
Vous devez être connecté
Category


Les photos sont à titre informatif uniquement. Voir les spécifications du produit
please use latin characters
The electrical resistance of a metal conductor increases as the temperature rises. This change is reversible. For sensors, the most commonly-used metal is platinum, which retains good linearity over a wide temperature range (from -200 °C to +850 °C). Its purity and chemical inertia ensure remarkable stability.
The relationship between the platinum resistance and the temperature is:
| Tolerance class | Tolerance (°C) |
|---|---|
| A | 0,15 + 0,002(t) |
| B | 0,30 + 0,005(t) |
Tolerance class A is not used for sensors operating at above 650 °C.
Standard products
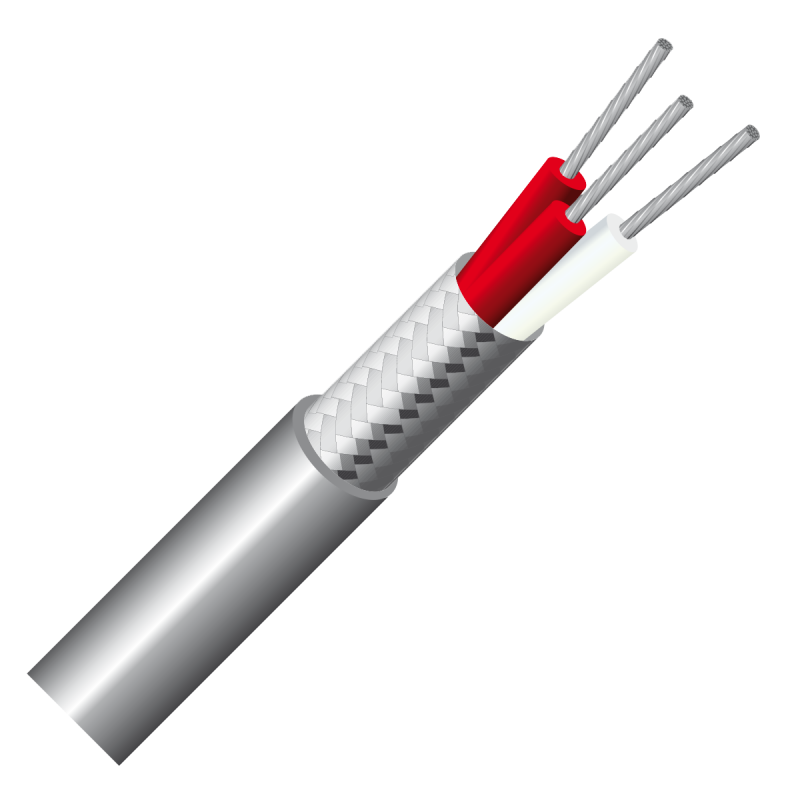
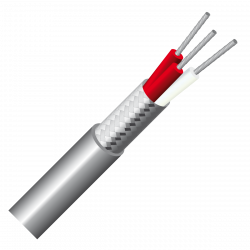
2 conductors: red / white.
3 conductors: 2 red / 1 white.
4 conductors: 2 red / 2 white.
Options
Applications
| 2-conductor cable Most frequently used but least precise as it introduces line resistance in the measurement. Must not be used for class A sensors. | |
| 3-conductor cable - Wheatstone bridge measurement Line wire resistance has little effect. Only contact resistances introduce an error. | |
| 4-conductor cable - Wheatstone bridge measurement Line resistance is eliminated. Only contact resistances introduce an error. | |
| 4-conductor cable - Kelvin measurement A current is present in the sensor. The potential difference (d.d.p) is measured at its terminals, which depends on its resistance. For this reason, only the sensor resistance has an effect on the measurement, which is more precise than previous ones. |
| Rodzaj izolacji | Żyła | Osłona | fibreglass in continuous operation | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2-Y2 MC-CS |
PVC 105 Silicone | PVC 105 Silicone |
-30 to +105° C -60 to +200° C |
|
| M5-5 M6-6 M7-7 |
FEP PFA ETFE |
FEP PFA ETFE |
-190°C do +260°C -190°C do +205°C -90°C do +155°C |
|
| MC-FEP | FEP | Silicone | -60 to +200 °C | |
| MV-PFA | PFA | Fibreglass | -60 to +260 °C | |
| MV-VS | Fibreglass | Fibreglass | -60 to +300 °C | |
| MV-VS-R | High temperature fibreglass | High temperature fibreglass | -60 to +400 °C | |
| MVK-KVS | Polymide + Fibreglass | Fibreglass | 60 to +350 °C |  |
| Number of conductors | Cross-section in mm2 | Equivalence AWG | Stranding number of strands x ø (mm) |
Nature of cores (identification / symbol in our references) Bare copper (CuA1 / -) Tin-plated copper (CuSn / E) Silver-plated copper (CuAg / A) Nickel-plated copper (CuNi / CN) Pure silver (Ag / Ag) Pure nickel (Ni / N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,14 | 26 | 7 x 0,16 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,15 | 26 | 19 x 0,10 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,22 | 24 | 7 x 0,20 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,25 | 24 | 19 x 0,13 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,34 | 22 | 7 x 0,25 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,34 | 22 | 19 x 0,15 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,5 | 20 | 7 x 0,30 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,6 | 20 | 19 x 0,20 |
| SONDIX® with electrical screen and/or flexible outer armour | ||
|---|---|---|
| With tin-plated copper electrical screen: xxxBE-xxx | With electrical screen of PET / aluminium tape + continuity wire: xxxBAL-xxx | With stainless steel braid flexible outer armour. Blxxx-xxx |
| in nickel-plated copper: xxxBCN-xxx | in galvanised steel: BGxxx-xxx | |
| in silver-plated copper: xxxBA-xxx | in tin-plated copper: BExxx-xxx | |

