trebuie să fii logat
SiC Power Modules for a Wide Application Range

SiC Power Modules for a Wide Application Range
Innovative Power Devices for a Sustainable Future
By J. Yamada Mitsubishi Electric, Power Device Works, Fukuoka, Japan and E. Thal Mitsubishi Electric Europe, Ratingen, Germany
Development Milestones of Mitsubishi SiC Power Modules
Today’s SiC power modules from Mitsubishi Electric (see Figure1) are belonging to the first phase of SiC-commercialization that had started around 2010.
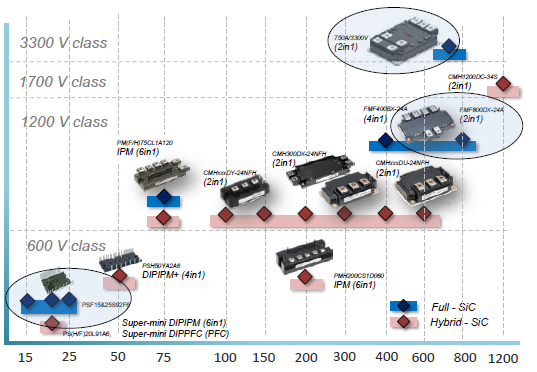
Figure 1: Today’s SiC-module range (X-axis: module rated current in A; Y-axis: voltage class)
However, the SiC technology development started in Mitsubishi Electric much earlier, more than 20 years ago, see [1]. In the first decade 1994…2004, the R&D efforts were mainly oriented on the SiC chip technology itself, both for SiC MOSFETs and SiC Schottky diodes. After this, in the years 2005…2009, the focus was on the achievable system benefits by using SiC-modules in inverters. For this purpose, several SiC-inverter demonstrators were designed and evaluated under different applications. The commercialization phase of SiCmodules started in the years 2010…2014. Several types of full- and hybrid SiC-modules were launched in this period and the first industrially manufactured inverters with Mitsubishi SiC-Modules appeared, mainly in Japan. In parallel, the SiC-MOSFET chip technology was continuously undergoing further improvement steps; see the 1200V development roadmap in Figure 2 for example.
Particularly since 2015, SiC-modules started to enter many new application areas. This expansion process is still ongoing and even gaining speed. The today available SiC–power modules from Mitsubishi Electric are covering a wide current and voltage range, see Figure 1.
This article is explaining the innovation potential of SiC-technology in power electronic systems by referring mainly to three examples of SiC power modules selected out of the product range given in Figure 1:
- 15A/600V Full SiC DIPIPM, type name PSF15S92F6
- 800A/1200V Full SiC Dual Module, type name FMF800DX2-24A
- 750A/3,3kV Full SiC Dual Module, type name FMF750DC-66A
15A/600V Full SiC Super mini DIPIPM (PSF15S92F6)
This full SiC Super mini DIPIPM was introduced in October 2016 into the new Mitsubishi room air conditioner “Kirigamine“ FZ and Z-Series
High energy efficiency is a key requirement for inverterized air conditioning systems. The PSF15S92F6 was developed for home appliances, such as air conditioners, washing machines, refrigerators [2].
