trebuie să fii logat
-
întoarce-teX
-
Componente
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductoare
- Diode
- tiristoare
- Module izolate electric
- Redresoare în punte
-
Tranzistoare
- tranzistoare GeneSiC
- Module MOSFET Mitsubishi SiC
- Module MOSFET STARPOWER SiC
- Module MOSFET ABB SiC
- Module IGBT de la MITSUBISHI
- Module de tranzistori MITSUBISHI
- module MITSUBISHI MOSFET
- Module de tranzistori ABB
- Module IGBT de la POWEREX
- Module IGBT - de la INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elemente semiconductoare din carbură de siliciu
- Accesați subcategoria
- Șoferii
- Blocuri de putere
- Accesați subcategoria
- Traductoare de curent și tensiune LEM
-
Componente pasive (condensatori, rezistențe, siguranțe, filtre)
- Rezistoare
-
Siguranțe
- Siguranțe miniaturale pentru sisteme electronice din seria ABC și AGC
- Siguranțe tubulare cu acțiune rapidă
- Inserții întârziate cu caracteristici GL/GG și AM
- Legături sigure ultra-rapide
- Siguranțe standard britanice și americane cu acțiune rapidă
- Siguranțe cu acțiune rapidă standard european
- Siguranțe de tracțiune
- Siguranțe de înaltă tensiune
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Condensatoare
- Condensatoare pentru motoare
- Condensatoare electrolitice
- Condensatori Icel Film
- Condensatoare de putere
- Condensatoare pentru circuite DC
- Condensatoare de compensare a puterii
- Condensatoare de înaltă tensiune
- Condensatoare pentru încălzire prin inducție
- Condensatoare de impulsuri
- Condensatoare DC LINK
- Condensatoare pentru circuite AC/DC
- Accesați subcategoria
- Filtre anti-interferențe
- Supercondensatoare
- Protecție la supratensiune
- Filtre de emisii revelatoare TEMPEST
-
Descărcător de supratensiune
- Descărcătoare de supratensiune pentru rețeaua de curent alternativ
- Descărcătoare de supratensiune pentru rețea de curent continuu
- Limitatoare de joasă tensiune ALVL
- Limitatoare de joasă tensiune PG
- Descărcătoare de trăsnet pentru rețele de curent alternativ până la 1000V
- Dispozitive de măsurare
- Accesați subcategoria
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Relee și Contactoare
- Teoria releelor și contactoarelor
- Relee cu stare solidă trifazată CA
- Relee cu stare solidă DC
- Regulatoare, sisteme de control și accesorii
- Porniri ușoare și contactoare inversoare
- Relee electromecanice
- Contactoare
- Comutatoare rotative
-
Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relee semifazate CA monofazate, seria CWA și CWD
- Relee semifazate CA monofazate seriile CMRA și CMRD
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria PS
- Relee cu stare solidă AC seria duble și cvadruple D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relee monofazate din seria GN
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria CKR
- Relee monofazate pentru șină DIN AC SERIA ERDA și ERAA
- Relee AC monofazate pentru curent de 150A
- Relee duble cu stare solidă integrate cu radiator pe șină DIN
- Accesați subcategoria
- Relee cu stare solidă imprimabile monofazate CA
- Relee de interfață
- Accesați subcategoria
- Miezuri și alte componente inductive
- Radiatoare, Varistoare, Protectie termica
- Fani
- Aer conditionat, Accesorii tablou, Racitoare
-
Baterii, încărcătoare, surse de alimentare tampon și convertoare
- Baterii, încărcătoare - descriere teoretică
- Baterii litiu-ion. Baterii personalizate. Sistem de management al bateriei (BMS)
- baterii
- Incarcatoare de baterii si accesorii
- UPS și surse de alimentare tampon
- Convertoare si accesorii pentru fotovoltaice
- Stocarea energiei
- Pile de combustibil cu hidrogen
- Celule litiu-ion
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Automatizare
