

Ви повинні увійти в систему
Category


Фотографії призначені тільки для інформаційних цілей. Подивитися специфікацію продукту
please use latin characters
Ambrell induction heating solutions are fast, efficient choices for all stages of the curing operation.
In preparation for coating, induction heating is used to remove surface moisture from pipes, preheating the pipe to the correct temperature for coating. Then – depending on the type of polymeric coating applied – the tube or pipe is heated to 150-300 °C (302-572°F) for curing the coating.
In addition to requiring less floor space than traditional furnaces and ovens, induction systems offer ergonomic benefits, are environmentally friendly, and have the unique capacity to selectively heat only portions of a tubular product.
Beyond these operational benefits, induction heating also delivers a higher quality coating solution. Unlike furnaces that rely on heating the coating first, induction heats the metal substrate beneath the coating – curing the coating from the inside out – leaving the surface soft and allowing solvents to evaporate and any outgassing to occur. Removing coatings to recover tubes and pipes for re-coating is another common use for induction heating. Typically, the pipe is heated to about 200 °C (392 °F), which breaks the bond between the surface and coating, allowing the coating to be peeled off. Using this method is more environmentally friendly than alternative methods of burning off or grinding off the coating.


With the use of more thin-wall steel alloy pipes in today’s oil and gas pipelines, manufacturers and installers are turning to the fast, accurate and uniform heating of Ambrell induction heating systems. During the process of butt welding, induction heating is commonly used to preheat the joint area to 150-200 °C (302-392 °F) to prepare the area for a consistent quality weld. After welding, the joint area is heated to 600-650 °C (1112-1202 °F) for thermal stress relief of the weld area. Traditional gas flame and resistance heating systems are often impractical when these higher temperatures are required. Not only are they too slow to meet the cycle times demanded by the industry, but also the heating can be inaccurate and can lack uniformity around the full circumference and bandwidth of the weld joints.
Other benefits of induction heating include:

Induction heating is the preferred heating method for bending of larger thicker walled pipes. This is due to the focused narrow band heating offered by the induction process with the resulting higher quality bends with lower quality and wall thinning than other bending methods. Because of this quality and accuracy, induction hot pipe bending is the preferred alternative to traditional fit-and-weld procedures, and can help companies meet the rigorous safety demands of the chemical and energy industries. Ambrell induction heating systems are available in the frequency and power levels to optimally heat any pipe for hot bending. Typically, induction hot bending is used on pipes with diameters from 2” (50mm) to 36” (915 mm), with wall thicknesses from Schedule 5 up to 2.5” (64mm).
Hot pipe bending with induction involves placing an induction heating coil around the pipe at the bend point, and heating a 1” (25mm) section of the pipe to 1000 °C (1832 °F). With the pipe at temperature, pressure is applied by a bending arm to bend it into the desired shape. Air and water quenches are used before and after the heat zone to promote bending solely at the hot zone.

Induction heating is the preferred heating method for bending larger thick-walled pipes used in the chemical and power generating industries.
Drill Pipe Manufacturing
Ambrell supplies induction heating systems to companies that manufacture oil and mineral drill pipe to meet the requirements of API 5DP and GOST R 50278. Induction heating offers many benefits over flame or resistance heating during the manufacturing processes in drill pipe heat treating and welding of the tool posts onto the pipe ends, including:

Ambrell induction heating systems allow the depth and rate of the heating to be precisely controlled, delivering the ideal temperature and timing for each step in the process, while meeting the 180 seconds floor to floor time cycle.
Tool Post Post Welding Heat Treating
After friction or arc welding of the tool post to the pipe end, the weld and surrounding pipe is brittle and requires a three-step heat treating process to toughen the joint area:

Heat Treating Ends of Thin Walled Mineral Drill Pipe
Both the internal and external threaded ends of mineral drill pipes are heat treated and surface hardened to provide a tough tube-end and to minimize wear during the repeated connecting and disconnecting during the drilling process.
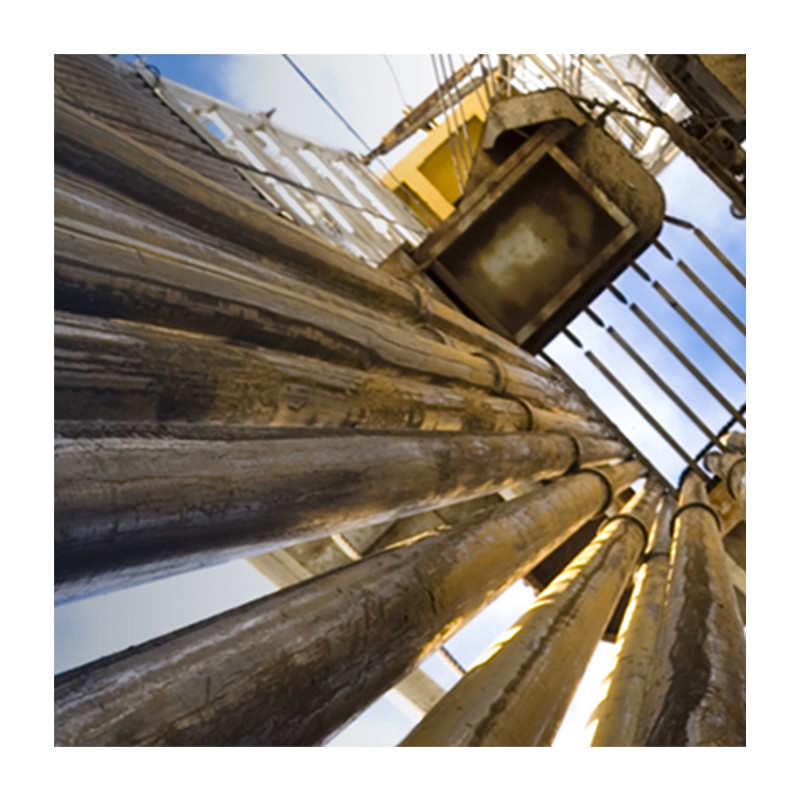
Outside and inside temperatures during the annealing process on a 100mm band around the Tool box weld on a 126mm diameter pipe.
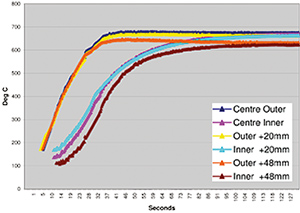
Austenitising 126mm Diameter Pipe
Through curie heating with inside and outside pipe 900 °C temperatures consistent before quenching.
Oil and Gas Well Drill Bits
In drill bit manufacturing operations, multiple tool inserts (typically between 40 and 60) are individually brazed onto a single drill bit. These inserts may be a polycrystaline diamond compact (PDC) or tungsten carbide inserts (TCI)
Induction heating is an excellent technique for pre-heating the drill bit to 600 °C (1100 °F) in preparation for the torch brazing of the diamond inserts.
Drill bits come in a range of different sizes ranging from 8-20” (203-508mm) diameter. It takes 10-30 minutes for the heat to fully soak through the drill bit, which prepares the insert area for the brazing process. The torch is then used to raise the temperature of each individual joint to 790 °C (1454 °F) to flow the braze.


The PDC or TCI inserts are the cutting portion of the drilling tool, so they will wear out with use. Induction heating is used in the reclaiming process to heat up the drill bit, which allows the inserts to be removed for rebuilding the drill bit. (The inserts image is courtesy of U.S. Synthetics, Orem, UT.)
The insert’s brazing silver and copper “eutectic alloy” has a melting temperature of 790 °C (1454 °F), well below the melting temperature of silver or copper. This lower melt temperature prevents overheating of the diamond bit during brazing, yet still results in a strong joint to the drill bit.



Ambrell offers a wide power and frequency range with its EASYHEAT and EKOHEAT systems. So, whether your tube or pipe application is large or small, Ambrell can help you maximize cost efficiencies and productivity.
Ambrell’s systems are versatile with multiple capacitor and tap transformer configurations. They offer efficient power conversion, which minimizes energy expenses. They are also user-friendly, offer agile frequency tuning for repeatable heating, and can be easily integrated into your process thanks to their small footprint.
Systems include:

Ви зацікавлені у цьому продукті? Вам потрібна додаткова інформація або індивідуальні розцінки?
Ви повинні увійти в систему
Ambrell induction heating solutions are fast, efficient choices for all stages of the curing operation.
In preparation for coating, induction heating is used to remove surface moisture from pipes, preheating the pipe to the correct temperature for coating. Then – depending on the type of polymeric coating applied – the tube or pipe is heated to 150-300 °C (302-572°F) for curing the coating.
In addition to requiring less floor space than traditional furnaces and ovens, induction systems offer ergonomic benefits, are environmentally friendly, and have the unique capacity to selectively heat only portions of a tubular product.
Beyond these operational benefits, induction heating also delivers a higher quality coating solution. Unlike furnaces that rely on heating the coating first, induction heats the metal substrate beneath the coating – curing the coating from the inside out – leaving the surface soft and allowing solvents to evaporate and any outgassing to occur. Removing coatings to recover tubes and pipes for re-coating is another common use for induction heating. Typically, the pipe is heated to about 200 °C (392 °F), which breaks the bond between the surface and coating, allowing the coating to be peeled off. Using this method is more environmentally friendly than alternative methods of burning off or grinding off the coating.