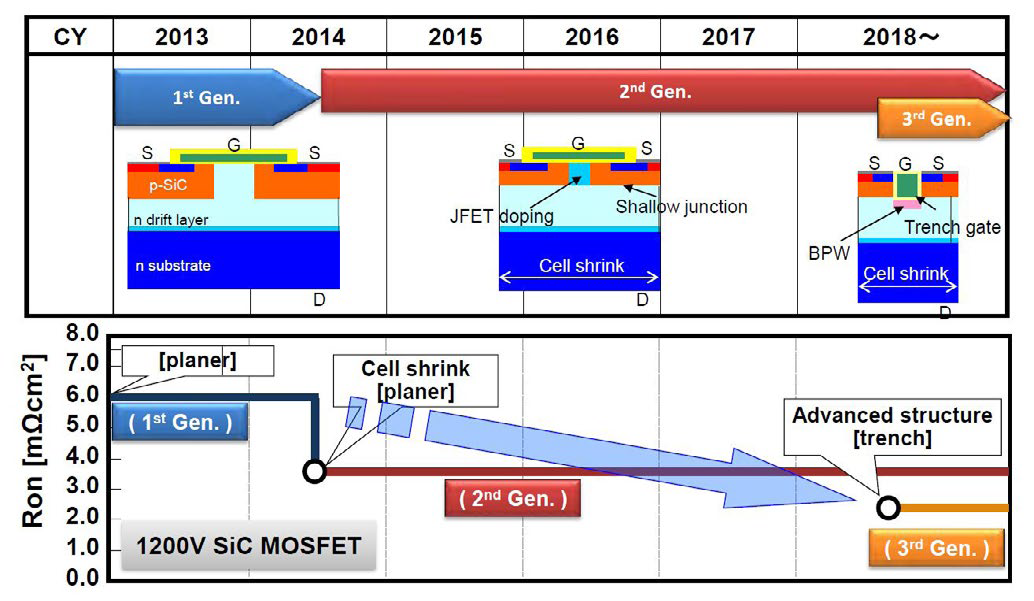
Figure 2: 1200V SiC MOSFET chip development roadmap

Figure 3: Room air conditioner “Kirigamine” series
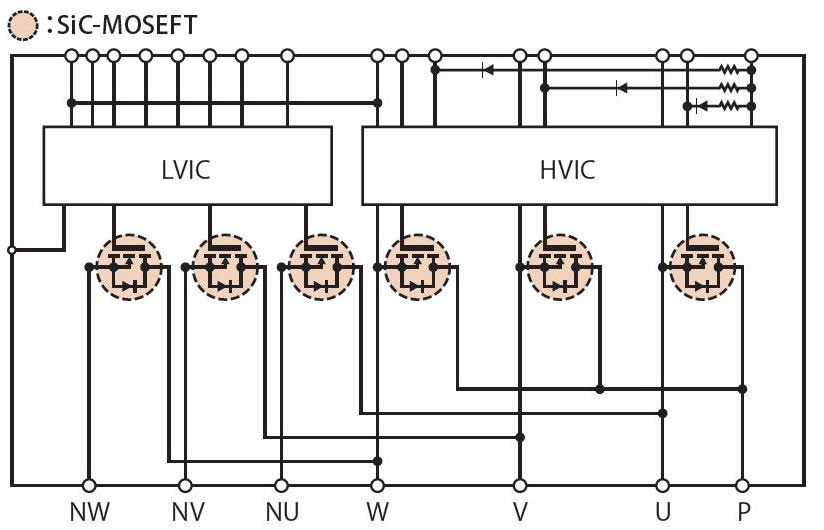
Figure 4: PSF15S92F6 circuit diagram
The circuit diagram is shown in Figure 4. It contains a 3-phase inverter with SiC-MOSFETs and their driving ICs. The package outline is shown in Figure 5. Compared with a conventional 15A Si-IGBTDIPIPM manufactured in the same module package the new full SiC DIPIPM is offering 70% lower power loss under same application conditions (see Fig.6). By using the PSF15S92F6 an outstanding energy efficiency of the new “Kirigamine” room air conditioners was reached.