- Elevatoare Spiralift
- Piese pentru drone Futaba
- Întrerupătoare de limită, Micro întrerupătoare
- Senzori, traductoare
- Pirometre
- Contoare, relee de timp, contoare de panou
- Echipament industrial de protectie
- Semnale luminoase și sonore
- Cameră termică
- Afișaje LED
- Butoane și întrerupătoare
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Cabluri, fire Litz, Conduite, Conexiuni flexibile
- Firele
- Presetupe și manșoane
- Chipurile
-
Cabluri pentru aplicatii speciale
- Cabluri de prelungire și compensare
- Cabluri de termocuplu
- Cabluri de conectare pentru senzori PT
- Cabluri cu mai multe fire de temperatură. -60°C până la +1400°C
- Cabluri de medie tensiune SILICOUL
- Cabluri de aprindere
- Cabluri de incalzire
- Cabluri cu un singur conductor temp. -60°C până la +450°C
- Fire de cale ferată
- Cabluri de încălzire în ex
- Cabluri pentru industria de apărare
- Accesați subcategoria
- tricouri
-
Impletituri
- Impletituri plate
- Impletituri rotunde
- Impletituri foarte flexibile - plate
- Impletituri foarte flexibile - rotunde
- Impletituri cilindrice de cupru
- Impletituri si capace cilindrice din cupru
- Curele flexibile de împământare
- Impletituri cilindrice din otel zincat si inoxidabil
- Impletituri de cupru izolate PVC - temperatura de pana la 85 de grade C
- Impletituri plate din aluminiu
- Kit de conectare - impletituri si tuburi
- Accesați subcategoria
- Echipament de tracțiune
- Capse de cablu
- Sine flexibile izolate
- Sine flexibile multistrat
- Sisteme de management al cablurilor
- Accesați subcategoria
- Vezi toate categoriile
-
Semiconductoare
-
-
- Furnizori
-
Aplicații
- Automatizare HVAC
- Automatizare industrială
- Băncile de energie
- Cercetare si masuratori de laborator
- Componente pentru zonele cu pericol de explozie (EX)
- Echipament industrial de protectie
- Echipamente pentru dulapuri de distributie si control
- Exploatare minieră, metalurgie și turnătorie
- Imprimare
- Încălzire prin inducție
- Inginerie energetică
- Mașini CNC
- Masini de sudura si sudori
- Mașini de uscare și prelucrare a lemnului
- Masini pentru termoformarea materialelor plastice
- Măsurarea și reglarea temperaturii
- Motoare si transformatoare
- Surse de alimentare (UPS) și sisteme redresoare
- Tracțiune cu tramvai și feroviar
- Unități DC și AC (invertoare)
-
Instalare
-
-
Inductori
-
-
Dispozitive de inducție
-
-
Serviciu
-
- Kontakt
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
7th Generation NX type (NX7) Converter Inverter Brake (CIB) Modules

7th Generation NX type (NX7) Converter Inverter Brake (CIB) Modules
Developed to address the requirements of high performance drives by utilizing an innovative packaging concept and an advanced chip technology.
Applications such as elevator drives or servomotors have several special requirements. One on hand, high efficiency is important, while on the other hand, the inverter unit be resilient to the different types of load cycling. Furthermore, the inverter must be designed as compact as possible. NX7 CIB modules aim to address these challenges.
By Toshinari Hirai and Narender Lakshmanan, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V
Advanced Chip Technology Combined with a New Packaging Concept:
Each CIB module consists of an integrated 3 phase inverter part, a converter (3 ph diode rectifier) part and a brake chopper part. The line-up of the latest NX7 CIB modules is shown in Figure 1. The NX7 CIB modules utilize the latest 7th generation CSTBT™ IGBT along with the RFC (Relaxed Field of Cathode) diodes. The electrical characteristics of the new thin wafer 7th generation chips have been tuned for the reduction of overall power losses.
