrement de température et humidité HN-CH
- Matériaux consommables pour enregistreurs
- Enregistreur graphique compact 71VR1
- Enregistreur KR3000
- Enregistreur PC série R1M
- Enregistreur PC série R2M
- Enregistreur PC, 12 entrés isolées – RZMS
- Enregistreur PC, USB, 12 entrées isolées – RZUS
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
-
Câbles et chemins de câbles
- Fils
- Fils de Litz
- Câbles pour les applications spéciales
- Gaines
-
Tresses
- Tresses plates
- Tresses rondes
- Tresses très souples - plates
- Tresses très souples - rondes
- Tresses cuivre cylindriques
- Tresses cuivre cylindriques et protection
- Bandes de mise à la terre souples
- Tresses en acier zingué et inox
- Tresses isolantes en PVC - temp. 85°C
- Tresses plates en aluminium
- Kit de liaison - tresses et gaines
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Equipement pour la traction
- Cosses
- Barres flexible isolées
- Barre flexibles multicouches
- Systèmes de traçage des câbles
- Gaines annelées, tuyaux
- Aller à la sous-catégorie
- Voir toutes les catégories
-
Semi-conducteurs
-
-
- Fournisseurs
-
Applications
- Alimentations (UPS) et systèmes de redressement
- Automatisation HVAC
- Chauffage par induction
- Composants pour atmosphères potentiellement explosives (EX)
- Dispositifs de protection industriels
- Energy bank
- Équipements pour armoires de distribution, de contrôle et de télécommunications
- Impression
- L'automatisation industrielle
- L'automatisation industrielle
- Machines à souder et machines à souder
- Machines de séchage et de traitement du bois
- Machines pour le thermoformage des plastiques
- Machines-outils CNC
- Mesure et régulation de la température
- Mesure et régulation de la température
- Mines, métallurgie et fondation
- Moteurs et transformateurs
- Traction de tram et de chemin de fer
- Variateurs CA et CC (onduleurs)
-
Installation
-
-
Inducteurs
-
-
Appareils à induction
-
-
https://www.dacpol.eu/pl/naprawy-i-modernizacje
-
-
Service
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
EX s – niveau supérieur de protection sous pression

Requirements for Equipment in Explosive Atmosphere Zones
According to the primary document regarding explosion protection applicable in the European Union, namely the ATEX directive (both 114 and 153), equipment intended for use in so-called explosive atmosphere zones must meet specific requirements. The hazard is related to the presence of an explosive atmosphere, which is a mixture of air—under atmospheric conditions—flammable substances in the form of gases, vapors, mist, or dust, where combustion spreads to the entire unburned mixture once ignition occurs. Additionally, in the section "Explosion Prevention and Explosion Protection" at the beginning of Article 3 of the ATEX User Directive, the employer is required to take technical and/or organizational measures corresponding to the nature of the specified hazard, as reflected in the Integrated Safety concept, which is briefly illustrated in the diagram below.
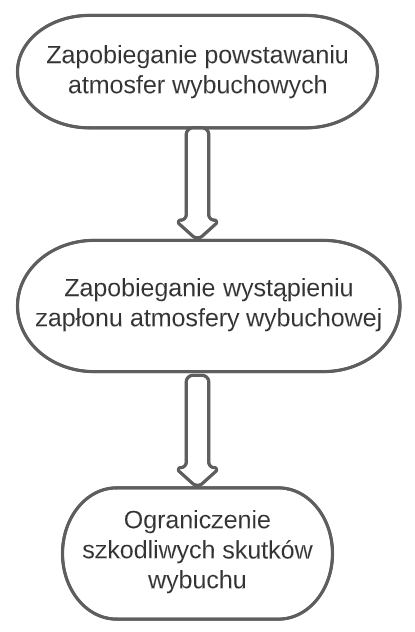
Electrical Equipment Protection
The protection of electrical equipment is included in the second layer. There is no single best method for minimizing—or ideally eliminating—the risk of an effective ignition source. Generally, equipment intended for use in explosive atmosphere spaces is designed, manufactured, tested, and marked according to the requirements of:
- ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU of February 26, 2014,
- Regulation of the Minister of Economy of December 22, 2005, on essential requirements for equipment and protective systems intended for use in explosive atmosphere spaces,
- The multi-part EN 60079 standard concerning the construction of explosion-proof equipment.