Figure 5: Package outline PSF15S92F6
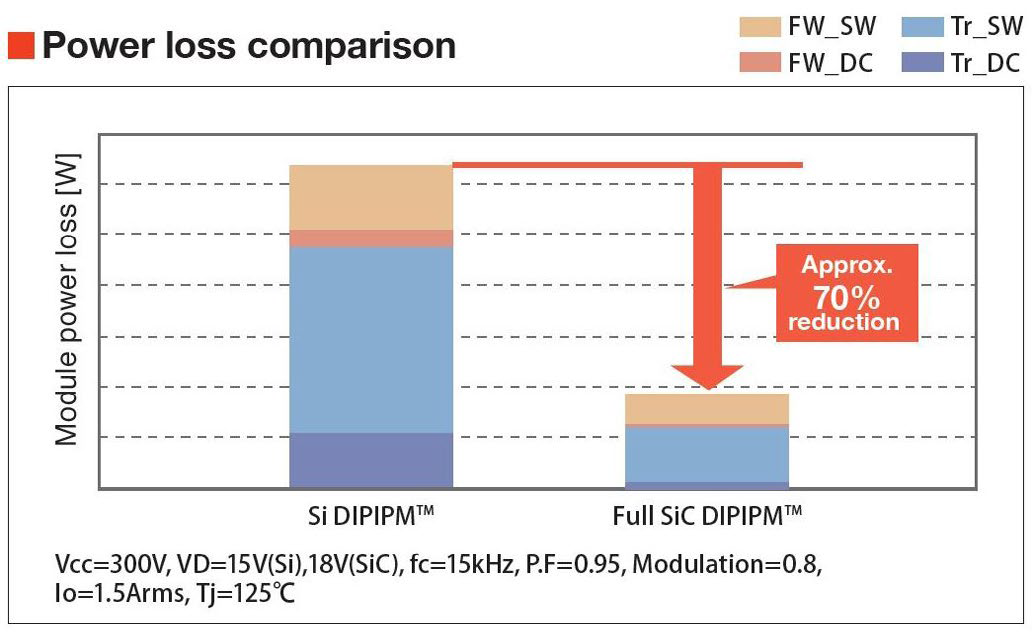
Figure 6: Power loss comparison Si- versus Full SiC-DIPIPM
Another application benefit of the Full SiC-DIPIPM is shown in Figure 7: The smooth diode recovery at MOSFET turn-on is remarkably reducing the radiated noise, thus relaxing the requirements towards the EMI-filters.
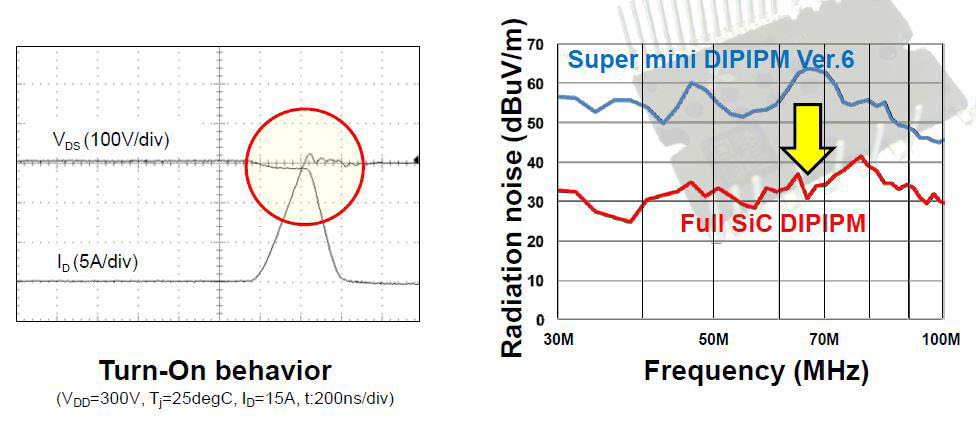
Figure 7: Improved EMI by smooth FWDi recovery
Advanced 800A/1200V full SiC Dual Module (FMF800DX2-24A)

Figure 8: Advanced 800A/1200V full SiC Dual module FMF800DX2-24A
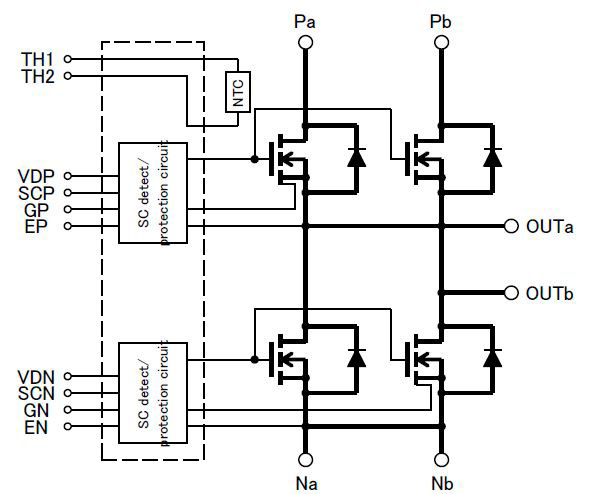
Figure 9: FMF800DX2-24A internal circuit diagram
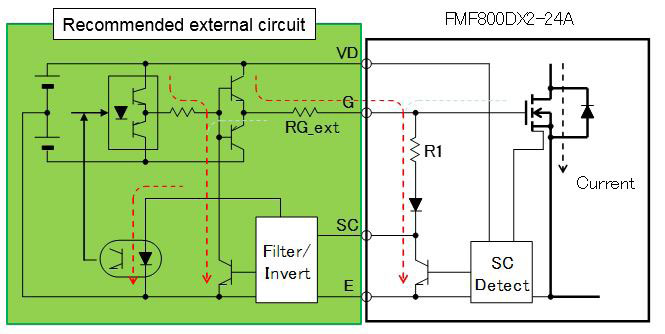
Figure 10: Recommended gate drive circuit for SC-protection
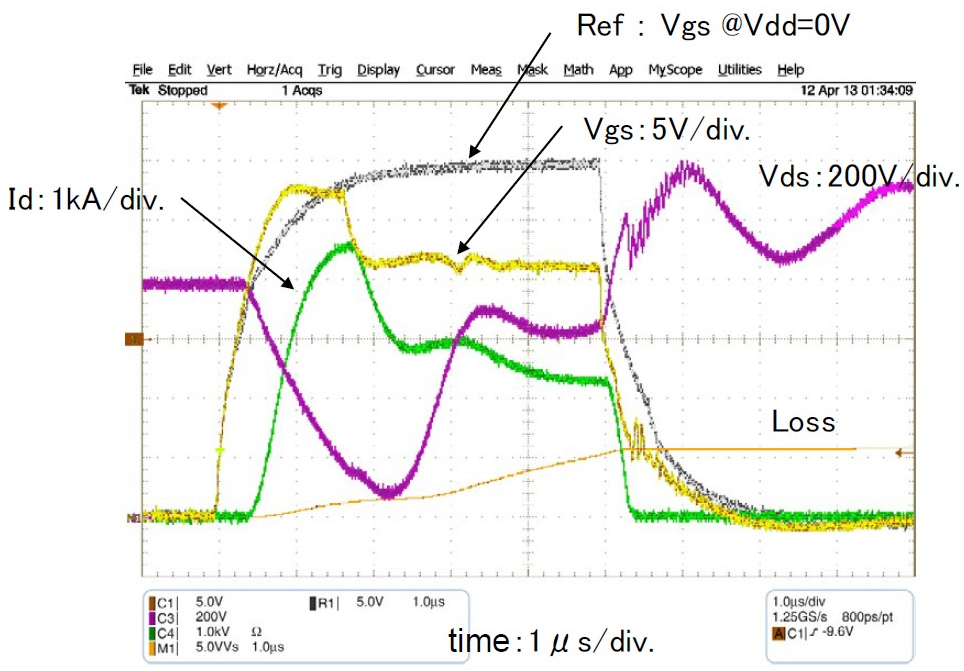
Figure 11: SC-waveforms during RTC-operation
In April 2015 we reported in Bodo’s Power [3] about a new 800A/1200V Full SiC Dual module (type name FMF800DX-24A). For efficient driving and protecting this device a dedicated gate driver was developed by Power Integrations GmbH [4]. Recently Mitsubishi has launched an advanced version of this 800A/1200V full SiC Module having the new type name FMF800DX2-24A. The low loss SiC-chip set is the same, but the package is modified compared to the previous version, see Figure 8. The internal package inductance is less than 10nH; the isolation voltage is Viso=4kV AC. Real Time Control (RTC) circuits are incorporated into the module both for P- and N-side SiC-MOSFETs, see Figure 9. This RTC is using the MOSFET-chipintegrated current sensors for SC-detection and efficient SC-current limitation by fast gate-voltage shutdown; see Figures 10 and 11.
