Jūs turite būti prisijungę
-
sugrįžtiX
-
Komponentai
-
-
Category
-
Puslaidininkiai
- Diodai
- Tiristoriai
-
Elektroizoliuoti moduliai
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | VISHAY (IR)
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | Semikronas
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | POWEREX
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | IXYS
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | POSEICO
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | ABB
- Elektrai izoliuoti moduliai | TECHSEM
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Lygintuviniai tilteliai
-
Tranzistoriai
- Tranzistoriai | GeneSiC
- SiC MOSFET moduliai | Mitsubishi
- SiC MOSFET moduliai | STARPOWER
- „ABB SiC MOSFET“ moduliai
- IGBT moduliai | MITSUBISHI
- Tranzistorių moduliai | MITSUBISHI
- MOSFET moduliai | MITSUBISHI
- Tranzistorių moduliai | ABB
- IGBT moduliai POWEREX
- IGBT moduliai INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Silicio karbido puslaidininkiniai elementai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Valdikliai
- Galios blokai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Elektrinių dydžių keitikliai
-
Pasyvūs komponentai (kondensatoriai, rezistoriai, saugikliai, filtrai)
- Rezistoriai
-
Saugikliai
- ABC ir AGC serijos miniatiūriniai saugikliai elektronikai
- Greitaeigiai cilindriniai saugikliai
- Uždelsimo elementai su GL/GG ir AM charakteristikomis
- Ultragreiti intarpai - saugikliai
- Didžiosios Britanijos ir JAV standartų greitaeigiai saugikliai
- Europos standarto greitaeigiai saugikliai
- Saugikliai geležinkeliui
- Aukštos įtampos saugikliai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
-
Kondensatoriai
- Kondensatoriai varikliams
- Elektrolitiniai kondensatoriai
- Snubbers tipo kondensatoriai
- Galios kondensatoriai
- Kondensatoriai DC grandinėms
- Kondensatoriai galios kompensavimui
- Aukštos įtampos kondensatoriai
- Kondensatoriai indukciniam kaitinimui
- Impulsiniai ir energijos kaupimo kondensatoriai
- DC LINK kondensatoriai
- AC / DC grandinių kondensatoriai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Slopinimo tinklo filtrai
- Superkondensatoriai
- Apsauga nuo viršįtampių
- TEMPEST spindulių aptikimo filtrai
- Viršįtampių ribotuvas
- Eikite į subkategoriją
-
Relės ir kontaktoriai
- Relių ir kontaktorių teorija
- Trijų fazių puslaidininkinės AC relės
- Puslaidininkinės DC relės
- Reguliatoriai, valdikliai ir jų priedai
- Soft starteriai (minkšto paleidimo įrenginiai) bei reversiniai kontaktoriai
- Elektromechaninės relės
- Kontaktoriai
- Rotaciniai jungikliai
-
Vienos fazės puslaidininkinės AC relės
- AC vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės 1 | D2425 | D2450 serijų
- AC vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės CWA ir CWD serijų
- AC vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės CMRA ir CMRD serijų
- AC vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės PS serijos
- AC puslaidininkinės dvigubos ir keturgubos relės D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D serijų
- Vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės gn serijos
- AC vienfazės puslaidininkinės relės CKR serijos
- AC vienfazės relės DIN bėgiams ERDA ir ERAA serijų
- Vienfazės kintamosios srovės relės, skirtos 150A srovei
- Dvigubos kietojo kūno relės, integruotos su radiatoriumi DIN bėgiui
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Vienos fazės puslaidininkinės AC relės spausdinimo plokštėms
- Interfejsų relės
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Indukciniai elementai
- Radiatoriai, varistoriai, termo apsauga
- Ventiliatoriai