With the use of more thin-wall steel alloy pipes in today’s oil and gas pipelines, manufacturers and installers are turning to the fast, accurate and uniform heating of Ambrell induction heating systems. During the process of butt welding, induction heating is commonly used to preheat the joint area to 150-200 °C (302-392 °F) to prepare the area for a consistent quality weld. After welding, the joint area is heated to 600-650 °C (1112-1202 °F) for thermal stress relief of the weld area. Traditional gas flame and resistance heating systems are often impractical when these higher temperatures are required. Not only are they too slow to meet the cycle times demanded by the industry, but also the heating can be inaccurate and can lack uniformity around the full circumference and bandwidth of the weld joints.
Other benefits of induction heating include:

Induction heating is the preferred heating method for bending of larger thicker walled pipes. This is due to the focused narrow band heating offered by the induction process with the resulting higher quality bends with lower quality and wall thinning than other bending methods. Because of this quality and accuracy, induction hot pipe bending is the preferred alternative to traditional fit-and-weld procedures, and can help companies meet the rigorous safety demands of the chemical and energy industries. Ambrell induction heating systems are available in the frequency and power levels to optimally heat any pipe for hot bending. Typically, induction hot bending is used on pipes with diameters from 2” (50mm) to 36” (915 mm), with wall thicknesses from Schedule 5 up to 2.5” (64mm).
Hot pipe bending with induction involves placing an induction heating coil around the pipe at the bend point, and heating a 1” (25mm) section of the pipe to 1000 °C (1832 °F). With the pipe at temperature, pressure is applied by a bending arm to bend it into the desired shape. Air and water quenches are used before and after the heat zone to promote bending solely at the hot zone.

Induction heating is the preferred heating method for bending larger thick-walled pipes used in the chemical and power generating industries.
Drill Pipe Manufacturing
Ambrell supplies induction heating systems to companies that manufacture oil and mineral drill pipe to meet the requirements of API 5DP and GOST R 50278. Induction heating offers many benefits over flame or resistance heating during the manufacturing processes in drill pipe heat treating and welding of the tool posts onto the pipe ends, including:

Ambrell induction heating systems allow the depth and rate of the heating to be precisely controlled, delivering the ideal temperature and timing for each step in the process, while meeting the 180 seconds floor to floor time cycle.
Tool Post Post Welding Heat Treating
After friction or arc welding of the tool post to the pipe end, the weld and surrounding pipe is brittle and requires a three-step heat treating process to toughen the joint area:

Heat Treating Ends of Thin Walled Mineral Drill Pipe
Both the internal and external threaded ends of mineral drill pipes are heat treated and surface hardened to provide a tough tube-end and to minimize wear during the repeated connecting and disconnecting during the drilling process.
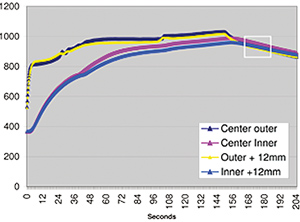
Outside and inside temperatures during the annealing process on a 100mm band around the Tool box weld on a 126mm diameter pipe.

Austenitising 126mm Diameter Pipe
Through curie heating with inside and outside pipe 900 °C temperatures consistent before quenching.

Oil and Gas Well Drill Bits
In drill bit manufacturing operations, multiple tool inserts (typically between 40 and 60) are individually brazed onto a single drill bit. These inserts may be a polycrystaline diamond compact (PDC) or tungsten carbide inserts (TCI)
Induction heating is an excellent technique for pre-heating the drill bit to 600 °C (1100 °F) in preparation for the torch brazing of the diamond inserts.
Drill bits come in a range of different sizes ranging from 8-20” (203-508mm) diameter. It takes 10-30 minutes for the heat to fully soak through the drill bit, which prepares the insert area for the brazing process. The torch is then used to raise the temperature of each individual joint to 790 °C (1454 °F) to flow the braze.


The PDC or TCI inserts are the cutting portion of the drilling tool, so they will wear out with use. Induction heating is used in the reclaiming process to heat up the drill bit, which allows the inserts to be removed for rebuilding the drill bit. (The inserts image is courtesy of U.S. Synthetics, Orem, UT.)
The insert’s brazing silver and copper “eutectic alloy” has a melting temperature of 790 °C (1454 °F), well below the melting temperature of silver or copper. This lower melt temperature prevents overheating of the diamond bit during brazing, yet still results in a strong joint to the drill bit.



Ambrell offers a wide power and frequency range with its EASYHEAT and EKOHEAT systems. So, whether your tube or pipe application is large or small, Ambrell can help you maximize cost efficiencies and productivity.
Ambrell’s systems are versatile with multiple capacitor and tap transformer configurations. They offer efficient power conversion, which minimizes energy expenses. They are also user-friendly, offer agile frequency tuning for repeatable heating, and can be easily integrated into your process thanks to their small footprint.
Systems include:

Вашу оцінку відгуку не було надіслано
Поскаржитись на відгук
Скаргу надіслано
Ваш відгук не надіслано
Написати свій відгук
Відгук надіслано
Ваш відгук не надіслано