When comparing the power loss of the 800A/1200V full SiC-module FMF800DX(2)-24A to its Si-counterpart under same application conditions, the advantage of SiC becomes evident [1], see the 110KWinverter example given in Figure 12.
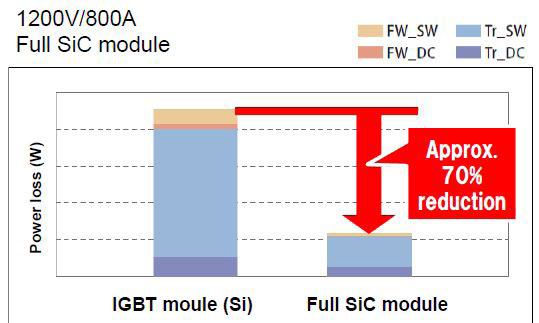
Figure 12: Power loss comparison Si-IGBT vs. Full SiC-module (both 800A/1200V)
There are two possible ways for utilizing this advantage:
- If keeping the switching frequency the same, as with conventional IGBT-modules, the inverter power loss will be drastically reduced. This is improving the inverter efficiency and is offering a new grade of freedom for shrinking the inverter size by reducing the heatsink dimensions. This is interesting for applications where high inverter power densities are required, specifically if the space for installing the inverter is limited.
- If keeping the inverter power loss at the same level as with IGBTmodules (means the inverter efficiency and heatsink size are kept the same) the switching frequency can be increased by a factor of 3…5. In applications having large inductive storage components this will offer a new grade of freedom for reducing the size (and cost) of those inductors.
Of course, any superposition of both aspects 1. and 2. is possible for obtaining the best advantage in a given application from using the full SiC-module FMF800DX(2)-24A.
750A/3300V Full SiC Dual Module (FMF750DC-66A)
In June 2015 Mitsubishi Electric announced the installation of first Railcar propulsion system using 1500A/3300V All-SiC Power Modules into a Shinkan-sen Bullet Train [5] (Fig.13). The system benefits were described as 55% inverter size reduction and 33% inverter weight reduction.
In [6] the newly developed 750A/3300V full SiC Dual module FMF750DC-66A was introduced. It contains SiC-MOSFETs with antiparallel SiC-Schottky-Barrier-Diodes. In order to get a low internal package inductance (<10nH) and a good current sharing between the paralleled chips a new dual package has been adopted, called LV100-package (see Figure 14).
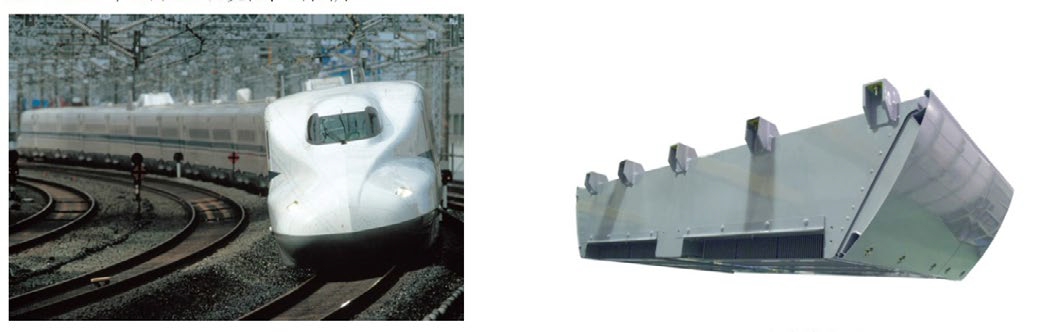
Figure 13: First All-SiC propulsion inverter in Shinkansen Bullet Train
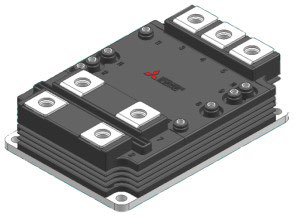
Figure 14: 750A/3300V full SiC Dual module in LV100-package
The switching waveforms of 750A/3300 Si-IGBT and FMF750DC-66A are compared in Figure 15 (turn-on) and Figure 16 (turn-off).