- Kondicioneriai, elektros spintų aksesuarai, aušintuvai
-
Baterijos, įkrovikliai, buferiniai maitinimo šaltiniai ir keitikliai
- Baterijos, įkrovikliai - teorinis aprašymas
- Ličio jonų baterijos. Individualios baterijos. Baterijų valdymo sistema (BMS)
- Akumuliatoriai
- Akumuliatorių įkrovikliai ir priedai
- UPS atsarginis maitinimo šaltinis ir buferiniai maitinimo šaltiniai
- Fotoelektros keitikliai ir priedai
- Energijos kaupimas
- Kuro elementai
- Ląstelės litio-joninės
- Eikite į subkategoriją
-
Automatikos komponentai
- Spiralift keltuvai
- Futaba dronų dalys
- Galiniai jungikliai, mikrojungikliai
- Jutikliai, keitikliai
- Pirometrai
- Skaitikliai, laiko relės, paneliniai matuokliai
- Pramoniniai apsaugos įrenginiai
- Šviesos ir garso signalizacija
- Terminio vaizdo kamera
- LED švieslentės
- Valdymo aparatūra - mygtukai ir jungikliai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
-
Laidai, pynės, laidų apsauginės žarnos, lankstūs sujungimai
- Laidai
- Kabelių įvadai ir movos
- Daugiagisliai laidai
-
Kabeliai ekstremalioms sąlygoms
- Kompensaciniai ir prailginimo kabeliai
- Laidai termoporoms
- PT jutikliams prijungimo laidai
- Daugiagysliai laidai temp. -60C iki +1400C
- Vidutinės įtampos kabeliai
- Uždegimo laidai
- Šildymo laidai
- Viengysliai laidai temp. -60C iki +450C
- Geležinkelio kabeliai
- Šildymo kabeliai Ex zonoms
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Apsaugos vamzdeliai
-
Pintinės
- Plokščios pintinės
- Apvalios pintinės
- Plokščios labai elastingos pintinės
- Apvalios labai elastingos pintinės
- Cilindro formos vario pintinės
- Vario cilindrinės pintinės su apsauga
- Elastingos įžeminimo juostos
- Cinkuoto ir nerūdijančio plieno cilindrinės pintinės
- PCV izoliuotos vario pintinės - temperatūra iki 85 C
- Plokščios aliuminio pintinės
- Sujungimo komplektas - pintinės ir vamzdeliai
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Aksesuarai geležinkeliams
- Kabelių antgaliai
- Lanksčios izoliuotos šynos
- Daugiasluoksnės lanksčios šynos
- Laidų pravedimo sistemos (PESZLE)
- Eikite į subkategoriją
- Žiūrėti visas kategorijas
-
Puslaidininkiai
-
-
- Tiekėjai
-
Pritaikymų sąrašas
- CNC staklės
- Energetika
- Energy bank
- Indukcinis kaitinimas
- Įranga ir komponentai sprogimo pavojaus zonoms (Ex)
- Kasyklos, metalurgijos ir liejimo pramonė
- Laboratoriniai ir moksliniai matavimai
- Maitinimo šaltiniai (UPS) ir lygintuvinės sistemos
- Medienos džiovinimo ir apdirbimo mašinos
- Nuolatinės ir kintamos srovės pavaros (keitikliai)
- Paskirstymo, valdymo ir telekomunikacijos spintų įranga
- Plastmasių liejimo mašinos
- Poligrafija
- Pramoninė apsaugos įranga
- Pramoninė automatika
- Suvirinimo aparatai
- ŠVOK automatika
- Temperatūros matavimas ir nustatymas
- Tramvajų ir traukinių pavaros
- Varikliai ir transformatoriai
-
Montavimas
-
-
Induktoriai
-
-
Indukciniai įtaisai
-
-
Aptarnavimas
-
- Kontaktai
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Robust High Voltage IGBT Power Modules Against Humidity and Condensation

Robust High Voltage IGBT Power Modules Against Humidity and Condensation
Mitsubishi Electric continuously improve the power device robustness even considering different environmental conditions like humidity and condensation.
By Eugen Wiesner, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC EUROPE B. V.K. Nakamura, K. Hatori, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
Introduction
The power electronics is exposed to extreme environmental conditions during the operation like dust, temperature, humidity, vibrations or chemicals. The mission profile of the temperature and relative humidity has a wide range dependent on application and the location of operation.