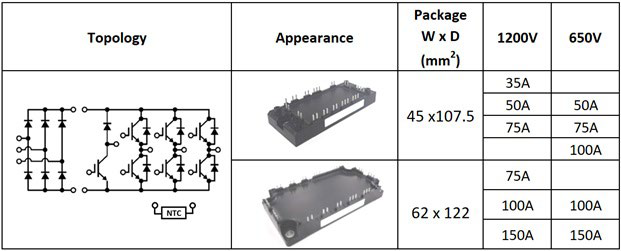
Figure 1: Line-up of the NX7 CIB Modules. NOTE: Pressfit and PCTIM options available.
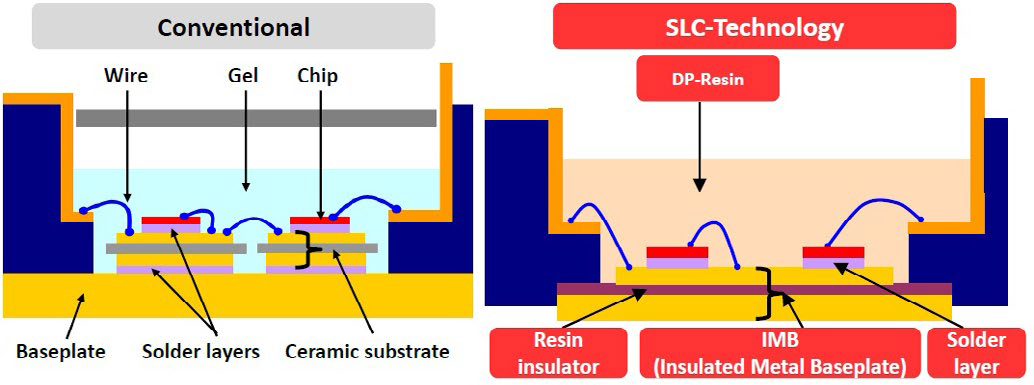
Figure 2: Cross section of the NX7 package versus a conventional module package.
The NX7 CIB employs a new packaging concept – the SLC (SoLid Cover) Technology which includes an insulated metal baseplate structure (refer to Figure 2). The conventional baseplate has been replaced by an insulated metal baseplate structure where the metal baseplate contains an organic insulation layer directly bonded to it. Therefore the conventional substrate solder between metal baseplate and isolation ceramic has been eliminated. The soft silicone gel of the conventional structure is replaced by the hard DP-resin (direct potting resin) [1].
Minimizing Losses and Maximizing Performance:
Operating the inverter at elevated switching frequencies helps in reducing the audible noise, hence low loss operation even at high switching frequencies is an important capability for applications such as elevators. In addition, limiting the IGBT chip temperature rise during low rotation speed (low output frequency) operation is a key requirement.
Figure 3 indicates the overall power loss comparison of an NX7 CIB module (CM50MXUA-24T) with a previous 6th gen. IGBT module (CM50MXA-24S) considering different switching frequencies and a low output current frequency of fout=5Hz. The benefit in terms of pow-
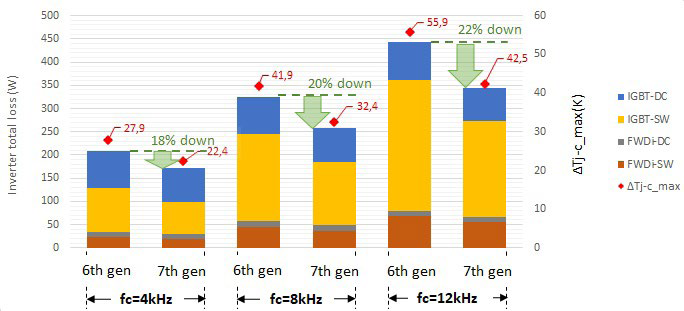
Figure 3: Power loss and junction temperature performance of the NX7 CIB vs conventional module. Conditions: VCC = 600V, Io = 24 Arms, PF = 0.9, M = 1, fout = 5 Hz, Data @ Tj = 125°C.W
er loss between a conventional module and an NX7 CIB module increases with increase in switching frequency. This can be attributed to the optimization in the trade-off between the switching losses and the ON state losses in the new 7th generation chip technology. A combination of loss reduction and the low thermal resistance (chip to case) offered by the 7th generation chip technology ensures that the maximum junction temperature can be reduced by utilizing the NX7 CIB module. The analysis indicated in Figure 3 has been carried out considering a target switching dv⁄dt (max)= 10 kV/μs.