Pressure Protection EX s
This article focuses on one specific method of protection, namely the ventilated type of protection called pressure protection EX s, which is currently offered by DACPOL. According to the standard PN-EN 60079-2:2015-02 – Explosive Atmospheres – Part 2: Protection of Equipment by Gas Pressure 'p' – it involves placing components that could spark or overheat during operation inside a closed enclosure filled with air or another inert (non-flammable) gas maintained at a constant pressure.
Differences Between EX p and EX s Systems
The difference between the EX p and EX s systems is primarily the need for ventilation. While ventilation is a necessity in the EX p system, it is optionally activated in the EX s system after analyzing the presence of flammable gas inside the enclosure. In both cases, a gas sensor adapted to the currently present flammable/explosive substance and its calibration once a year are required. Technically, the EX s system features a set of valves used by a permanently connected compressor and, if the current exceeds 5A, a special contactor. The principle of operation is based on the phenomenon of overpressure, that is, utilizing the pressure difference between the outside of the enclosure (where there is an explosive atmosphere) and the inside (safe zone). The inability of the explosive atmosphere to penetrate ensures that the devices and components inside are safe, allowing the placement of non-ATEX certified equipment. This is a very convenient feature of this protection method, making EX s a versatile solution with many applications. Gas pressure protection is most commonly used for protecting high-power electric motors, especially high-voltage ones, as well as distribution and control panels.
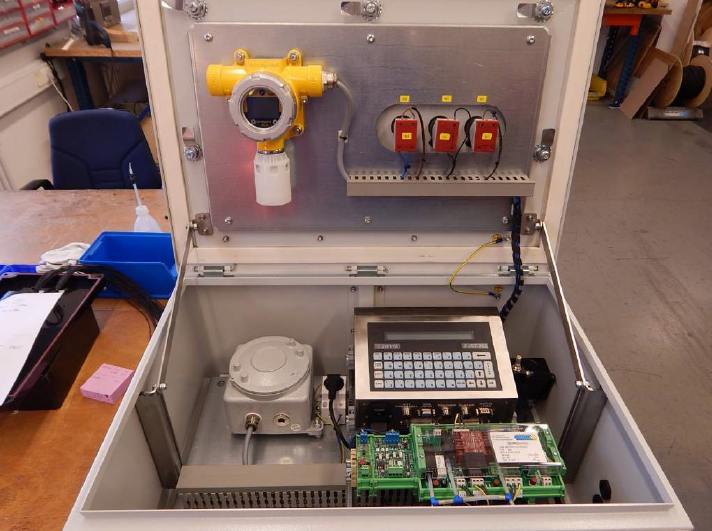

Modularity and Versatility of the EX s System
What distinguishes the pressure systems supplied by DACPOL from others available on the market is the possibility of shifting a significant part of the assembly to the customer. In the past, with older solutions, after determining the BOM (Bill of Materials), everything was assembled and delivered by the manufacturer. Now, thanks to special certification (EX s), there is the possibility to purchase just the control unit, with the enclosure and assembly being the responsibility of the user. Of course, along with the Quinguard module responsible for system control, a manual is provided regarding the requirements for the enclosure and other elements, as well as the method for testing the tightness, which is absolutely required if the system is to operate in an explosive atmosphere zone.
Requirements for EX s Systems
From the perspective of process safety, the EX s system adheres to the principle of Integrated Safety, which states that the entire problem of preventing explosion risks can be broken down into three layers:
- Preventing the formation of explosive atmospheres,
- Preventing the occurrence of an effective ignition source,
- Limiting the harmful effects of an explosion.