The FMF750DC-66A switching energy is much lower compared with its Si-counterpart: Eon is reduced by 61%; Eoff is reduced by 95%.
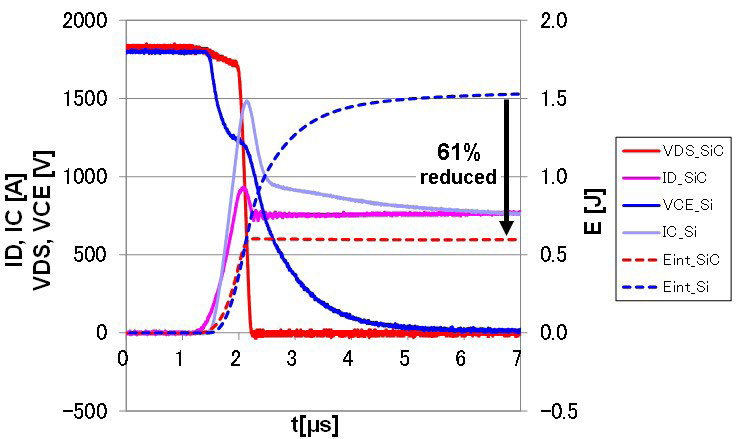
Figure 15: Turn-on waveforms
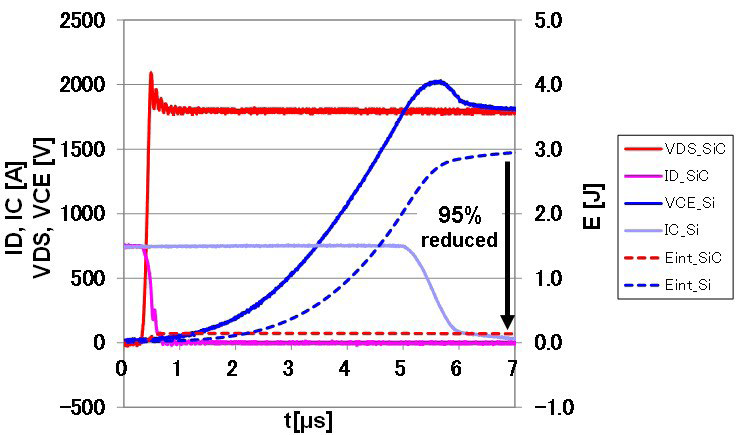
Figure 16: Turn-off waveforms
This dramatic switching loss reduction by SiC can be utilized in several directions, as described earlier in chapter 3: 1. for reducing the inverter system size or 2. for increasing the switching frequency or, as a combination of 1. and 2., depending on the priorities in the given application.
In order to meet the specific environmental and reliability requirements in traction applications the new FMF750DC-66A has passed several confirmation tests [6]:
- 1000h HTRB at Vds=2810V; Vgs=-10V; Tj=175°C
- Cosmic radiation stability test
- 1000h HTGB at Vgs=+/-20V; Vds=0V; Tj=175°C
- Power cycling test at Tj(max)=175°C
- 1000h H3TRB test at Ta=85°C; RH=85%; Vds=2100V; Vgs=-10V
- 1500h switching test at Vds=1650V; Id=354A; fo=20Hz; fc=1kHz
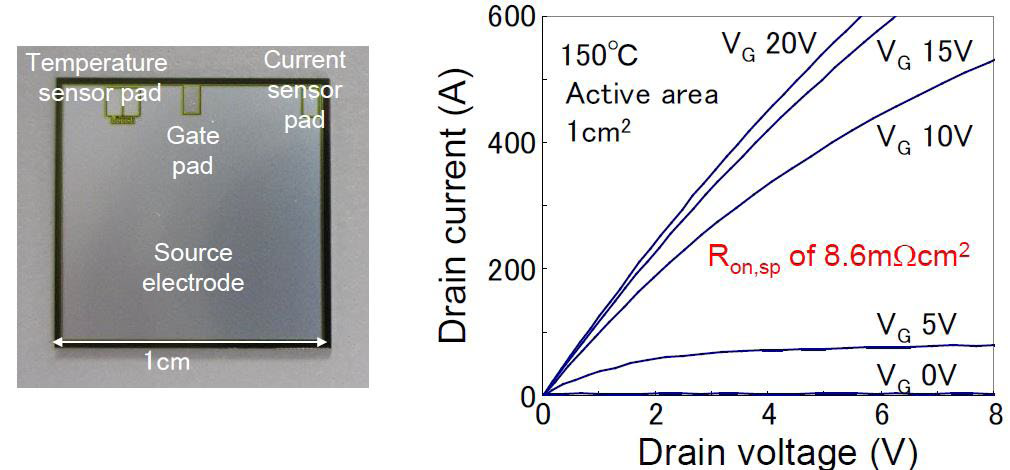
Figure 17: 300A/1200V SiC-MOSFET chip
As result, it was confirmed that the performance of FMF750DC-66A is suitable for traction system use. This new all-SiC power module has about 80% lower switching loss than a conventional Si power module. By applying the FMF750DC-66A to the propulsion inverter in a railcar it was possible to reduce the total power loss by 30% compared with the existing system.