In some mining applications the relative humidity level reach even almost 100% with condensation, drip and high pressure water spray for dust control [1].
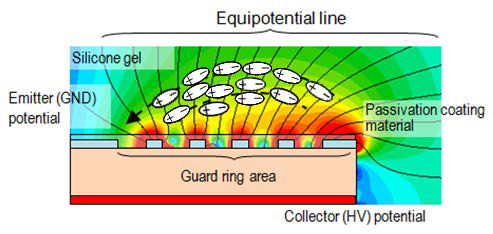
Figure 1: Principle chip guard ring area with gel polarization effect
The IGBT power module as a key components of power electronics is suspended even to such harsh environment. Although the temperature influence on power semiconductor life-time was investigated quite intensively, the humidity was not taken into the account so far due to the missing life-time models or knowledge about failure mechanisms. Especially for case type high voltage IGBT power modules the humidity becomes important parameter due to the non-hermetic package design and the high electric field at semiconductor interfaces, like passivation area. As a result it was necessary to investigate the humidity caused failure mechanisms more deeply and to establish the needed life-time models.
In this article the Mitsubishi Electric investigation results are presented in regards to the humidity and condensation influence on high voltage IGBT power modules durability.
Humidity failure mechanisms and life-time model
The electromechanical migration (ECM) and aluminum corrosion are two possible and well described [2] failure mechanisms of power semiconductors caused by humidity. In the first case (ECM) a dendrite grow of Cu or Ag can be detected on the chip passivation area. In the second case the Aluminum metallization is corroded on the guard-ring.
Besides above described two failure mechanisms caused by humidity and requiring a long time influence Mitsubishi Electric found and published one other failure mechanism that may happen even after short humidity or condensation impact [4]. This failure may appear in case of gel polarization and surface charge accumulation at high voltage above guard ring area. In the figure 1 the principle structure of chip guard ring area with the gel polarization effect is shown. The moisture absorption in the module accelerates the polarization. From the polarization resulting surface charge accumulation above the chip’s guard ring area causes the blocking capability degradation of the device. This may finally lead to device failure.
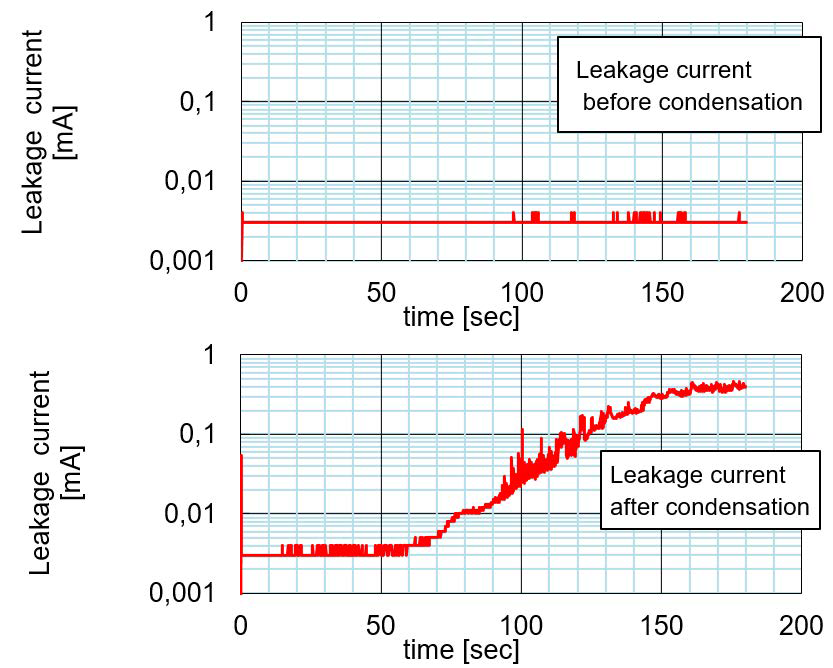
Figure 2: Leakage current increase after condensation event
This phenomenon can be detected by leakage current increase after condensation event. The leakage current increase happens not immediately. It takes several seconds before the current rises after voltage is applied. In figure 2 the comparison of the leakage current characteristic between dry condition and after condensation is shown.