Designed for High Reliability:
Intermittent operation is a characteristic feature of applications such as elevators. The impact of load cycling can be categorized into two types of cycling phenomena: power cycling and thermal cycling. Power cycling refers to a cycling of the junction temperature which affects the reliability of the chip-tobond wire contact whereas thermal cycling refers to the cycling of baseplate temperature which conventionally affect the solder layer connecting the isolation substrate and the baseplate. But due to the elimination of the ceramic substrate and the solder layer, the limitation pertaining to thermal cycling is not present in NX7 CIB modules.
Case 1: Extended Loading Conditions (temperature swing at the heatsink and case):
It is common for applications such as elevators to experience operation cycles where the heatsink temperature rises to an allowable point and then falls back to the ambient temperature. Session involving continuous operation which would generate a temperature swing at the heatsink, would also involve temperature swings at the case of the power module and at the chip surface (junction). An example of such operation is represented in Figure 4. For this analysis, the Mitsubishi Electric 6th generation modules represent the conventional modules.
The following points are the key conclusions from Figure 4:
- Bottleneck identification: For conventional modules which utilize a baseplate solder layer, thermal cycling performance is the lifetime limitation factor for long operation cycles due to the degradation of the solder layer under such conditions.
- Solution: The bottleneck (solder layer) has been eliminated in the new NX7 module due to the adoption of the IMB structure.
Case 2: Short term loading conditions (temperature swing predominantly at the chip):
Operating cycles (in the range of a few seconds) which generate temperature swings only at IGBT chip (ΔTj) affect the reliability of the chip to bond wire contact. The amplitude of the ΔTj is the deciding factor with regards to the power cycling lifetime. This point has been addressed by employing the low loss 7th generation chip technology
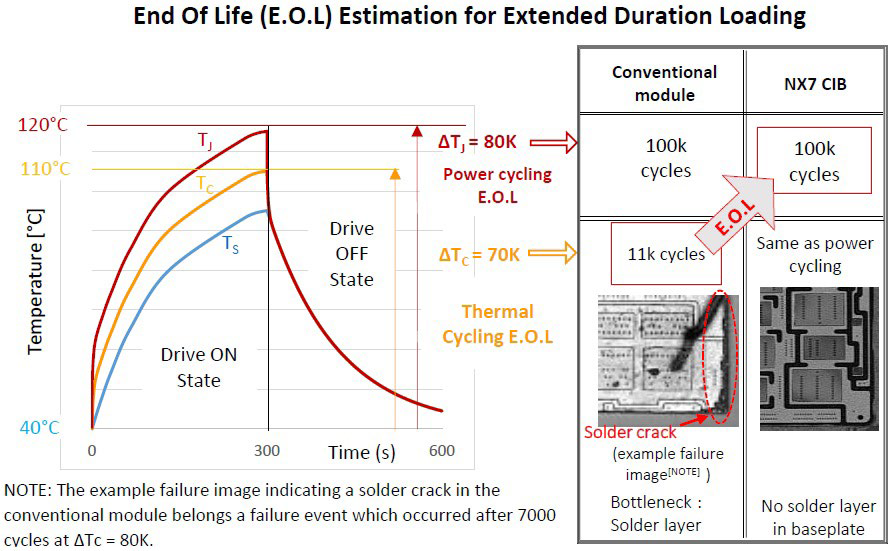
Figure 4: Lifetime estimation for extended duration loading (Conventional module vs NX7 CIB).
