

Vous devez être connecté
Category


Les photos sont à titre informatif uniquement. Voir les spécifications du produit
please use latin characters
Lamp generators (the lamp is a triode) are devices used for surface heat treatment operating at a frequency range from 100 kHz to 4 MHz. However, the most commonly used industrial devices operate at a frequency of about 400 kHz. Modernization of lamp generators means replacing essential components of the device. The replacement of these components aims to repair or improve the device’s technical performance as well as achieve better technological results. Generators subject to modernization are most often devices designed and constructed by both domestic and foreign manufacturers in the 1950s, 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. Lamp generators are currently often (due to the appearance of fast semiconductor switches on the market) replaced by transistor generators (with IGBT or MOSFET type transistors).
Transistor generators have the following advantages:
Lamp generators have the following advantages:
A lamp generator basically consists of two blocks:
Generator modernization should be considered in several aspects:
Performing the above-described modernization activities means that generators produced several decades ago can still be very useful for even technologically demanding heat treatment processes and with much lower financial expenditures than investing in modern transistor generators would require.
The company DACPOL offers comprehensive selection of replacements for no longer produced LAMINA lamps: T-25W, T-25P, T26W/22, T26W/23, T-26P/22, T-26P/23, T-10P/22, T-12W/21, T-60W/12, T-60W/22, T-60V/12. We select the replacement and provide a comprehensive lamp replacement service along with starting the generator on the replaced lamp.
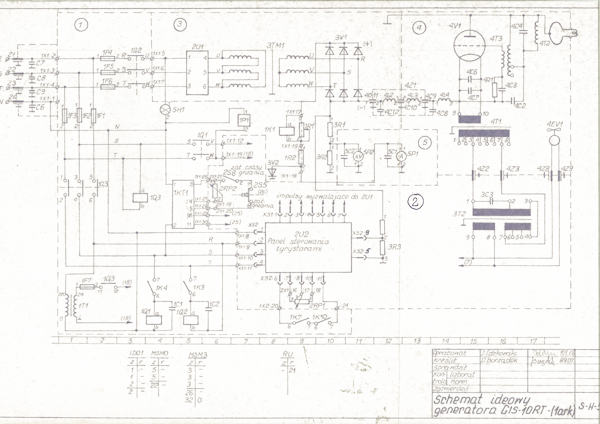
The attached drawing shows the basic schematic diagram of the modernized GIS-10 type generator; after modernization, the generator was named GIS-10RT (RT – thyristor regulator). Numbers in circles 1, 3 indicate the high-current path of the high-voltage power supply. Number 4 indicates the actual induction generator block. Numbers 2, 5 indicate control, measurement, protection, and triode cathode power supply blocks. GIS-type generators were produced in the 1960s and early 1970s at WAREL plants and, after modernization, continue to operate successfully in small workplaces. Before modernization, power regulation was provided by a thyratron rectifier on the high-voltage transformer side 3TM1 (now replaced by a diode rectifier 3V1). Modernization involved removing the thyratron regulator and installing a thyristor regulator 2U1 with a control panel 2U2 and, on the high-voltage side, a diode rectifier (diode stacks) 3V1. If necessary, the resonant circuit 4V1, 4T3, 4T4, 4T2 is modernized.
The modernization of the HFG/J40 type generator was carried out in 2017 at FAMUR S.A. – a company producing equipment for mining. The HFG/J40 generator was manufactured in 1962 by the Austrian company ELIN. Its operating frequency: 400 kHz, and the output power (guaranteed by the manufacturer) at the exciter terminals was 40 kW. In the early 1990s, the company ELCAL performed a modernization that involved replacing the BBC-produced triode with a domestically produced triode type T26W and replacing the thyratron regulator with a thyristor regulator type PRW 210/440 and diode rectifier stacks. In 2017, after about 25 years of operation, Dacpol Service undertook another modernization of the device. Below are selected photos showing the device before modernization.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Below are selected photos showing the device after modernization.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Êtes-vous intéressé par ce produit? Avez-vous besoin d'informations supplémentaires ou d'une tarification individuelle?
Ajouter à la liste de souhaits
Vous devez être connecté
Lamp generators (the lamp is a triode) are devices used for surface heat treatment operating at a frequency range from 100 kHz to 4 MHz. However, the most commonly used industrial devices operate at a frequency of about 400 kHz. Modernization of lamp generators means replacing essential components of the device. The replacement of these components aims to repair or improve the device’s technical performance as well as achieve better technological results. Generators subject to modernization are most often devices designed and constructed by both domestic and foreign manufacturers in the 1950s, 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. Lamp generators are currently often (due to the appearance of fast semiconductor switches on the market) replaced by transistor generators (with IGBT or MOSFET type transistors).
Transistor generators have the following advantages:
Lamp generators have the following advantages:
A lamp generator basically consists of two blocks:
Generator modernization should be considered in several aspects:
Performing the above-described modernization activities means that generators produced several decades ago can still be very useful for even technologically demanding heat treatment processes and with much lower financial expenditures than investing in modern transistor generators would require.
The company DACPOL offers comprehensive selection of replacements for no longer produced LAMINA lamps: T-25W, T-25P, T26W/22, T26W/23, T-26P/22, T-26P/23, T-10P/22, T-12W/21, T-60W/12, T-60W/22, T-60V/12. We select the replacement and provide a comprehensive lamp replacement service along with starting the generator on the replaced lamp.

The attached drawing shows the basic schematic diagram of the modernized GIS-10 type generator; after modernization, the generator was named GIS-10RT (RT – thyristor regulator). Numbers in circles 1, 3 indicate the high-current path of the high-voltage power supply. Number 4 indicates the actual induction generator block. Numbers 2, 5 indicate control, measurement, protection, and triode cathode power supply blocks. GIS-type generators were produced in the 1960s and early 1970s at WAREL plants and, after modernization, continue to operate successfully in small workplaces. Before modernization, power regulation was provided by a thyratron rectifier on the high-voltage transformer side 3TM1 (now replaced by a diode rectifier 3V1). Modernization involved removing the thyratron regulator and installing a thyristor regulator 2U1 with a control panel 2U2 and, on the high-voltage side, a diode rectifier (diode stacks) 3V1. If necessary, the resonant circuit 4V1, 4T3, 4T4, 4T2 is modernized.
The modernization of the HFG/J40 type generator was carried out in 2017 at FAMUR S.A. – a company producing equipment for mining. The HFG/J40 generator was manufactured in 1962 by the Austrian company ELIN. Its operating frequency: 400 kHz, and the output power (guaranteed by the manufacturer) at the exciter terminals was 40 kW. In the early 1990s, the company ELCAL performed a modernization that involved replacing the BBC-produced triode with a domestically produced triode type T26W and replacing the thyratron regulator with a thyristor regulator type PRW 210/440 and diode rectifier stacks. In 2017, after about 25 years of operation, Dacpol Service undertook another modernization of the device. Below are selected photos showing the device before modernization.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Below are selected photos showing the device after modernization.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Modernisation du générateur d'induction REL30Tr - Une nouvelle ère d'efficacité
Modernisation du générateur d'induction REL30Tr - Une nouvelle ère d'efficacité
Votre avis ne peut pas être envoyé
Signaler le commentaire
Signalement envoyé
Votre signalement ne peut pas être envoyé
Donnez votre avis
Avis envoyé
Votre avis ne peut être envoyé