The knowledge of failure mechanism only is not enough to decide whether the power device will operate the desired time under given conditions. That’s why Mitsubishi Electric developed and proposed a life time model considering the humidity as below [2]:
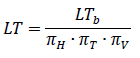
LI is the estimated life time of the power device. The coefficients πH, πT and πV are the acceleration factors proposed by [3]. These factors, can be defined by HV-H3TRB measurements at different conditions. The LTb is the basic life time. It can be calculated from the transformation of different conditions used during the HV-H3TRB evaluation to only one reference condition for example 75%RH, 25°C and 1500V (for 3300V IGBT-Module)
In the following example it is shown how the humidity related parameters can be defined and calculated using 3300V IGBT Module. In the first step the humidity acceleration factor πH can be calculated using the results from two HV-H3TRB tests. One test (test A) was performed at 85% RH the second test (test B) was performed at 95% RH.
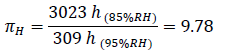
For this calculation the 50% Weibull distribution values were used. Other test parameters like temperature and voltage were kept same for both tests. Detailed evaluation result are shown in figure 3 below.
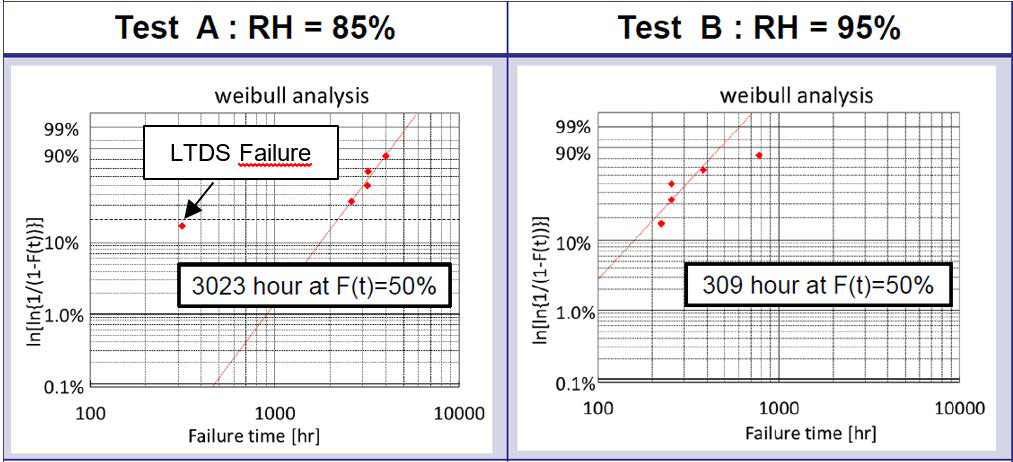
Figure 3: HV-H3TRB evaluation result with 3300V IGBT
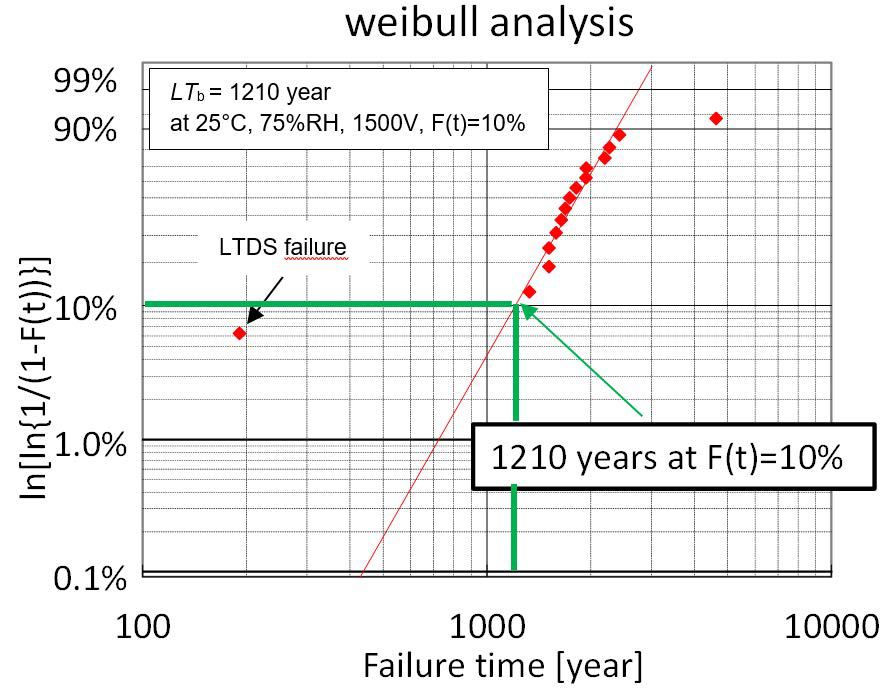
Figure 4: Estimation of basic life-time from HV-H3TRB evaluation test results for 3300V IGBT
In the second step the empirical factor x using Peck’s model can be calculated as below:
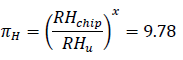
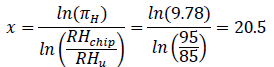
In the final third step each testing point from HV-H3TRB evaluation can be transformed to the base line at reference conditions (75%RH, 25°C, 1500V) to define the basic life time (LTb).