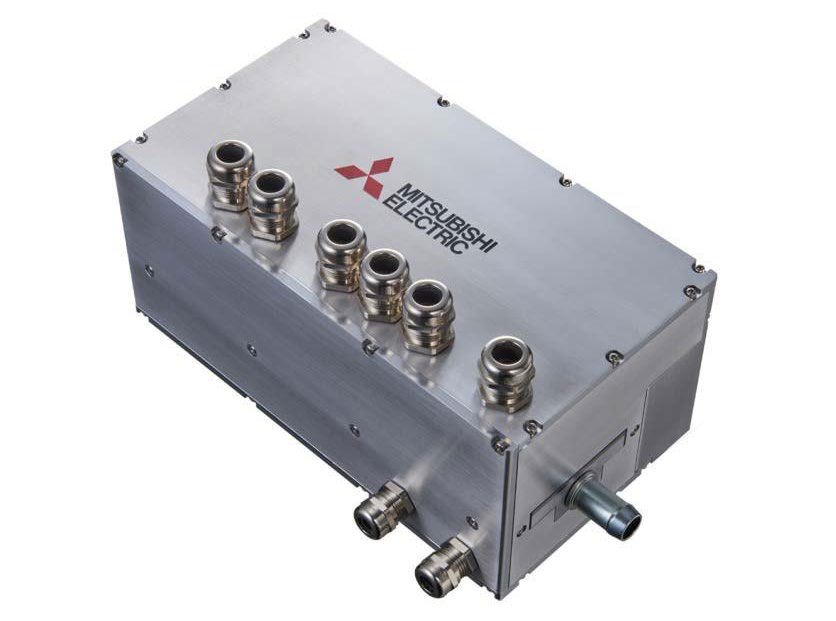

Figure 18: Ultra-compact inverter with 86kVA/dm³ for HEV
R&D efforts for expanding the SiC technology
In parallel to the design-in-activities of already existing SiC power modules (see Figure 1) there are multiple R&D activities ongoing for adopting the SiC-technology to new applications.
One very promising direction is the use of SiC in automotive power train applications. In [7] the test production of 300A/1200V SiC-MOSFET chips was reported, having the size of 10x10mm² and a specific Ron=5,9mΩcm² @ Vg=15V; Ids=300A, see Figure 17. Even though this is a 2 years old result, it is still (as of Sept.2017) the world’s largest size 1200V SiC-MOSFET chip.
Another example for Mitsubishi’s pioneering efforts to introduce SiCtechnology into automotive applications is shown in Fig.18. This ultracompact 430kVA-inverterized power control unit for HEV-application is incorporated into a housing of 275x151x121mm³. It represents the world’s highest inverter power density of 86kVA/dm³ [8].
Another important R&D activity is focusing on the expansion of SiCtechnology towards higher blocking voltages. In [9] the successful fabrication of 8,1x8,1mm² 6500V SiC-MOSFET chips with embedded Schottky-barrier-diode (SBD) was reported, see Figure 19 & Figure 20.