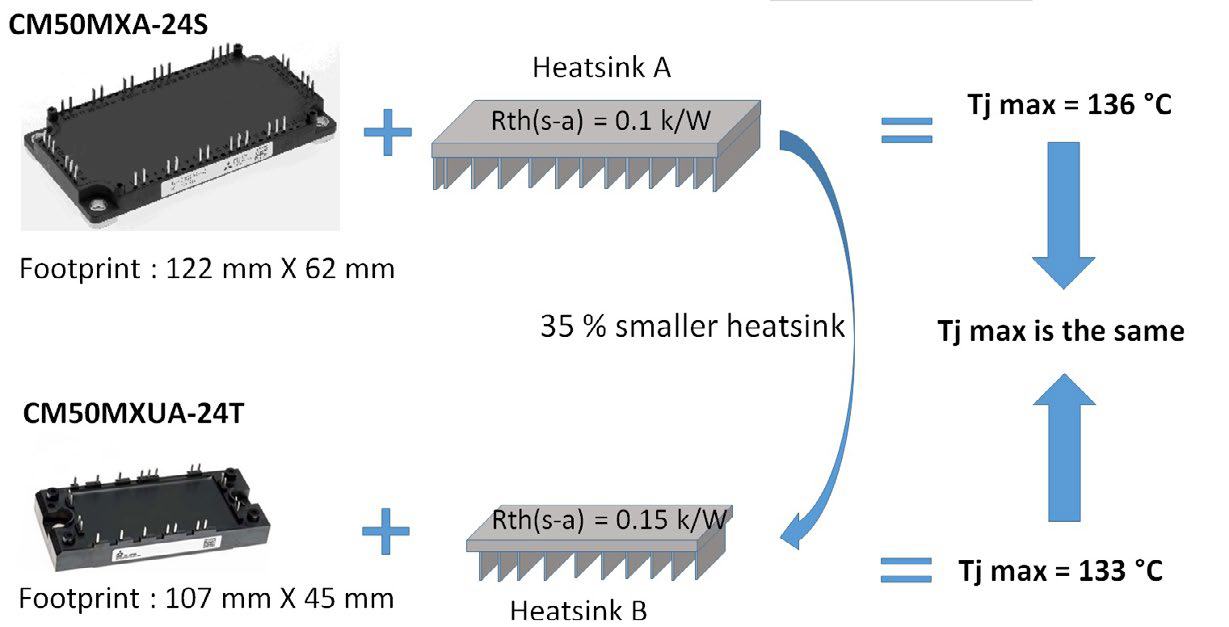
Figure 5: Compactness by heatsink reduction. Conditions: Vcc = 600V, fc = 12 kHz, fout = 5 Hz, M = 1, PF = 0.9, Ic = 24 Arms, Ta = 30 °C, data @ Tj = 125 °C
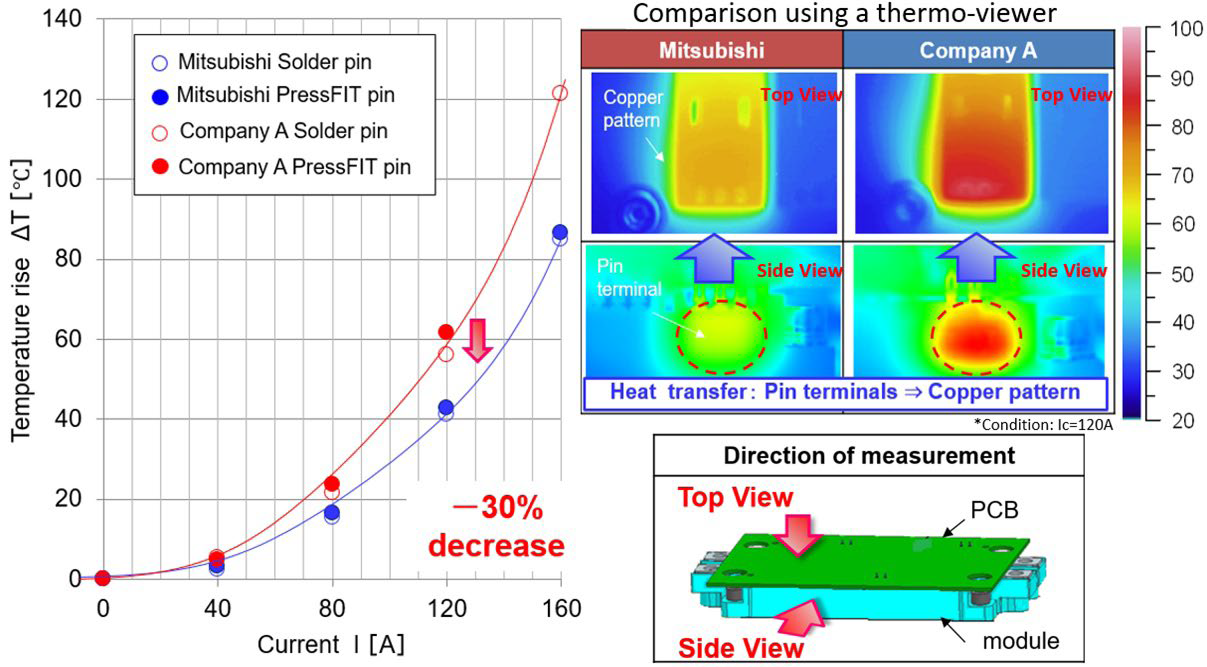
Figure 6: Optimization of terminal temperature in the NX7 CIB module.