All the transferred testing points from different HV-H3TRB test can be plotted into one Weibull diagram as shown in figure 4. As a result the basic life time can be estimated at the reference conditions fo example considering 10% probability value from this Weibull distribution.
From the established humidity life-time model the user can learn a lot. For example the IGBT-Module life-time curves can be drawn in humidity vs. temperature diagram to investigate the impact of temperature increase on the life-time as shown in figure 5. During the operation the absolute humidity is almost constant on the other hand the temperature is fluctuating. The diagram in figure 5 shows that even small increase of temperature by 4 °C at the same absolute humidity can increase the device life time by 30 times. That is why the starting of the inverter should be carefully considered because of low temperature.
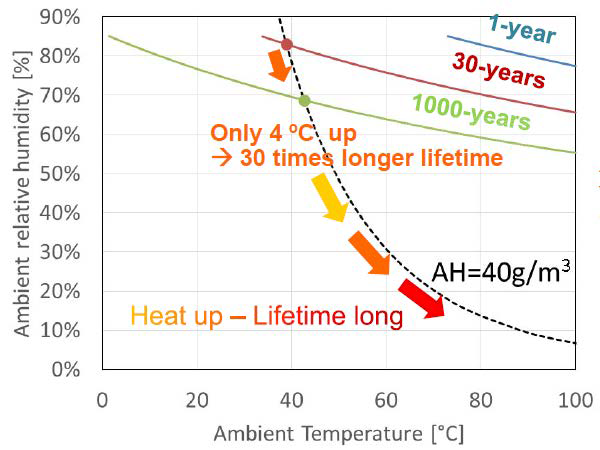
Figure 5: Impact of temperature increase on the module life-time
IGBT-Module condensation test method
The original condensation test method to check power device robustness against condensation was proposed by Mitsubishi Electric in 2015 [4]. Before condensation event the power module was placed into the humidity chamber at the conditions of 85°C and 85%RH for 36 hours. This time is required to ensure that the humidity reached all parts inside the IGBT module. The power device will be like “saturated” with humidity. After the storage in the humidity chamber the samples will be cooled down rapidly from 85°C to 10°C using a heat sink outside the climate chamber. This rapid cooling event causes the condensation inside the power module. Finally the leakage current will be monitored after the condensation and compared with t characteristic before condensation. The worst case field conditions are usually not so hard as used during the performed condensation testing. According to IEC 60721-3-5 5K2 standard the pre-condition for rapid temperature change is 35°C and 95%RH. The testing with the conventional approach at such conditions would be very time consuming.