1 - Registered trademark of OMERIN
2 - Reference (example): MCBE-EFEP SONDIX® with tin-plated copper core, FEP insulation, tin-plated copper braid electrical screen, silicone sheath
3 - Number of conductors
4 - Core cross-section in mm2 or AWG
5 - Number of strands
6 - Diameter of each strand (in mm)
7 - Nature of core (see table above)
Êtes-vous intéressé par ce produit? Avez-vous besoin d'informations supplémentaires ou d'une tarification individuelle?
Ajouter à la liste de souhaits
Vous devez être connecté
The electrical resistance of a metal conductor increases as the temperature rises. This change is reversible. For sensors, the most commonly-used metal is platinum, which retains good linearity over a wide temperature range (from -200 °C to +850 °C). Its purity and chemical inertia ensure remarkable stability.
The relationship between the platinum resistance and the temperature is:
| Tolerance class | Tolerance (°C) |
|---|---|
| A | 0,15 + 0,002(t) |
| B | 0,30 + 0,005(t) |
Tolerance class A is not used for sensors operating at above 650 °C.
Standard products
2 conductors: red / white.
3 conductors: 2 red / 1 white.
4 conductors: 2 red / 2 white.
Options
Applications
| 2-conductor cable Most frequently used but least precise as it introduces line resistance in the measurement. Must not be used for class A sensors. | |
| 3-conductor cable - Wheatstone bridge measurement Line wire resistance has little effect. Only contact resistances introduce an error. | |
| 4-conductor cable - Wheatstone bridge measurement Line resistance is eliminated. Only contact resistances introduce an error. | |
| 4-conductor cable - Kelvin measurement A current is present in the sensor. The potential difference (d.d.p) is measured at its terminals, which depends on its resistance. For this reason, only the sensor resistance has an effect on the measurement, which is more precise than previous ones. |
| Rodzaj izolacji | Żyła | Osłona | fibreglass in continuous operation | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY2-Y2 MC-CS |
PVC 105 Silicone | PVC 105 Silicone |
-30 to +105° C -60 to +200° C |
|
| M5-5 M6-6 M7-7 |
FEP PFA ETFE |
FEP PFA ETFE |
-190°C do +260°C -190°C do +205°C -90°C do +155°C |
|
| MC-FEP | FEP | Silicone | -60 to +200 °C | |
| MV-PFA | PFA | Fibreglass | -60 to +260 °C | |
| MV-VS | Fibreglass | Fibreglass | -60 to +300 °C | |
| MV-VS-R | High temperature fibreglass | High temperature fibreglass | -60 to +400 °C | |
| MVK-KVS | Polymide + Fibreglass | Fibreglass | 60 to +350 °C |  |
| Number of conductors | Cross-section in mm2 | Equivalence AWG | Stranding number of strands x ø (mm) |
Nature of cores (identification / symbol in our references) Bare copper (CuA1 / -) Tin-plated copper (CuSn / E) Silver-plated copper (CuAg / A) Nickel-plated copper (CuNi / CN) Pure silver (Ag / Ag) Pure nickel (Ni / N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,14 | 26 | 7 x 0,16 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,15 | 26 | 19 x 0,10 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,22 | 24 | 7 x 0,20 | |
| 2, 3, 4, 6 or 8 | 0,25 | 24 | 19 x 0,13 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,34 | 22 | 7 x 0,25 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,34 | 22 | 19 x 0,15 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,5 | 20 | 7 x 0,30 | |
| 2, 3 or 4 | 0,6 | 20 | 19 x 0,20 |
| SONDIX® with electrical screen and/or flexible outer armour | ||
|---|---|---|
| With tin-plated copper electrical screen: xxxBE-xxx | With electrical screen of PET / aluminium tape + continuity wire: xxxBAL-xxx | With stainless steel braid flexible outer armour. Blxxx-xxx |
| in nickel-plated copper: xxxBCN-xxx | in galvanised steel: BGxxx-xxx | |
| in silver-plated copper: xxxBA-xxx | in tin-plated copper: BExxx-xxx | |

1 - Registered trademark of OMERIN
2 - Reference (example): MCBE-EFEP SONDIX® with tin-plated copper core, FEP insulation, tin-plated copper braid electrical screen, silicone sheath
3 - Number of conductors
4 - Core cross-section in mm2 or AWG
5 - Number of strands
6 - Diameter of each strand (in mm)
7 - Nature of core (see table above)
Votre avis ne peut pas être envoyé
Signaler le commentaire
Signalement envoyé
Votre signalement ne peut pas être envoyé
Donnez votre avis
Avis envoyé
Votre avis ne peut être envoyé