in combination with the optimized chip to case thermal resistance in the NX7 module. This combination ensures that for the same operating condition, the corresponding ΔTj is lower (compared the performance of the conventional module). This tendency can be understood from the following results indicating power cycling capability based on the conditions mentioned in Figure 3 (for fc = 12 kHz):
- Conventional CIB (CM50MXA-24S): ΔTj = 54.52 K: 600 thousand cycles (approx.)
- NX7 CIB (CM50MXUA-24T): ΔTj = 36.64 K:WWWW 6 million cycles (approx.)
Summary – Overall lifetime enhancement
Overall improvement in lifetime has been ensured by the following two-step strategy:
- Elimination of the thermal cycling bottleneck
- Reduction of ΔTj to achieve better power cycling capability
Compact Design:
To achieve a compact design, several important considerations have to be made. The following points illustrate the advantage offered by adopting an NX7 CIB module.
1. Since the NX7 CIB module exhibits an improved loss performance and superior thermal performance (refer Figure 4), the designer can shrink the size of the heatsink in order to achieve an overall compact design. The example presented in Figure 5 illustrates a 35% reduction of the heatsink without causing an increase in the maximum junction temperature.
2. To achieve compactness, the classical copper busbar structure can be replaced by a PCB which would be connected to the terminals of the power module via pressfit or soldering. The challenge with this approach is that, due to high current density at the terminal pins, the temperature developed at the terminal could impose a limitation on the maximum operating current. This possibility has been taken into consideration while developing the NX7 CIB and accordingly the pin structure has been designed to reduce the temperature developed at the terminal during operation. As indicated in Figure 6, the temperature rise developed at the terminals of the Mitsubishi module (NX7 CIB) is lower in comparison with a competitor’s design. The improved thermal conductivity of the potting material (DP-resin) versus gel is an added advantage.
Scalable solutions:
The NX7 CIB line-up allows the designer to develop platform solutions – one mechanical design for multiple power ratings. For example, (refer Figure 1), in the 1200V category, the 45mm x 107.5mm module is available in 3 different current ratings (35A, 50A and 75A and the 62mm x 122mm module is available in 3 different current ratings (75A, 100A, 150A). This allows the designer to develop one mechanical design for 3 different power levels.
Conclusion:
The requirements of applications such as elevator drives have been taken into consideration while developing the NX7 CIB module. The unique combination of the SLC technology packing and the 7th generation chip technology allows the designer to develop an efficient, reliable and a compact inverter that can be used as a platform solution for multiple power levels.
References:
[1] Thomas Radke, et al: Enhanced IGBT Module Power Density Utilizing the Improved Thermal Conductivity of SLCTechnology, Bodo’s Power systems, June 2016
[2] Thomas Radke, et al : New Horizons in Thermal Cycling Capability Realized with the 7th gen. IGBT module Based on SLC-Technology, Bodo’s Power systems, May 2017
[3] MELCOSIM: IGBT thermal and loss simulation software, available at www. mitsubishielectric.com/semiconductors/ simulator/
Related posts
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Leave a comment