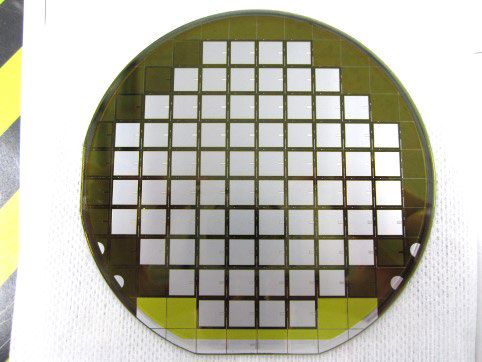
Figure 19: Wafer of 6500V SiC-MOSFET with embedded SBD
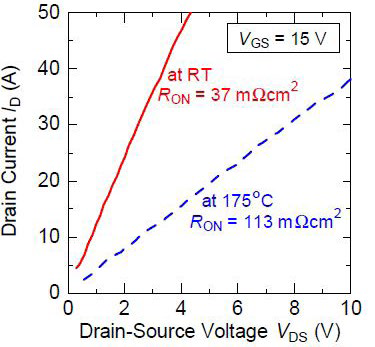
Figure 20: Drain characteristics of SBD-embedded 6,5kV SiC-MOSFET
This new approach is offering two advantages:
- The integration of an antiparallel SBD into the SiC-MOSFET-chip allows reducing drastically the needed active chip area in a power module. The example in [9] is indicating a reduction factor of 3 to 4 compared to modules with separate SBD-chips, thus allowing module designs with very high current densities.
- The chip-embedded SBD is enabling a full unipolar operation of the MOSFET in both directions without degradation. No parasitic increase of on-resistance of the diode operation will happen for such chip design, because the bipolar body diode of the SiCMOSFET is always safely by-passed by the embedded SBD. The long-term reliability test results reported in [9] show that such SiCMOSFET- structure is completely free from the well-known bipolar degradation effect caused by the expansion of stacking faults.
Summary and outlook
Mitsubishi Electric is a pioneer in exploring the SiC-technology for power modules. A wide range of SiC-power modules with currents between 15A and 1200A and voltage ratings between 600V and 3300V is already available. The main advantage of today’s SiC power modules vs. conventional Si-IGBT-modules are the drastically reduced switching losses. Depending on the specific requirements in a given inverter application this advantage can be used either for reducing the inverter size/improving the inverter efficiency or for increasing the switching frequency. The application area of SiC-based inverter systems is continuously expanding. By its wide R&D activities on SiC Mitsubishi Electric is continuously enlarging the fundaments for the coming SiC-power semiconductor age.
References
[1] SiC Power Devices Catalogue 2017; Mitsubishi Electric Publication HG-802D, April 2017
[2] DPH13502-E: Super Mini Full SiC DIPIPM Application Note; published February 2017
[3] E.Thal et.al: New 800A/1200V Full SiC Module; Bodo’s Power Systems, April 2015, pp.28-31
[4] E.Wiesner et.al: Advanced protection for large current full SiCmodules; PCIM-Europe 2016, conference proceedings pp.48-52
[5] Mitsubishi Electric Press Release No.2942: Mitsubishi Electric Installs Railcar Traction System with All-SiC Power Modules on Shinkansen Bullet Trains; Tokyo, 25th June 2015
[6] T.Negishi et.al: 3,3kV All-SiC Power Module for Traction use, PCIM-Europe 2017, Conference proceedings, pp.51-56
[7] M.Furuhashi: Recent Developments in High Power SiC MOSFETs and Modules; presentation at the ECPE User Forum: Potential of Wide Bandgap Semiconductors in Power Electronic Applications; 20-21 April 2015 University of Warwick, UK.
[8] Mitsubishi Electric Press Release No. 3088: “Mitsubishi Electric Develops World’s smallest SiC Inverter for HEVs”; Tokyo, March9, 2017
[9] K.Kawahara et.al: 6,5kV Schottky-Barrier-Diode embedded SiCMOSFET for Compact Full-Unipolar Module; 29th ISPSD-Conference, May28 - June1, 2017, Sapporo, Japan.




Leave a comment