A new automatic condensation test approach was proposed by Mitsubishi Electric to perform the cycling condensation test more efficient using the humidity chamber [5]. This automatic test is helpful t derive the acceleration factors between the field conditions and the hard qualification tests. The proposed new test sequence for condensation test is shown in figure 6. Instead of cooling down the power module externally using the heatsink the climate chamber is used to generate the condensation. The advantage is that the comparable results to the conventional test can be achieved more efficient and quicker.
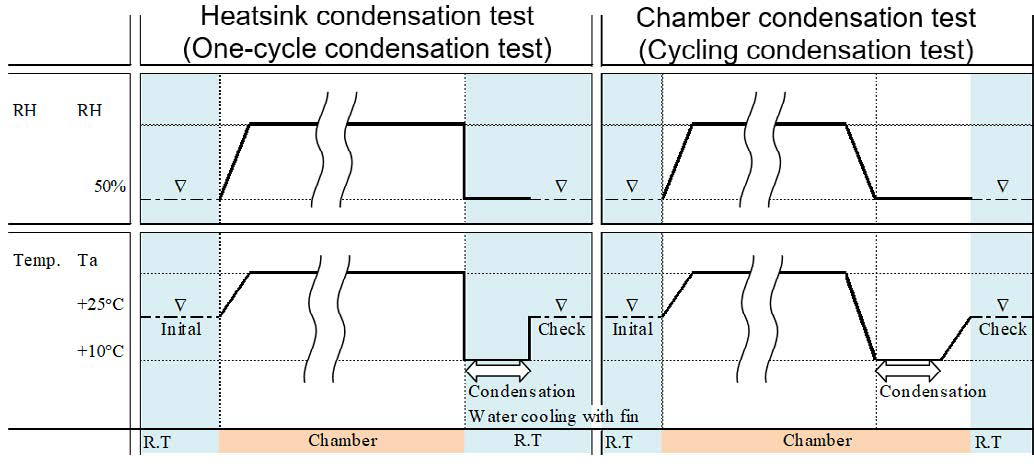
Figure 6: New test sequence for cycling condensation test
Latest high voltage IGBT module technologies
During the humidity investigation of the existing power modules the most sensitive design components were identified. The big influence on the device robustness against humidity had the selection of the proper silicone gel and the design of the chip passivation structure (guard-ring). Especially the passivation structure improvement leads to an enhancements of the device robustness against humidity. The invented by Mitsubishi Electric surface charge control (SCC) technology of the passivation area is the key factor to improve power device durability. It contains a semi-insulation layer above the Si guard ring structure as shown in figure 7.
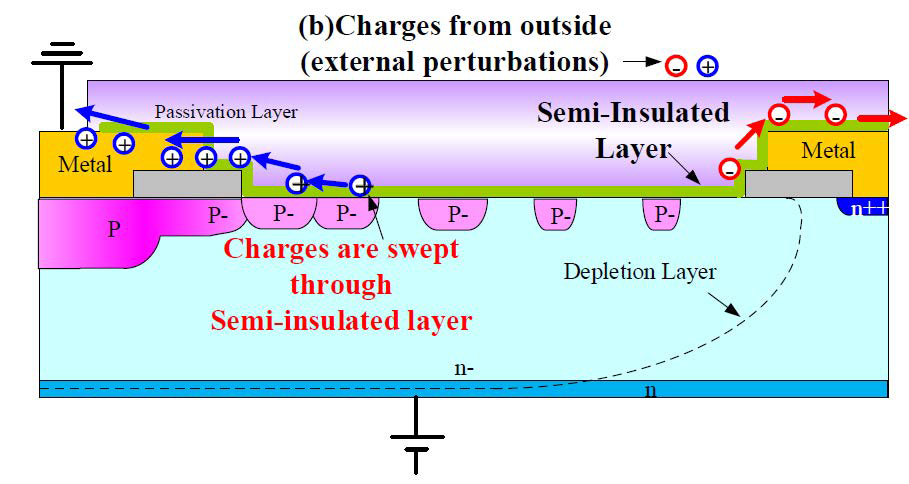
Figure 7: Surface charge control technology
This semi-insulation layer avoids the accumulation of surface charges [6]. The latest X-Series high voltage power modules from Mitsubishi Electric use the SCC - technology.