Methods of protecting electrical equipment that could generate a spark during normal operation (i.e., at rated voltage and current) qualify as preventing the appearance of an ignition source. In the case of EX s protection, the situation is somewhat less straightforward because, although an ignition source may appear, due to the overpressure, ignition or explosion propagation to the surroundings does not occur. Therefore, from the perspective of protection layers, it is a method based on explosion isolation. The inert gas pumped into the sealed enclosure also acts as a cooling medium, which further reduces the risk of excessive heating of the components inside. Safety is ensured by a system that monitors pressure differences, supplements the inert gas deficiency (or blocks its supply), and disconnects the circuit in case of leakage.

Benefits of Using the EX s System
The greatest advantage of the EX s pressure system is its modularity and versatility. The former is reflected in the ability to deliver it in various ways. For the customer, these options include:
- Purchasing the entire solution as a "black box" – the customer provides the enclosure components, and assembly and wiring are handled by the manufacturer, followed by the return shipping of the ready-to-use system.
- Purchasing the enclosure and control (Quinguard, valve modules, power supply) with assembly handled by the customer.
- Purchasing the control only, with the enclosure and assembly handled by the customer.
Regarding the detector, there is flexibility: it can be provided by either the customer or the manufacturer.
Versatility, on the other hand, means broad application possibilities in various conditions. The EX s system can operate in gas zones 1 and 2 as well as dust zones 21 and 22, and it also allows for the protection of devices or component sets with unusual geometries. The nature of the protection means that with EX s, almost any device can be adapted for use in an explosive atmosphere because it does not need to have ATEX certification, yet it can still operate in an EX zone. For large installations like electrical distribution panels, this is a significant advantage that avoids the need to move equipment out of the hazardous area or use large, costly fireproof enclosures.
This solution is simple and convenient to operate but requires close cooperation between the supplier and the customer from the very early stages of the project, so early contact is recommended.
EX s System Guide
To ensure optimal use of the EX s system, it is crucial for the user to adhere to a few key principles. Firstly, when purchasing the enclosure and control with assembly on the customer’s side, it is recommended to thoroughly review the technical documentation provided by the manufacturer. This documentation includes detailed information on enclosure requirements, installation, system calibration, and leakage testing procedures. In case of any doubts, it is advisable to consult with a DACPOL representative who can assist in performing the proper tests and ensure that the system is correctly configured for operation in an explosive atmosphere zone.
Installation and Calibration Process
During the installation of the EX s system, it is crucial to ensure that all components are correctly installed and configured. For the EX s pressure system, it is essential that the enclosure is airtight and maintains constant internal pressure. Any leaks could reduce protection efficiency and increase the risk of an explosion. Calibration of gas sensors and pressure control should be performed according to the manufacturer's instructions, and the results of these tests should be documented and archived.
Examples of EX s System Applications
The EX s system finds broad application in various industrial sectors. Here are some examples where this technology can be particularly useful:
- High-performance electric motors – especially those operating under high voltage conditions, where the gas pressure protection ensures safe operation.
- Distribution and control panels – the EX s system effectively protects sensitive components from explosive atmospheres, ensuring their long-term and safe operation.
- Industrial installations – in large installations, such as electrical distribution panels, the EX s system provides protection without the need for costly fireproof enclosures.
Benefits of Using the EX s System
Using the EX s system offers several benefits, including:
- Modularity – the ability to purchase various components and customize the system to meet the user’s specific needs.
- Versatility – applicability in various conditions, including gas and dust zones, making it a versatile solution.
- Cost savings – reducing the costs associated with large and expensive fireproof enclosures in large industrial installations.
- Flexibility – the ability to adapt almost any device for use in an explosive atmosphere, even without ATEX certification.
Summary
The EX s pressure system is a modern solution offering advanced protection in explosive atmosphere zones. Its modularity, versatility, and adaptability make it an attractive option for various industrial sectors. By allowing customization to specific needs and requirements, the EX s system represents an effective protection method that enhances safety in challenging conditions. For proper functioning, strict adherence to manufacturer recommendations and regular testing and calibration of the system are essential.
Produit associé
Articles similaires
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers





Laissez un commentaire