The X-Series power device capability against condensation was tested using the above described cycling condensation test and compared to the conventional module. When evaluating the conventional module an acceleration factor of 80 was found between 85°C/85%RH and 36°C/95%RH. When comparing the new X-series with conventional design at 85°C/85%RH an improvement by more than 100 times was confirmed by testing. From these test results an unprecedented robustness against 8000 condensation events under IEC 60721-3-5 5K2 reference conditions can be derived for the new X-series, see Fig.8
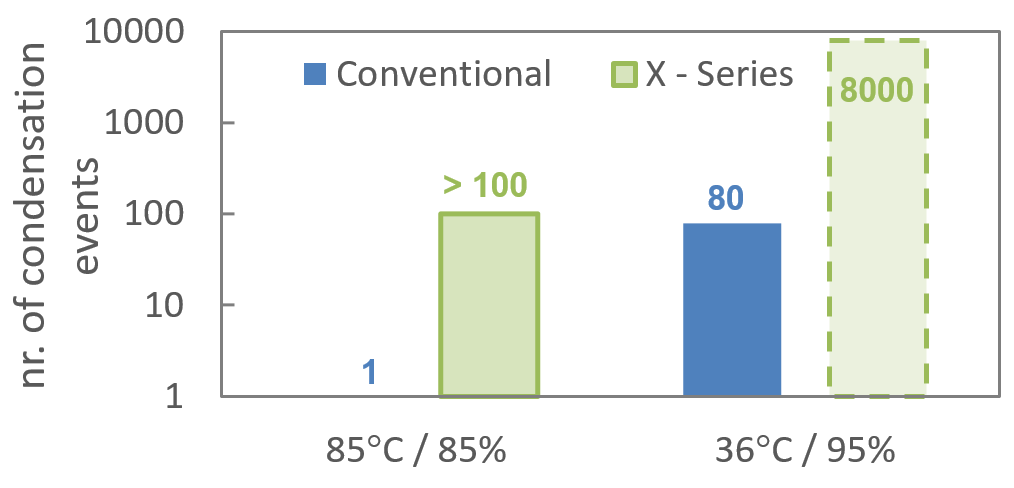
Figure 8: X-Series technology against humidity and condensation in comparison to the conventional product
Conclusion
With the latest X-Series high voltage IGBT modules the device capability could be improved against the humidity and condensation. Also the basic approach to define the life time model for the humidity is established providing to the user the confidence of the proper inverter operation. On the other hand the upcoming SiC technology is still challenging especially considering the smaller structures and new materials. The lessons learned in the past with Si IGBT can be partially utilized and used also for SiC high voltage power modules in the future.
References
[1] Dustin Selvey, “Overview of the Unique Requirements and Challenges for Power Electronics in Mining Equipment” APEC, Long Beach, California, 2016.
[2] Y. Kitajima et al., “Lifetime Estimation Model of HVIGBT Considering Humidity,” PCIM Europe 2017, Nuremberg, Germany, 2017.
[3] C. Zorn and N. Kaminski, “Temperature Humidity Bias (THB) Testing on IGBT Modules at High Bias Levels,” CIPS 2014; Nuremberg, Germany, 2014.
[4] N. Tanaka, “Robust IVIGBT module design against high humidity”, PCIM 2015.
[5] K. Nakamura, “The test method to confirm robustness against condensation”, EPE 2019.
[6] S. Honda, T. Harada, A. Nishii, Z. Chen and K. Shimizu, “High voltage device edge termination for wide temperature range plus humidity with surface charge control (SCC) technology,” ISPSD 2016, Prague, 2016.
Related posts
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Leave a comment